Annual report highlights Houston's big innovation wins across tech, life science, space, VC funding, and more
by the numbers
Houston, a city known for its energy legacy, is rapidly transforming into a diverse hub of innovation, life science, technology, and aerospace, according to the 2023 Houston Facts report, released by the Greater Houston Partnership.
Here are some highlights from the report.
The thriving tech ecosystem

Chart via 2023 Houston Facts
With over 230,800 tech workers representing 6.9 percent of the workforce, Houston has firmly established itself as a digital tech talent hub, per the report, which adds that the city is home to a staggering 9,100 tech-related firms, including more than 1,000 venture-backed startups. These startups have secured $6.42 billion in venture capital funding over the past five years, with $1.95 billion in funding in 2022 alone, according to GHP analysis of Pitchbook data.
Houston's technology landscape witnessed significant growth in 2022, with the most heavily invested industries being Energy, Information Technology, and Business Products and Services. A study by Dice revealed that Houston led all cities in tech job posting growth in 2022, boasting a remarkable 45.6 percent year-over-year increase.
Among Houston's largest employers are tech giants such as Asurion, AWS, Dell, HighRadius, HP Enterprise, HP Inc., IBM, PROS, BMC Software, Siemens, Honeywell, Oracle, and Microsoft.
Health startups and biotech advancements

Houston's health tech and life science innovation sector will continue to grow with Helix Park. Courtesy of Elkus Manfredi Architects
Houston's life science and biotech sector is continuing to develop, the GHP finds, with a vast pool of medical professionals, including over 161,800 healthcare practitioners and technical workers, as well as 15,400 life science and biotech researchers.
In 2022, several health startups received significant venture capital funding, showcasing Houston's commitment to advancing medical technologies. The largest deals were from: NuProbe, RadioMedix, Medical Informatics, XCath, Stream Biomedical, Decisio, Adient Medical, Coya Therapeutics, Octagos Health, and Luna Genetics. Collectively, these startups raised over $220 million in funding to develop innovative solutions in diagnostics, monitoring, therapeutics, and more.
The Texas Medical Center Innovation Factory serves as the nucleus of Houston's life science startup activity. With the TMC's Helix Park continuing to rise as an expanded campus, even more activity is on its way to Houston.
Growing innovation infrastructure
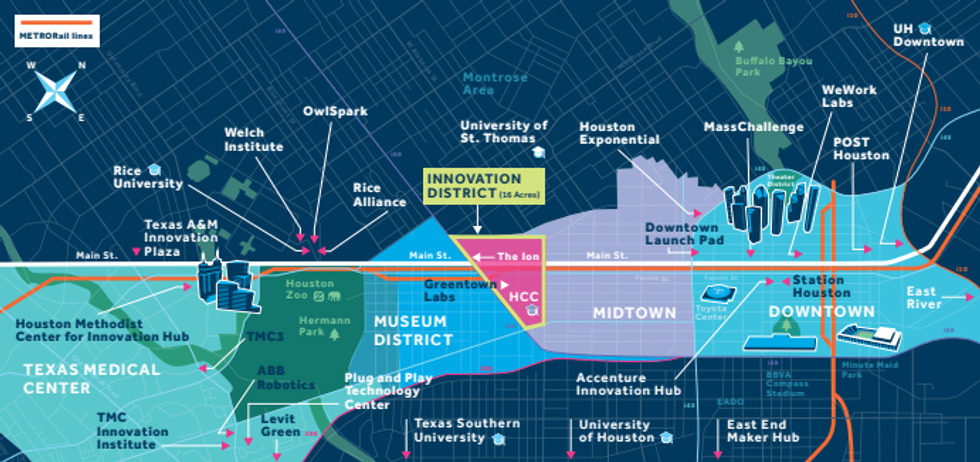
Houston's innovation corridor continues to develop. Map via 2023 Houston Facts
When it comes to the development of Houston's innovation ecosystem, the report called out a few milestones the region reached in 2022. Here are some of those wins from last year.
- The Houston area grew to include more than 80 SDOs, including incubators and accelerators, makerspaces, coworking spaces, nonprofits, and academic institutions. Per the report, there are at least 30 incubator and accelerator programs currently running in Houston — including MassChallenge, Ion Smart Cities Accelerator, Gener8tor, JLABS, Greentown Labs, TMC Innovation and more.
- The Houston Innovation corridor, which consists of a a four-mile expanse across the city’s urban core and is anchored by Rice University's Ion, continues to take shape.
- Both Rice University and University of Houston held onto the top spots on The Princeton Review's report on top entrepreneurship programs. And, the annual Rice Business Plan Competition remains the richest pitch competition in the country, according to the Princeton Review, doling out nearly $2.0 million in prizes.
Aerospace advancement

