7 Houston entrepreneurs pitch their companies to famed Silicon Valley investor
#HTXTechRodeo
Imagine having to pitch your company to a famed investor who has made investments in over 200 companies — seven of which achieved unicorn status. Now, imagine having to do that onstage in front of an audience — in person and virtually viewing.
That was seven Houston entrepreneurs' morning on March 4 during Houston Tech Rodeo. Jason Calacanis heard from the founders and gave his feedback on their business models, as well as general pitch advice. While some of his notes were in the realm of constructive criticism, he stayed pretty positive — for the most part.
"If you're a founder, you're signing up for a 70 percent failure. It's basically a suicide mission, except you don't actually die. You just hit the reset button and go again," Calacanis says to the crowd.
Calacanis also has a great deal of optimism for the region itself, noting on the potential of the innovation ecosystem, and, as an aside, the local basketball team.
"There's no reason Houston as big as a center as Austin has become," Calacanis says. "All it takes is for some of the rich people to say, 'instead of investing in some bond or Wall Street somewhere where they don't know what's going on and to take it and pay it forward with an entrepreneur."
Here are the seven Houston companies that pitched fir Calacanis, as well as some of his feedback.
Topper Luciani, CEO and founder of Goodfair

Houston-based Goodfair sells bundles of used clothing at a low cost. Photo courtesy of Goodfair
Kicking things off was Topper Luciani, CEO and founder of Goodfair, CEO and founder of Goodfair. On a mission to counteract the pollution of fast fashion, the company, which launched in 2018, sells second-hand clothing using "mystery shopping," shipping all of their clothing in variety packs chosen according to a customer's size and taste. This eliminates the cost of photographing, measuring, lowering the price for both the customer and the company.
"Climate chance is Gen Z's crisis, and they are our customers," Luciani tells Calacanis and the crowd.
Goodfair expects to do $5 million in revenue this year, as well as raise its seed round. Calacanis give Luciani advice to make sure he answers the question of, in a world with recycled clothing stores and a growing need for environmentalism, why now?
Katharine Forth, CEO and founder of Zibrio

Balancing is important throughout your life, and Zibrio has the tools and tips for you to use to stay centered. Pexels
From NASA to your bathroom floor — Katharine Forth, CEO and founder of Zibrio, has found a new way to track balance. With her company, people can have the everyday ability to figure out how balanced they are on scale of 1 to 10. The scale gathers data from your weight, your postural control, your muscles and other factors to calculate the rating.
But Forth's business is split between two products — a consumer-focused scale and a scale made for medical professionals to use. Calacanis says it's one scale too many and to focus on just one for now. He compared the company to if Uber tried to launch its upgrades its made over the years all at once.
"You're coming out of the gate with UberPool and UberBlack. Big mistake," he says.
Amy Gross, founder and CEO, VineSleuth Inc

Houston-based VineSleuth created a custom algorithm to match you with new wines based on wines you've had in the past. Courtesy of VineSleuth
Picking wine out isn't rocket science, and yet, "confusion is costing the industry billions," says Amy Gross, founder and CEO, VineSleuth Inc. The company's custom algorithm is backed by research from sensory scientists at Cornell University, and relies on both data collection and machine learning to determine specific wines that will match an individual customer's tastes.
The B2B approach has launched in a few restaurants around town and, as of this week, the Houston Livestock Show and Rodeo's Wine Garden. But how Gross is currently approaching business isn't exactly attractive to investors.
"The business comes across as a small niche business, which is going to cause investors to run," Calacanis explains.
His advice is to use the technology to prove to restaurants and bars that they are overpaying for their wines.
Panos Moutafis, CEO and co-founder, Zenus Biometrics

Zenus Biometrics uses its facial recognition software to provide seamless check in at events around the world. Courtesy of Zenus Biometrics
What started as a convenient way to check into events is now a facial recognition solution to event data. Zenus Biometrics can scan faces of event attendees for security — but also for data analytics, says Panos Moutafis, CEO and co-founder.
While the tech company has already evolved, Calacanis saw even more potential for the software, comparing it to the iPhone. The device is used more for a camera and app usage than an actual phone.
"As technologists we build something," Calacanis says. "Then we find out what people actually use it for."
While based in Houston now, Moutafis mentions that he will soon be relocated to Austin.
Safir Ali, co-founder and CEO of Hamper

