Houston's summer has been heating up in terms of innovation news, and there might be some headlines you may have missed.
In this roundup of short stories within Houston startups and tech, a Houston unicorn is reportedly opening a new facility, a data science organization names new CEO, and more.
Mercury Data Science names new CEO

Angela Holmes, former COO of Mercury Data Science, has been named the CEO. Photo courtesy of MDS
A Houston-based AI solutions consultancy has made changes to its C-suite. Dan Watkins is passing on the CEO baton to Angela Holmes, who has served on MDS's board and as COO. As Holmes moves into the top leadership position, Watkins will transition to chief strategy officer and maintain his role on the board of directors.
"Over the last three years, as COO and a member of the board of directors, Angela has been instrumental in MDS’s growth, especially in building MDS’s Strategy Consulting practice and UI/UX and Machine Learning Engineering capabilities," saus Watkins in a news release. "The magic at Mercury Data Science is all about the diverse team who have created a culture of excellence, trust and purpose with the goal of using AI/ML to solve some of the most important health and social problems facing the world today.
"Angela was instrumental in building our culture and customer base over the last three years and will do a great job taking the company to the next level," he continues.
Mercury Data Science was incubated and launched out of Houston-based VC firm Mercury Fund. MDS works with the Mercury portfolio companies as well other startups in the life sciences and health care space.
"It is an exciting time to lead Mercury Data Science as we advance the development of innovative data science platforms at the intersection of biology, behavior, and AI," says Holmes in the release. "I am particularly excited about the demand for our Ergo insights platform for life sciences, allowing scientists to aggregate a vast set of biomedical data to better inform decisions around drug development priorities.
"The increasing understanding of biology, accessibility of large data sets, and accelerating computational capabilities is creating a golden age of life science innovation," she adds. "We are committed to using our expertise to accelerate our clients’ advances in human health, nutrition, therapeutics, diagnostics, and behavior, to create profound advances for humanity."
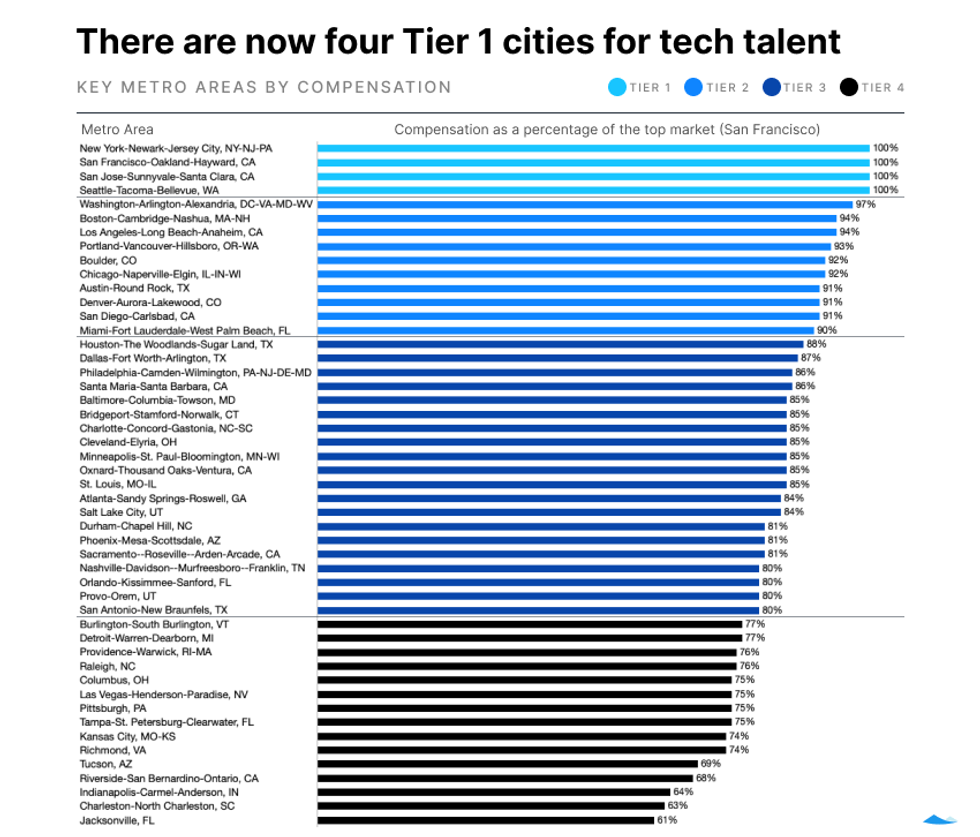
Here's how Houston ranks in terms of startup compensation

This chart from Carta shows the four tiers of the US markets. Houston, in 15th place, leads the third tier. Image courtesy of Carta
A new report looked into compensation at startups across the country, and the Texas market fared pretty well overall. The report from Carta, a San Francisco, California-based technology company that specializes in capitalization table management and valuation software, factored in data using more than 127,000 employee records from startups that use Carta Total Comp, the premier compensation management platform for private companies.
"At Carta, we see it as our responsibility to share the insights that come from an unmatched amount of data about the private market," per the report. "That includes data on startup headcount, payroll and equity metrics, salary medians, and remote work."
The greater Houston area ranked No. 15 in the list, which lands it at the top of the third tier just ahead of Dallas. As the chart depicts, Houston has 88 percent of the compensation of the top market — which this year is a four-way tie between the San Francisco, New York, San Jose, and Seattle areas. Austin landed in the middle of the top tier, and San Antonio snuck into the bottom of the third tier. The full report with national trends is online.
Axiom to open in former electronics store space

