Research Roundup
Here are 3 breakthrough innovations coming out of research at Houston institutions
Research, perhaps now more than ever, is crucial to expanding and growing innovation in Houston — and it's happening across the city right under our noses.
In InnovationMap's latest roundup of research projects, we look into studies on robotics advancing stroke patient rehabilitation, the future of opioid-free surgery, and a breakthrough in recycling plastics.
The University of Houston's research on enhancing stroke rehabilitation
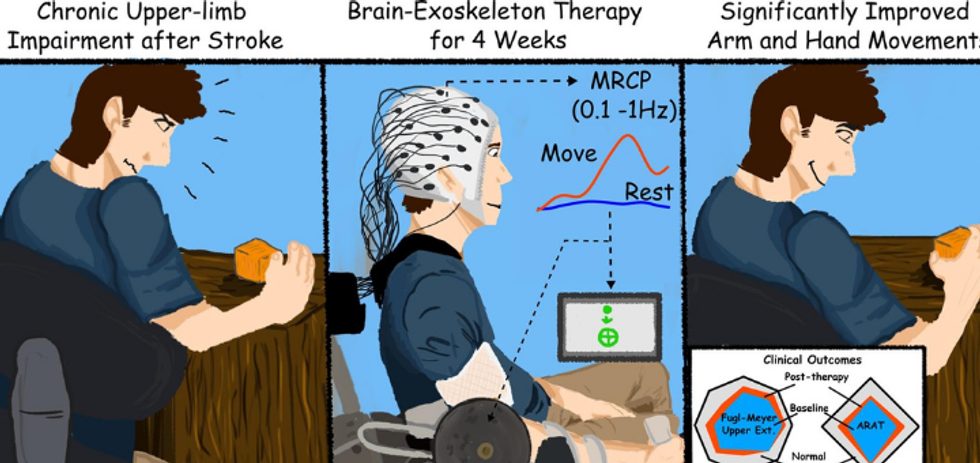
A clinical trial from a team at UH found that stroke survivors gained clinically significant arm movement and control by using an external robotic device powered by the patients' own brains. Image via UH.edu
A researcher at the University of Houston has seen positive results on using his robotics on stroke survivors for rehabilitation. Jose Luis Contreras-Vidal, director of UH's Non-Invasive Brain Machine Interface Systems Laboratory, recently published the results of the clinical trial in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical.
The testing proved that most patients retained the benefits for at least two months after the therapy sessions ended, according to a press release from UH, and suggested even more potential in the long term. The study equipped stroke survivors who have limited movement in one arm with a computer program that captures brain activity to determine the subject's intentions and then works with a robotic device affixed to the affected arm, to move in response to those intentions.
"This is a novel way to measure what is going on in the brain in response to therapeutic intervention," says Dr. Gerard Francisco, professor and chair of physical medicine and rehabilitation at McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston and co-principal investigator, in the release.
"This study suggested that certain types of intervention, in this case using the upper robot, can trigger certain parts of brain to develop the intention to move," he continues. "In the future, this means we can augment existing therapy programs by paying more attention to the importance of engaging certain parts of the brain that can magnify the response to therapy."
The trial was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and Mission Connect, part of the TIRR Foundation. Contreras-Vidal is working on a longer term project with a National Science Foundation grant in order to design a low-cost system that would allow people to continue the treatments at home.
"If we are able to send them home with a device, they can use it for life," he says in the release.
Baylor College of Medicine's work toward opioid-free surgery

A local doctor is focused on opioid-free options. Photo via Getty Images
In light of a national opioid crisis and more and more data demonstrating the negative effects of the drugs, a Baylor College of Medicine orthopedic surgeon has been working to offer opioid-free surgery recovery to his patients.
"Thanks to a number of refinements, we are now able to perform hip and knee replacements, ranging from straightforward to very complex cases, without patients requiring a single opioid pill," says Dr. Mohamad Halawi, associate professor and chief quality officer in the Joseph Barnhart Department of Orthopedic Surgery, in a press release.
"Pain is one of patients' greatest fears when undergoing surgery, understandably so," Halawi continues. "Today, most patients wake up from surgery very comfortable. Gone are the days of trying to catch up with severe pain. It was a vicious cycle with patients paying the price in terms of longer hospitalization, slower recovery and myriad adverse events."
Halawi explains that his work focuses on preventative measures ahead of pain occurring as well as cutting out opioids before surgery.
"Opioid-free surgery is the way of the future, and it has become a standard of care in my practice," he says. "The ability to provide safer and faster recovery to all patients regardless of their surgical complexity is gratifying. I want to make sure that pain is one less thing for patients to worry about during their recovery."
Rice University's breakthrough on recycling plastics

A team of scientists have found a use for a material that comes out of plastics recycling. Photo via Rice.edu
Houston scientists has found a new use for an otherwise useless byproduct that comes from recycling plastics. Rice University chemist James Tour has discovered that turbostratic graphene flakes can be produced from pyrolyzed plastic ash, and those flakes can then be added to other substances like films of polyvinyl alcohol that better resist water in packaging and cement paste and concrete, as well as strengthen the material.
"This work enhances the circular economy for plastics," Tour says in a press release. "So much plastic waste is subject to pyrolysis in an effort to convert it back to monomers and oils. The monomers are used in repolymerization to make new plastics, and the oils are used in a variety of other applications. But there is always a remaining 10% to 20% ash that's valueless and is generally sent to landfills.
Tour's research has appeared in the journal Carbon. The co-authors of the study include Rice graduate students Jacob Beckham, Weiyin Chen and Prabhas Hundi and postdoctoral researcher Duy Xuan Luong, and Shivaranjan Raghuraman and Rouzbeh Shahsavari of C-Crete Technologies. The National Science Foundation, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Department of Energy supported the research.
"Recyclers do not turn large profits due to cheap oil prices, so only about 15% of all plastic gets recycled," said Rice graduate student Kevin Wyss, lead author of the study. "I wanted to combat both of these problems."
