Editor's Picks: Top 10 Houston startup feature stories of 2019
2019 in review
Thousands of startups call Houston home. According to the Greater Houston Partnership's data, the Houston area added 11,700 firms between 2013 to 2018. And, if you consider Crunchbase's tally, at the end of 2018, Houston had over 1,400 tech startups on the investment tracking website's radar.
This past year, InnovationMap featured profiles on dozens of these Houston startups — from blockchain and software companies to startups with solutions in health care and oil and gas. Here are 10 that stood out throughout 2019.
Topl — a blockchain startup connecting every step of the way

Houston-based Topl can track almost anything using its blockchain technology. Getty Images
For Topl, 2019 was a year of laying the groundwork. In a January 2019 article on InnovationMap, Kim Raath, president of the Houston-based blockchain company, explained that Topl's mission originated out of the fact that 60 percent of the world lives on $10 a day — and it's in the poorest regions of the world where it's the hardest to get funding for a new business.
Raath says that in her experience backpacking and volunteering all around the world she learned that banks are too overwhelmed to evaluate these potential businesses. Topl has created a technology where banks can easily generate a report on these entrepreneurs that evaluates and makes a loan or investment recommendation on the business.
"We are a generation that wants a story," she says. "We want an origin, and don't want to be fooled. And, because you might be able to reduce the cost by having this transparency, you might be able to bring down the cost on both sides."
Later that year, the company closed a 20 percent oversubscribed $700,000 seed round. With the money, Topl will be able to grow its platforms, provide better product features, and increase marketing efforts. Topl's customers are drawn to the technology because of the business efficiency the blockchain adds to their supply chain, but they are also excited about how having this technology differentiates them from their competition. Raath says she's interested in growing Topl's ability to do joint marketing campaigns with their customers.
Incentifind — finding green incentives for commercial and residential building

Natalie Goodman founded Incentifind, which connects home builders and commercial developers with green incentives. Courtesy of Incentifind
When asked about the origin story of IncentiFind — a Houston-based startup that connects real estate developers and home builders with green construction incentives — founder Natalie Goodman doesn't mince words.
"We're a complete accident," Goodman tells InnovationMap in an interview in March. "I'm an architect. We didn't set out to have a startup."
IncentiFind's mission is to increase the amount of green developments and construction projects in the U.S. The company is equipped with a massive database of green incentives that are offered by utility, county, city, state and federal agencies. Many home builders or commercial developers don't take advantage of green incentives because they're simply not aware of them, Goodman says. Commercial developers can expect to spend around $1,500 with IncentiFind, while homeowners can expect to spend between $50 and $150.
Lazarus 3D — 3D printed organs to better train surgeons
Lazarus 3D is using 3D printing to help advance surgeons' skills. Photo via laz3d.com
It's pretty standard for surgeons in training to practice complicated surgeries on produce — slicing bananas open and sewing grapes back together. But for a pair of Baylor College of Medicine-educated doctors, that didn't seem like sufficient prep for working with living bodies; fruit surgery was not fruitful enough. In 2014, Drs. Jacques Zaneveld and Smriti Agrawal Zaneveld founded Lazarus3D to build a better training model — and layer by layer, they created models of abs and ribs and even hearts with a 3D printer.
"We adapted pre-existing 3D printing technology in a novel proprietary way that allows us to, overnight, build soft, silicone or hydrogel models of human anatomy," Jacques, who serves as CEO, tells InnovationMap in July. "They can be treated just like real tissue."
This year, the company grew to seven people and aims to expand even more to add to its sales and manufacturing teams. Having been funded mostly by friends and family investors, Lazarus3D plans enter its first equity round to raise $6 million, InnovationMap reported last summer.
Mental Health Match — connecting people to the right therapists

Ryan Schwartz realized online dating was easier than finding a therapist. He created a tool to change that. Courtesy of Mental Health Match
Nearly five years ago, Ryan Schwartz sat in a coffee shop in crisis mode. His mother had just died suddenly and he was struggling to find an appropriate therapist. Across the table, his friend sat making a profile on a dating app. Quickly, her endeavor was complete and she was ready to swipe right, but Schwartz was still on the hunt for mental help.
"In two minutes she could have a profile matching her with a partner potentially for the rest of her life and I was sitting there for hours and hours trying to find a therapist," he told InnovationMap in June. "I thought it should be easier to find a therapist than a life partner. That's what sent me on my journey."
That journey reached a watershed last month when Schwartz launched Mental Health Match, a website designed to pair patients with their ideal therapist. The idea gained traction as Schwartz described it to people he met and found that many said they had experienced similar difficulties in finding the right practitioner for their needs.
Grab — making ordering food at the airport easier

