Overheard: Houston experts weigh in on the future of tech in real estate
eavesdropping online
The residential and commercial real estate industries have both evolved drastically as new technologies have emerged and in light of the pandemic. But where does that leave renters, homeowners, Realtors, brokers, and everyone else?
A panel of experts looked into their crystal balls and tried to answer this question at a panel for Houston Tech Rodeo last week. They discussed diversity and inclusion, home buying and rental trends, post-pandemic office design, and more on the virtual panel moderated by Allen Thornton, CEO of Money For Your Mission.
To hit the highlights from the virtual panel, check out some overheard moments below. To stream the full broadcast, click here.
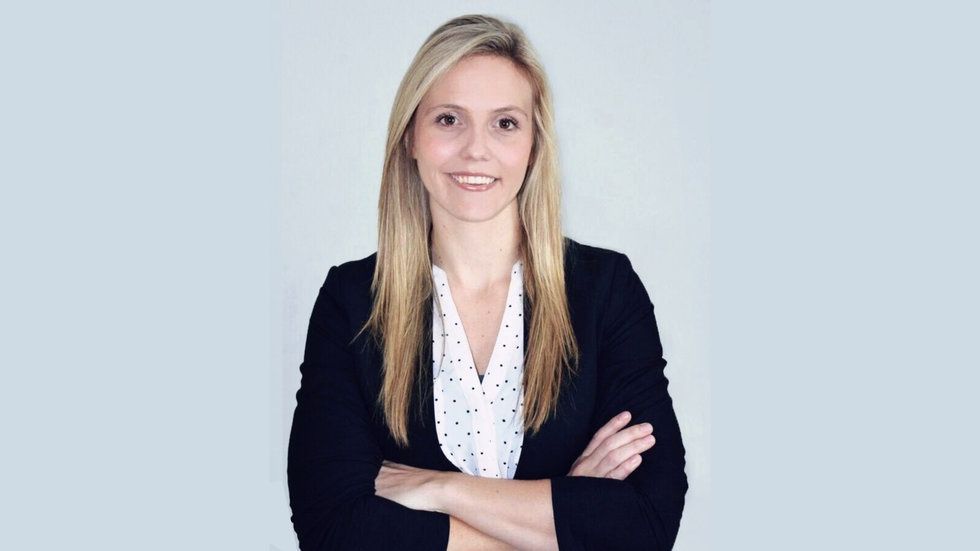
“We’re dealing with a different consumer. When you look at the largest pool of buyers of residential real estate — it’s millennials.”