Axiom Space — as well as a few other Houston space tech companies — had some big wins in 2022. Photo courtesy of NASA
Anchored by NASA's Johnson Space Center and the Houston Spaceport, the city's aerospace industry continues to play a major role in the future of space exploration and commercialization.
The Orion, Gateway, and Human Landing System programs, which are part of NASA's Artemis missions, are headquartered at JSC.
Three Houston space tech companies made major moves recently, as Houston Facts calls out:
- Axiom Space broke ground on the first phase of a 22-acre campus that will house astronaut training and develop Axiom Station, a commercial module that will attach to the ISS.
- Intuitive Machines, which went public last year, started construction on a 12.5-acre campus. "Intuitive will build lunar landers, operate its mission control center, and make guidance, navigation, and make guidance, navigation, and control products at its site," per Houston Facts.
- Collins Aerospace, which has a significant presence in Houston, began operations at their eight-acre campus where it will develop systems for NASA’s human spaceflight programs. The company is working with Axiom Space to create the next generation of NASA spacesuits via a NASA contract that is valued at up to $3.5 billion.
Tracking the energy transition
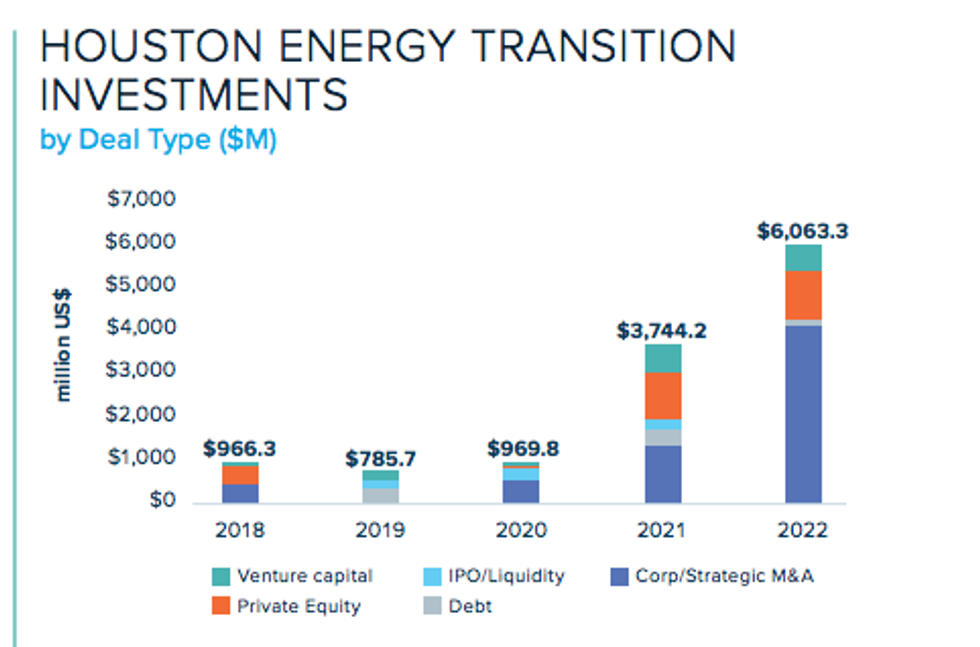
Chart via 2023 Houston Facts
The report highlights the fact that last year Houston's energy transition brought in $6.1 billion in financing from private market investments, which represents a 61.9 percent increase compared to 2021.
"Over the last five years, Houston has seen constant growth in annual energy transition investments, with a notable surge observed from 2020 onwards," reads the report.
Corporate and strategic merger and acquisition investments are what dominated the five deal types, according to the report, representing 68.8 percent of the total investment in 2022. Additionally, private equity accounted for 19.3 percent of all deals, with venture capital comprising 9.5 percent.
EnergyCapital, a sister site to InnovationMap, covered the complete section on the energy industry in the Houston Facts in an article. Read it here.
------
This article was generated in part by artificial intelligence.