Axiom Space will reportedly move engineering into a former retail space. Photo via Facebook
According to a Facebook post from Deer Park Economic Development, Houston unicorn startup Axiom Space has leased a 146,000-square-foot space in what used to be a Fry's Electronics store in Webster. Reportedly, the new facility will house its engineering operations.
"Axiom's initial plans for the building are to support 400 employees, all assigned to engineering work on the Axiom Station, including development across all of its subsystems," reads the post from July 6. "The buildout will be able to accommodate up to 540 people. Axiom plans a move in late July or early August."
Axiom hasn't put out an official news release on this particular facility, but in May the company broke ground on its headquarters at Ellington Airport, the site of the Houston Spaceport. That campus just down the street will house employee offices, astronaut training, and mission control facilities, engineering development and testing labs, and a high bay production facility to house Axiom’s space station modules under construction, according to Axiom.
TRISH awards three postdoctoral fellowships to further space health research

Three scientists were tapped for funding from this Houston organization. Photo via Pexels
Baylor College of Medicine's Translational Research Institute for Space Health — along with its partners California Institute of Technology and Massachusetts Institute of Technology — announced the new fellowship cohort of postdoctoral researchers supported by the TRISH Academy of Bioastronautics who will receive funding and resources for further career growth for two years.
“Cultivating the next generation of space health researchers is one of our strategic goals,” says Dr. Dorit Donoviel, TRISH executive director and associate professor in Baylor’s Center for Space Medicine, in a news release. “We aim to prepare a diverse workforce from a variety of scientific backgrounds to help us solve the challenges facing space explorers on future missions to the Moon and beyond. We are thrilled to welcome this next batch of postdocs as they help bring us closer to that goal.”
These fellows join a cohort of more than 20 previously supported TRISH postdoctoral researchers.
"My career was launched with a fellowship from the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI), the predecessor to TRISH, so I greatly appreciate the value of mentorship and community to those starting out in the field of space biomedical research,” says Dr. Jeffrey Willey, associate professor of radiation oncology at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, in the release.
This 2022 postdoctoral fellows and their research projects are:
- Xu Cao —Identifying Genetic Factors in Radiation Injury with Pooled Single Cell Sequencing
- Ashley Nemec-Bakk — The Use of Two New Ground-based Models of Deep Space Travel to Study the Role of Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Effects
- David Temple — Systematically Assessment of Noisy Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation as a Sensorimotor Countermeasure
Greentown Labs announces second carbon innovation cohort

Greentown Labs announced its latest carbon-focused cohort. Photo via GreentownLabs.com
The The Carbon to Value Initiative is a multi-year collaboration between the Urban Future Lab at NYU Tandon School of Engineering, Greentown Labs, and Fraunhofer USA, which is supported by the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. In its second year, the carbontech accelerator program has selected eight startups in partnership with Fluor Corporation, the initiative’s Year Two Cohort Champion.
With almost 100 applicants from about 20 countries, the C2V Initiative named the following startups to the program, per a release from Greentown:
- Aluminum Technologies (New Orleans, U.S.) has developed Carbo-Chloride Reduction (CCR) aluminum manufacturing technology, which captures process CO2 and also reduces power consumption relative to conventional methods.
- Carbon Upcycling Technologies (Calgary, Canada) utilizes point-source CO2 and mineralizes it with waste materials to create supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) that can be used in building materials.
- Carbonova Corp (Calgary, Canada) utilizes CO2 and methane as a feedstock to produce carbon nanofibers (CNF) that may be used in various fields such as transportation and buildings.
- ecoLocked (Berlin, Germany) converts waste biomass into biochar to create admixes that can replace a share of the cement used in concrete manufacturing, and thus sequester carbon within buildings.
- Full Cycle Bioplastics (San Jose, U.S.) has a patented bacteria-based technology that converts organic waste into Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a biopolymer that can be used to replace a wide range of oil-based plastic applications.
- Lydian (Somerville, U.S.) develops an electro-thermal reactor technology that converts captured CO2 into fuels and chemicals.
- Molecule Works (Richland, U.S.) develops a solid sorbent Direct Air Capture (DAC) system using a novel reactor and contactor configuration.
- Osmoses (Boston, U.S.) develops polymers for gas separation, enabling membrane-based carbon capture applications.
“If we are to succeed in reaching carbon neutrality, then carbontech must play a critical role,” says Ryan Dings, COO and general counsel of Greentown Labs. “For carbontech to do so, we must convene entrepreneurs, market leaders, investors, and policymakers deeply committed to rapidly creating a carbontech ecosystem, which is what our efforts with the C2V Initiative represent and why we’re so proud to be working with this incredible group of partners.”
While the program and its cohort companies aren't based in Houston, Greentown's local presence and member companies will play a role in the initiative.
 Angela Holmes is the CEO of OmniScience. Photo via omniscience.com
Angela Holmes is the CEO of OmniScience. Photo via omniscience.com


 Angela Holmes is the CEO of OmniScience. Photo via mercuryds.com
Angela Holmes is the CEO of OmniScience. Photo via mercuryds.com