Houston-based Grab makes it so you're waiting in one less line at the airport. Getty Images
Most airport lines are unavoidable, but a Houston startup has cut out at least some of those lines with its mobile ordering app. Houston-based software company Grab was founded by Mark Bergsrud in 2015, who worked in senior leadership roles for almost 20 years at Continental Airlines and then United Airlines, following the merger. For Bergsrud, Grab feels like another major mobile game changer the industry experienced.
"I spent many years thinking about the travel experience and how to make it better and faster," Bergsrud told InnovationMap in July. "This feels like how mobile check in felt. There was a problem customers didn't know they had — check in wasn't that difficult anyway, but to be able to have that control, people love it."
Grab now has a presence in over 37 airports around the world, including Dallas and Austin though, ironically, not yet either of Houston's airports. Expansion is in the works for Grab, which closed a multimillion-dollar Series A round this year — London-based Collinson Group was the sole contributor.
NurseDash — An app that connects nurses to shifts

Houston-based NurseDash is the Uber of staffing nursing shifts in medical facilities. Photo via nursedash.com
Across the country, medical facilities are short on nurses. Agencies play a role in matchmaking nurses to open shifts, but agencies charge a high percentage for placement and lack transparency, says Andy Chen, former CFO for Nobilis Health Corporation. That's why he and Jakob Kohl created their app, NurseDash in 2017. The project manager for the app is in New York, but official headquarters in Houston's Galleria area, where a staff of five works with the team spread out around the world.
Since its debut, NurseDash has attracted 40 facilities in Houston, InnovationMap reported in May, including hospitals, surgery centers, and senior living, and about 400 nurses. Chen says he isn't sure just what to call his technology yet, but compares it to the ride hailing of Uber or Lyft and calls it "a virtual bulletin board."
Syzygy — hydrogen cells battery to minimize natural gas

Trevor Best, CEO of Syzygy Plasmonics, walked away from EarthX $100,000 richer. Photo via LinkedIn
A Houston technology company is doing something that, for many decades, wasn't thought to be possible. Syzygy Plasmonics is creating a hydrogen fuel cell technology that produces a cheaper source of energy that releases fewer carbon emissions. The hydrogen-fueled technology originated out of research done over two decades by two Rice University professors, Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander.
Syzygy's technology, CEO Trevor Best told InnovationMap in August, is structured more like a battery than that of a combustion engine. Inside the technology, there are cells, lights, and mirrors making as bright as possible, which then spurs a reaction that creates energy. It has the potential to be cheaper — it's made with cheaper materials — and, of course, cleaner than traditional fueling technology with fewer carbon emissions released.
This new photocatalytic chemical reactor has the potential to shake up the industrial gas, chemical, and energy industries — something that hasn't gone unnoticed by investors. Syzygy just closed a $5.8 million Series A round, and the funds will allow for Syzygy to continue to develop its technology and grow its team. Best tells InnovationMap that he expects to launch a full-size pilot by the end of 2020 and is already in talks with potential clients who are interested in the technology for industrial purposes.
Volumetric — 3D printed human tissue
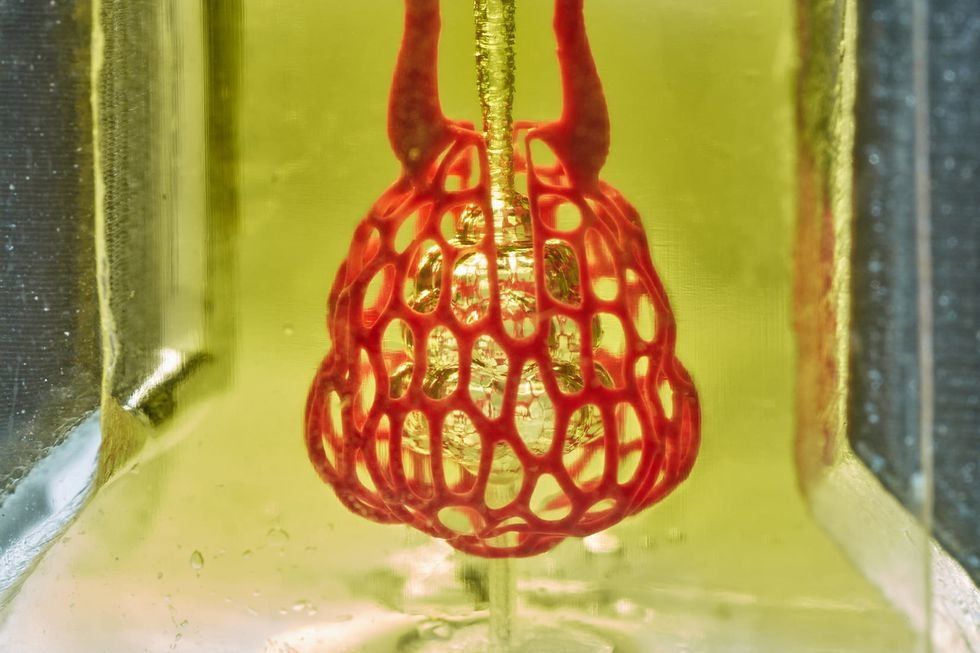
Houston researchers are commercializing their organ 3D printing technology. Jordan Miller/Rice University
There may come a time when you or someone you love is in need of a new pair of lungs. Or perhaps it's a liver. It's not a scenario anyone dreams of, but thanks to Houston company Volumetric, you may never end up on a waiting list. Instead, that organ is made to order and 3D printed using a mix of medical plastics and human cells.
And this possibility isn't necessarily in the distant future. On the cover of the May 3 issue of the journal Science, is a contraption that looks a bit like a futuristic beehive. It's a working air sac complete with blood vessels, the beginnings of a technology that is perhaps only a decade from being implanted in humans. And it was crafted on a 3D printer in Jordan Miller's lab at Rice University. Miller and his bioengineering graduate student Bagrat Grigoryan are primed to profit from their inventions.
In 2018, they started Volumetric Inc., a company that sells both the hydrogel solutions used for printing organs like theirs and the printers themselves. Touring Miller's lab in the Houston Medical Center is a visual timeline of his team's progress designing printers. The version being manufactured is a slick little number, small enough to fit under chemical exhaust hoods, but fitted with everything necessary to print living tissues. It's made and sold in cooperation with CellInk, a larger bioprinting company.
"Our technology is based on projection," Miller told InnovationMap in May. Specifically, it's stereolithography, a type of 3D printing that produces the finished product layer-by-layer. Shining colored light of the right intensity turns the polymers into a solid gel.
Voyager — Email-less communication tool for maritime shipping