— Bobby Bryant, CEO of Ask Doss. Bryant says these buyers want information than just pictures, square footage, and the school it's zoned to. They want to know about the neighborhood they will be a part of.
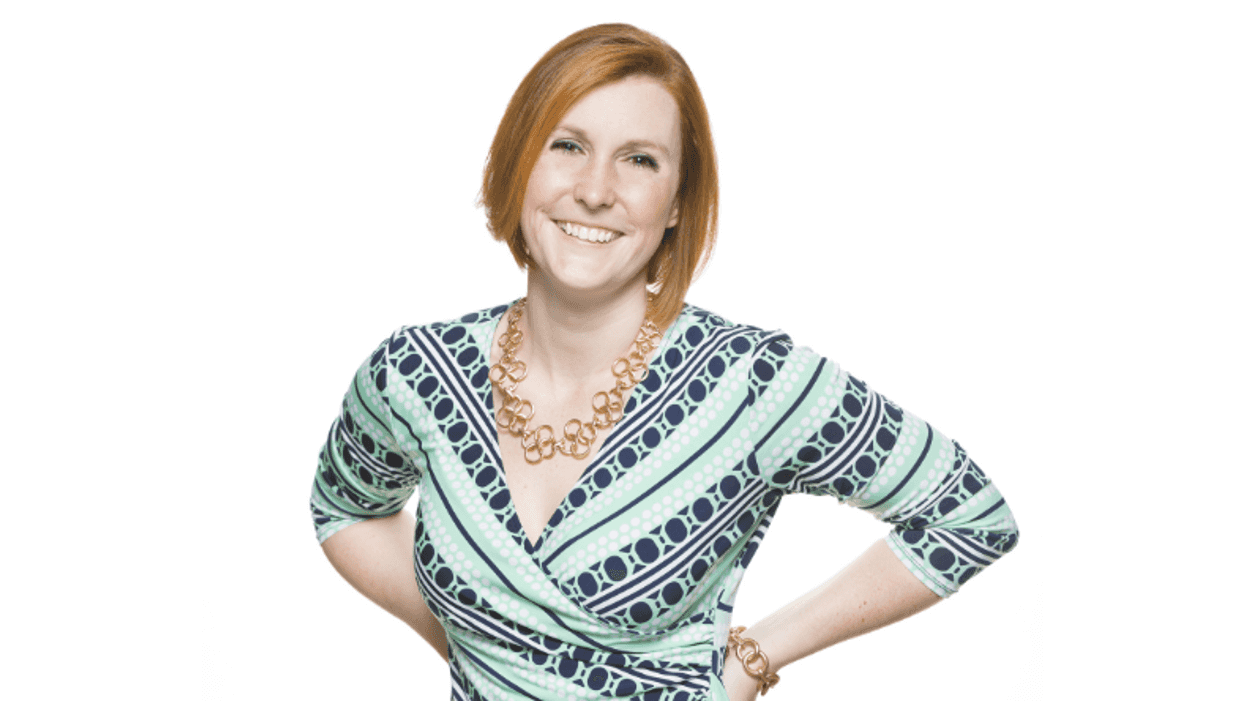
“Folks are realizing how much waste comes from buildings — the buildings we spend 90 percent of our time in.”
— Natalie Goodman, CEO of Incentifind. She adds that renters and homebuyers, as well as commercial tenants, are increasingly demanding more sustainable options. And the government will pay you to implement these things, Goodman says.
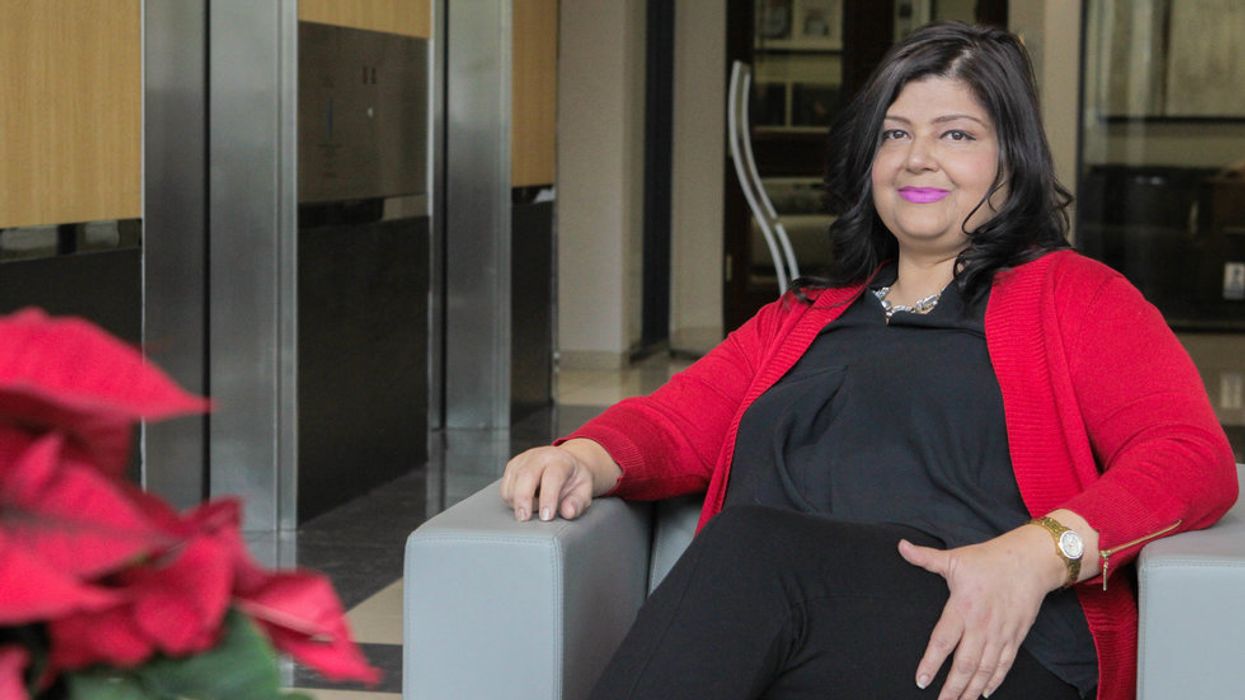
“Before the pandemic, there were already over 60 million freelancers across the country. If the pandemic has taught us anything, it’s that a whole lot more people than just that 60 million are capable of doing a really fantastic job of powering the economy from home."
