University of Houston to install nanotech-coated air filters on campus to prevent COVID-19 spread
who's house
A nanotechnology developed at the University of Houston is about to make a big difference right on campus.
UH's Facilities/Construction Management Preventive Maintenance team is working on a project that will install air filters that are nanocoated with a material that was first developed at the UH Technology Bridge. UH Professor of Physics Seamus Curran has an extensive background in nanotech, and, as he learned more about COVID-19 and how it spreads, he started nano-coating facemasks to make them more resistant to the small particles that enable the spread of the virus.
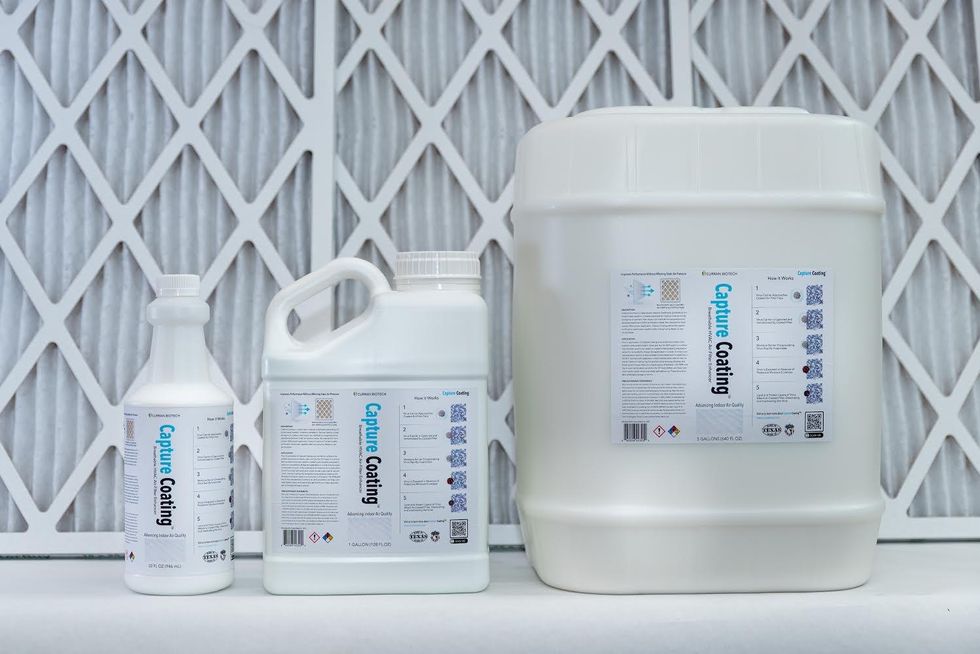
Originally developed for the construction business, Curran's coating material could also be used to create hydrophobic facemasks, Curran discovered, and he founded a spin off company, Curran Biotech, to develop his next pandemic-proof innovation: nano-coated air filters.
"The big thing for me when we were shut down was that people couldn't go to work or school. The country can't live that way — but you can't send people back to work in a world that's not safe," Curran said last October in an interview for the Houston Innovators Podcast. "How do you create a safer environment? That's the thing that really got me going in the beginning in the summer. We looked at filters."
Listen to Professor Curran on the Houston Innovators Podcast:
Curran, who says he's learned more about air filters than he ever cared to, realized that even the most expensive air filters can only protect from 10 to 25 percent of viruses. And most buildings' HVAC systems would have to be replaced completely to allow for these pricier, more protective filters. But Curran Biotech's Capture Coating can be used on existing filters and HVAC systems.
Air filters coated with Curran Biotech's sealant were then tested at the New York Family Court Building, by DCAS-Energy Management Division, and now, ahead of the fall semester, UH is implementing the innovation in all buildings that have less than MERV-13 rated filters.





 Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)
Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)
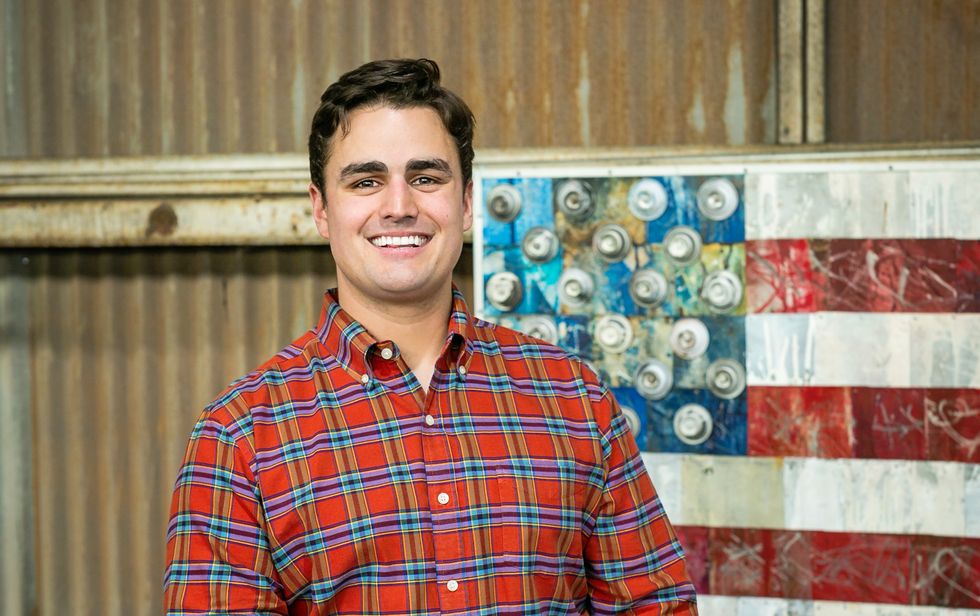
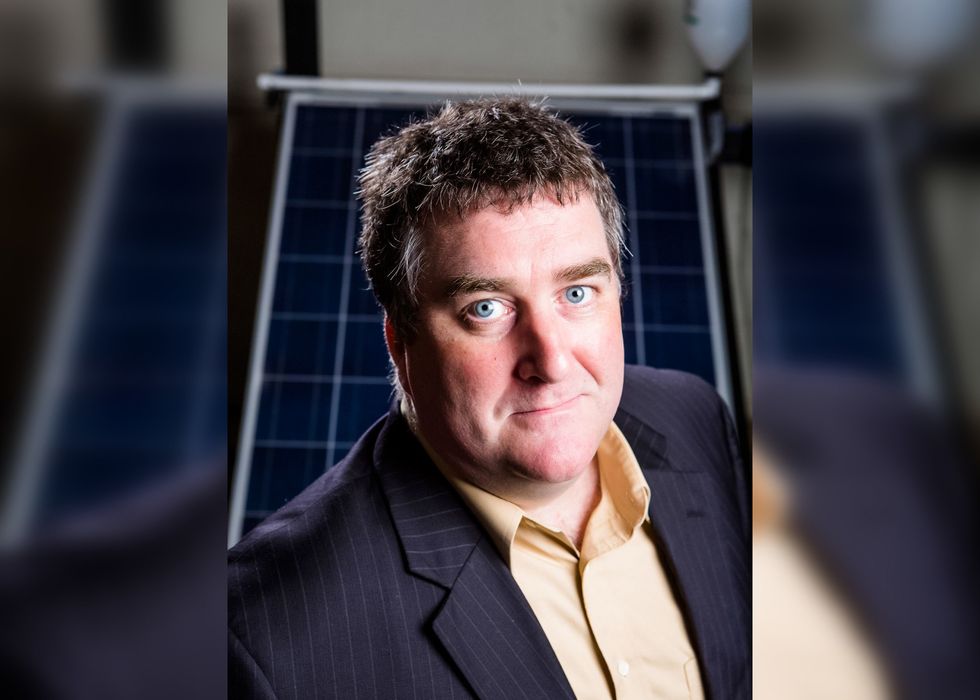
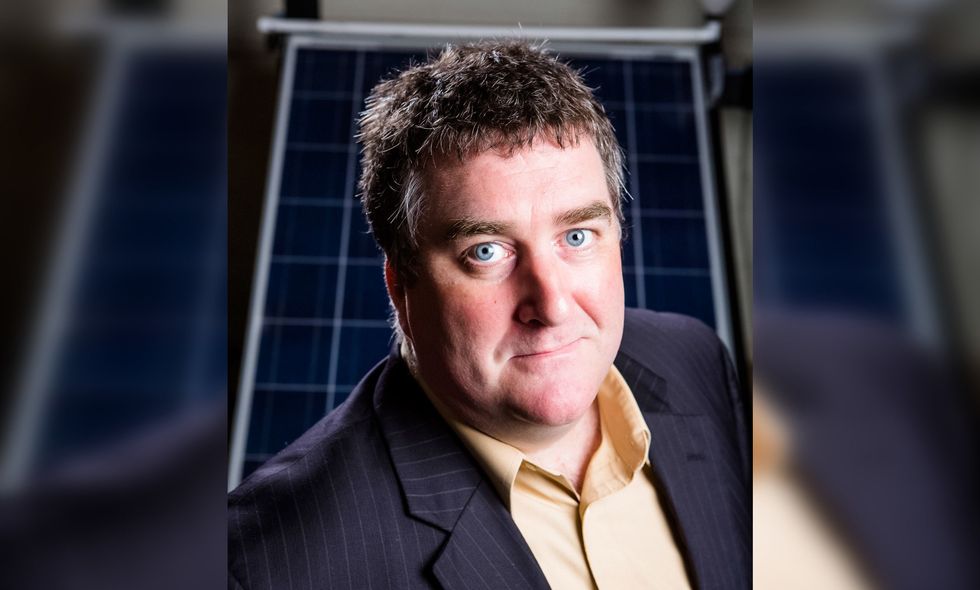