Houston-based Hamper, which makes dry cleaning convenient, won the Rockets and BBVA Compass' LaunchPad competition. Courtesy of Hamper
Safir Ali grew up in his parents' dry cleaning store, and he observed that the biggest inconvenience for customers was them trying to make it to the cleaners to get their clothes before it closed. His company, Hamper, aims to provide a solution as "the Red Box of dry cleaning." Customers can deposit their dry cleaning in a kiosk in their office building, and it will be delivered to pick-up locations.
Calacanis liked that Ali has a background in the dry cleaning business."It takes somebody who is so obsessed that they aren't going to give up," he says, adding that he liked Ali's story.
"When you have something new – something that's novel, you could get a lot of attention," Calacanis says. "For things that are not novel, you have to use performance. You have to use the metrics."
Dyan Gibbens, founder and CEO, Trumbull Unmanned

Trumbull Unmanned equips energy companies with data-retrieving drones. Photo via trumbullunmanned.com
Trumbull Unmanned has created an enterprise software company to analyze data collected from drones flying over oil and gas sites. The technology allows workers to maintain a safe distance and still collect the information needed. Dyan Gibbens, founder and CEO, has secured some impressive contracts with companies, including Exxon.
Calacanis asked Gibbens about those contracts and how much they were usually for, but didn't like her first answer.
"Every answer we get as investors is, 'It depends,'" Calacanis says, explaining a "pro tip" for entrepreneurs. " You want to lead with some examples and get some ground truth. Sell us that ground truth."
Calacanis' next piece of advice for Gibbens was to add a second set of data collecting technology, such as a moisture sensor or heat sensor, creating two sets of data for clients.
"Being agnostic to how you solve the problem is [a big opportunity]. Also, that becomes an upsell," Calacanis says.
Ksenia Yudina, founder and CEO, UNest
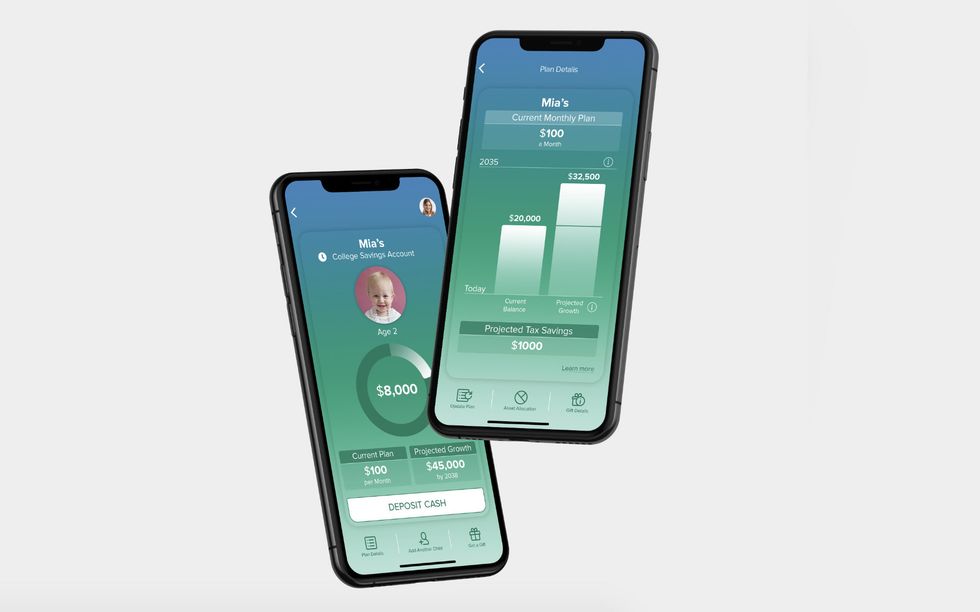
UNest is a tax-free way to save money for your children's education. Photo via unestapp.com
UNest is using user-friendly app technology to set up college funds for millennial parents. And Founder Ksenia Yudina has gotten some great reception, which has caused financial advisers to take note and even reach out. But Calacanis says they are, in a way, the enemy for her product and she needs to not spread out her resources trying to partner with financial advisers.
"Part of being a successful founder is knowing what you need more and what to stay focused on," Calacanis says. "If you remain a product that people like, everyone is going to drown you in opportunities. And as CEO you have to know when to say no."