— Reda Hicks, CEO of GotSpot. People are going to be using space differently, so it's about finding those needs and providing the right access to them.
“As human beings, we’ll be drawn to operating and cooperating with other people in environments that are conducive to collaborating and creativity. We’ll probably see innovation ecosystems transition their operational pieces to an online platform. … But we’ll just naturally want to engage with other humans again."
— Alexander Gras, managing director of The Cannon. Gras adds that the opportunity for in-person collisions is too important to us as humans.
“People are getting educated and educating themselves, and there’s more inclusion. That means more opportunities for individuals of color to invest in or own residential or commercial real estate.”
— Mark Erogbogbo, influencer at 40 Acre Plan. These emerging opportunities, he adds, need to continue.
“When you don’t need to go to a specific office every day and you can work anywhere, well then you can live anywhere.”
— Sebastien Long, CEO of Lodgeur. The pandemic changed how people regarded their housing. Many opted for more spacious rentals with backyards in less crowded areas. Americans don't have a much time off as Europeans, he adds, so they are rethinking how they work remotely.
“Residential real estate has to be the only industry that sells a product that it doesn’t service.”
— Bryant says, explaining how homebuying is one of the most expensive purchases in people's lives that they use for 8 years on average, yet it's a one-time transaction that also spans across many platforms. "The future of real estate brings everything together in one place."
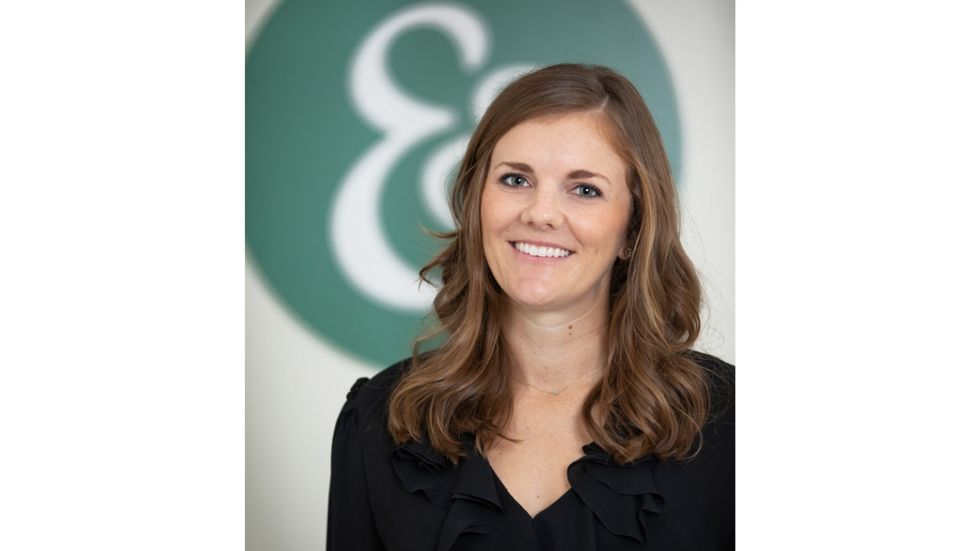
“What CRE needs to think about if they are going to attract and retain tenants … then they need to think about resilience and build for more extreme weather. And that’s where incentives are going to spike.”