Voyager, a Houston SaaS company, has received fresh funds to develop its bulk shipping software. Tom Fisk/Pexels
Houston software startup Voyager is making waves in its quest to improve efficiency — and stem billions of dollars in losses — in the maritime bulk-shipping business. Now, it's got some fresh capital to help it achieve that mission.
InnovationMap reported in August that Houston-based Voyager revealed it secured $1.5 million in seed funding from four investors from around the world: Austin-based ATX Venture Partners, Houston- and California-based Blue Bear Capital, New York City-based GreenHawk Capital, and Oman-based Phaze Ventures. Previous investors include Boulder, Colorado-based Techstars and Spring-based Knightsgate Ventures.
With its software-as-a-service offering, Voyager aims to modernize the workflows of operators in the maritime bulk-commodities industry. The company says its technology will become more vital as autonomous shipping and internet- and Internet of Things-enabled cargo vessels grow in popularity. Voyager's technology enables all communication tied to a shipment to be handled via its web dashboard and app, essentially creating a one-stop shop for people who need to track messages about maritime bulk shipments.
"With Voyager, what it allows companies to do is essentially have all of those counter parties working together in a shared environment to manage the voyage together — entirely email free," Matthew Costello, CEO, tells InnovationMap in December.
Galen Data — cloud-based platform for connecting medical devices to the internet
 Houston-based Galen Data is growing its clientbase and just formed two new partnerships with medical device companies. Photo via galendata.com
Houston-based Galen Data is growing its clientbase and just formed two new partnerships with medical device companies. Photo via galendata.comEducated as an engineer, Chris DuPont has stepped outside his professional comfort zone to generate funding for his Houston-based startup, Galen Data Inc. DuPont's pool of technical contacts in Houston is "wide and deep," he says, but his pool of financial contacts had been shallow.
Overcoming obstacles in Houston's business waters, DuPont has raised two rounds of angel funding — he declines to say how much — that have enabled Galen Data to develop and market its cloud-based platform for connecting medical devices to the internet, including pacemakers and glucose monitors. DuPont is the startup's co-founder and CEO.
Galen Data's patent-pending technology lets medical device manufacturers tailor the cloud-based software to their unique needs. DuPont says his company's software is geared toward medical devices that are outside, not inside, hospitals and other healthcare facilities. He declines to divulge how many customers the startup has.
Hatched within Houston-based Tietronix Software Inc., DuPont's previous employer, Galen Data launched in 2016 but didn't roll out its first product until 2018. Galen Data's emergence comes as the market for internet-connected mobile health apps keeps growing. One forecast envisions the global space for mobile health exceeding $94 billion by 2023.
"We want to be at the forefront of that technology curve," DuPont tells InnovationMap in May. "We might be six months early, we might be a year early, but it's starting to happen."