By the numbers
4 things you need to know from the Greater Houston Partnership's annual report as it pertains to innovation
Every year, the Greater Houston Partnership — the city's economic development arm — gathers up data and reports to paint a full picture of the Bayou City. In the past few editions, innovation has been a key component.
The GHP's innovation coverage spans three pages under the top industry and sectors category. From tech startup growth to money raised, here's what you need to know from the 2019 Houston Facts.
Houston has the 12th largest tech sector in the United States

Christina Morillo/Pexels
The innovation section starts pretty strong with this fun fact. The No. 12 tech sector ranking comes from Computing Technology Industry Association, which cites that Houston has more than 223,000 tech workers. According to the report, about two-thirds of Houston's tech workers are in industries outside of computer and software.
GHP credits Houston's large population of tech workers to its connection to aerospace and oil and gas.
"As the home of NASA's Johnson Space Center and headquarters to the global energy industry, Houston has long been a global hub of engineering talent," the report reads. "In recent years, those skills have given rise to a thriving ecosystem of digital technology companies."
GHP's data reflect that Houston has more than 8,200 tech-related firms, which includes over 500 tech startups.
Venture funding was up over 50 percent between 2017 and 2018
Via Houston Facts
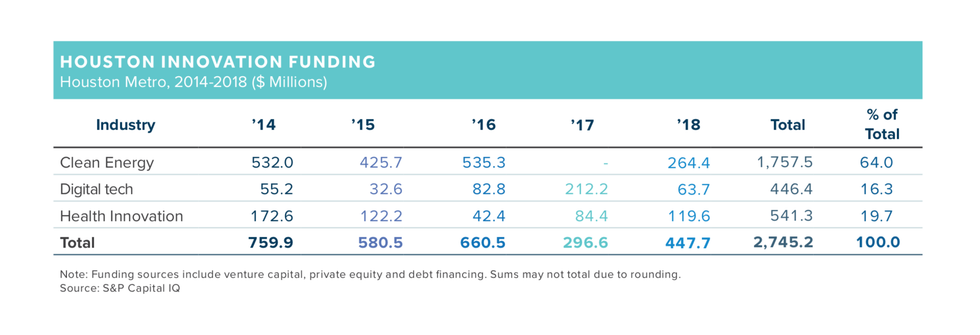
Houston's recorded venture funding doesn't have a hockey stick chart to brag about. Over the past few years, venture funding has been up and down, according to S&P Capital IQ.
"Houston companies in clean energy, health innovation and digital technology have received $3.1 billion in venture capital and growth funding across 333 deals since 2014, averaging $576 million every year," the report reads.
But between 2018 and 2017, VC funds were up 50.9 percent. Of the three categories, clean energy technology pulled in the most money each year and was responsible for 64 percent of the funding during the 2014-2018 period. Sunnova, a residential solar company, had the most money raised during this time with $1.3 billion.
The largest deals reported in Houston in 2018 were:
- Sunnova Energy — $183 million
- OncoResponse — $40 million
- Trisun Energy Services — $39 million
- Arundo Analytics — $25 million
- Procyrion — $16 million
- QuVa Pharma — $15 million
- NeoSensory — $12 million
University-backed entrepreneurship remains strong

Courtesy of Rice University
The Princeton Review ranks Rice University and the University of Houston as having among the best entrepreneurship programs in the country. Rice runs its Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship out of its Jones Graduate School of Business, while University of Houston's Cyvia and Melvyn Wolff Center for Entrepreneurship is housed in the Bauer College of Business.
Both schools have run accelerator programs for seven years — the past six of which have been in collaboration. Rice's OwlSpark and UH's RED Labs finished this summer's program on August 1 at the Bayou Startup Showcase with 16 startup pitches.
Meanwhile, the Rice Business Plan Competition is deemed the "richest pitch competition" in the country. In 2019, the competition saw $3 million invested. RBPC companies have gone on to raise $1.2 billion in capital during the competition's 18-year history.
At UH, which has its own set of pitch events, the Wolff Center's graduate students manage a million-dollar Cougar Venture Fund. The fund has a group of experts that analyze and invest in early stage technology companies.
The life science industry continues to grow
Via Houston Facts
In 2018, Houston housed 20.5 percent of the country's clinical trials, with over 1,800 active. The city has more than 1,760 life sciences companies and over 25,100 biotech experts and 7,200 medical researchers.
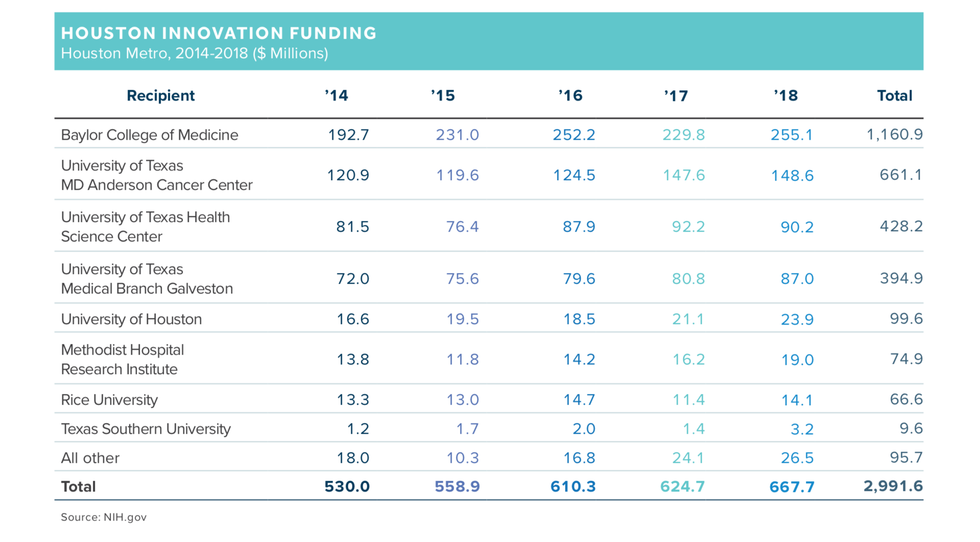
Thankfully, the money seems to match this volume of activity. Last year, Houston's medical research grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, which totaled $668 million in 2018, was up almost 7 percent from 2017. The city's medical institutions have received nearly $3 billion from NIH since 2014 — an average of $600 million a year.
According to the GHP, the top Houston institutions receiving NIH funding in 2018 were:
- Baylor College of Medicine — $255 million
- University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center — $149 million
- University of Texas Health Science Center — $90 million
- University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston — $87 million
- University of Houston — $24 million
- Methodist Hospital Research Institute — $19 million
- Rice University — $14 million
- Texas Southern University — $3 million
As mentioned before, venture capital and private equity investment has increased in Houston, and that trend is also represented in the life science sector. In 2018, life science startups raked in $119 million, which represents a a 41.7 percent increase from $84 million in 201717, according to S&P Capital IQ.
In 2018, the top biotech firms receiving investment were:
- OncoResponse — $40 million
- Procyrion — $16 million
- QuVa Pharma — $15 million
- Pulmotect — $10 million
- Tvardi Therapeutics — $9 million