— Goodman adds, referencing the winter storm and the hurricanes Houston gets every season.
“For a very long time, (commercial real estate) has been an industry based on a 10-year lease. There are few people who are willing to take on that kind of relationship because that’s a decade, and nobody knows what’s going to happen tomorrow.”
— Hicks says about the challenge CRE owners face with finding new tenants.
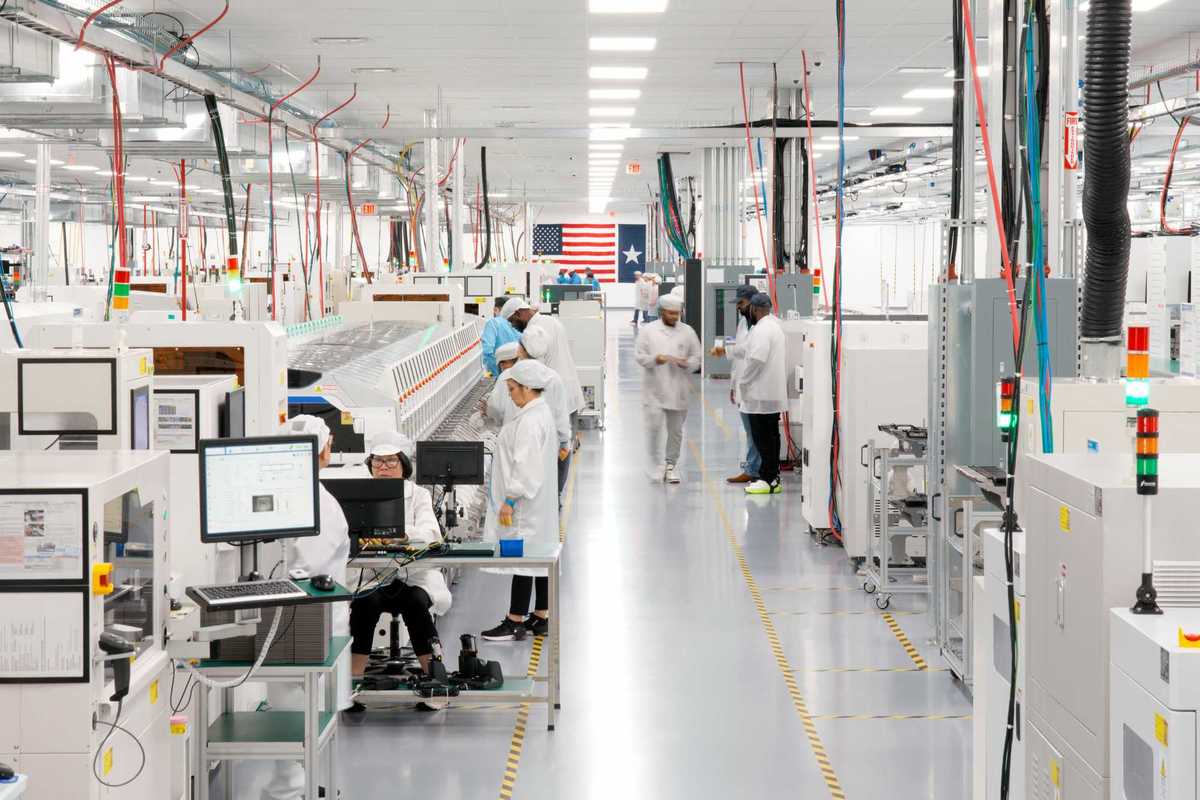




















 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.