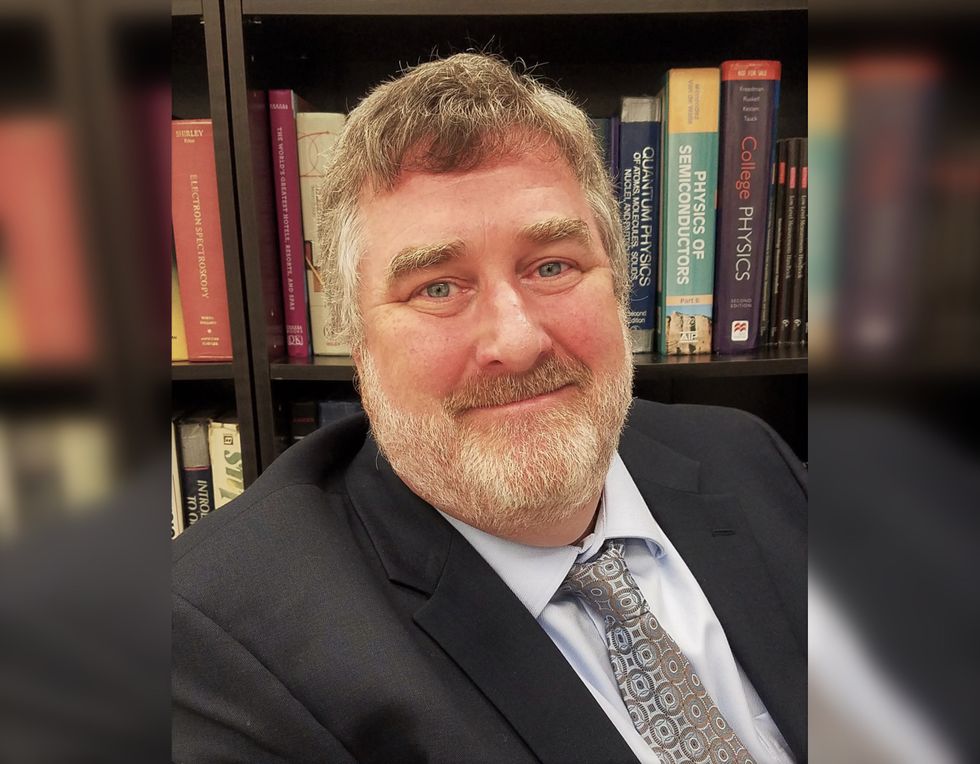
 University of Houston's Dr. Seamus Curran. Photo courtesy of University of Houston
University of Houston's Dr. Seamus Curran. Photo courtesy of University of Houston