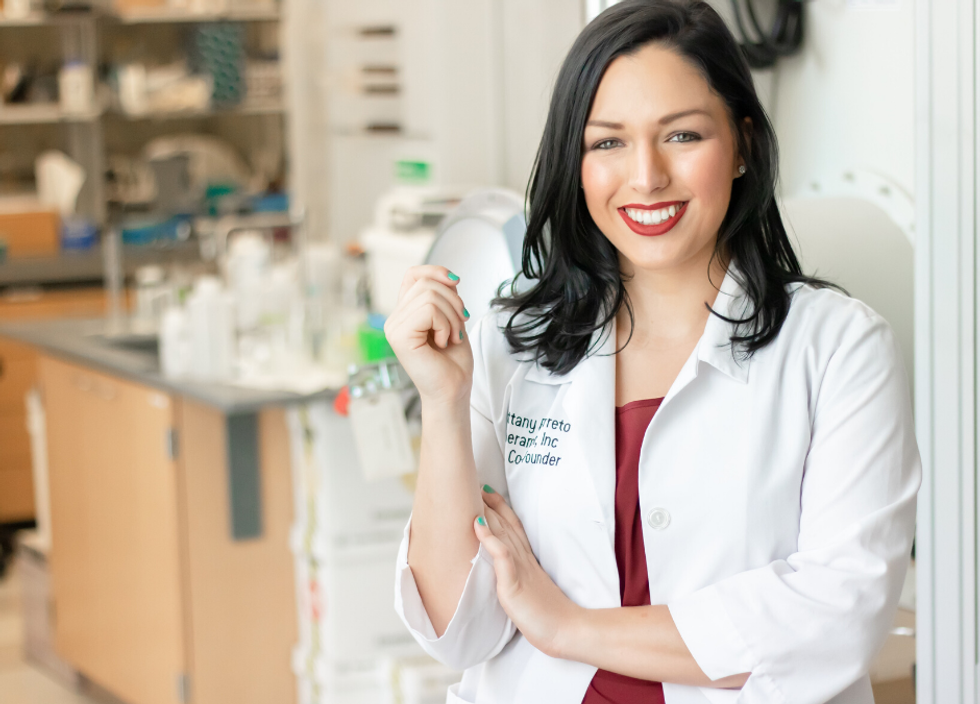
When Brittany Baretto was 18 years old and sitting in an undergraduate genetics seminar, she raised her hand. She asked, to her professor's point, if particular DNA trait differences between two people can result in attraction, could she, based on that logic, make a DNA-based dating tool. With that question, she set in motion a series of events.
These events included teaming up with Bin Huang to start a dating app, called Pheramor, that factored in user DNA; raising millions for the company; hiring a team from across the country; and signing up users in all 50 states. Though, Pheramor's hockey stick growth came to a sudden stop this year when Apple pulled the app from its store, and there was nothing the founders or their investors could do about it.
"They are gatekeepers in innovation," Barreto learned the hard way.
InnovationMap recently spoke with Barreto to discuss the rise and fall of Pheramor and lessons learned.
Launching the first nationwide DNA-based dating app
Barreto mulled over the idea for the company through college and through her genetics PhD program before starting the company in 2017.
"I actually formed the C-Corp the same month that Accenture put out its report on Houston needing more attention on its startups and innovation," she says. "I didn't know about that report. I was really lucky with Pheramor to ride the wave of Houston growing its startup community."
She went on to fundraise $1.3 million, and, at its height, Pheramor had 10 employees working out of WeWork in the Galleria. Pheramor was the first nationwide DNA-based dating app, and for that she will always be proud, Barreto says.
"We were growing something not necessarily unicorn status growth, but we were doing something really different," she says. "And we knew we were growing something valuable. At our peak, we had 250 downloads a day."
Venture capitalists were taking note, Barreto says, and she was on her way to closing another round — this time for $2.2 million.
Getting the call
In March, Barreto and Huang attended Enventure's bioventure pitch event, where, just three years prior, the duo had pitched and won thousands of dollars. It was a real turning point, Barreto remembers.
Earlier that day, they had seen some issues with Apple's app store and filed a service request. As she left the event, Barreto's phone rang, and it was an Apple representative explaining that the Pheramor app had been pulled from the store. New rules for the App Store had been set in place — rules that forbid dating apps from procuring DNA samples from users.
Once the DNA element was removed from the app, Pheramor would be allowed back on, Barreto was told.
"That was our differentiator," she says. "That was the thing that made us Pheramor."
For the next three weeks, Barreto called every app reviewer at Apple and challenged each "no" she got.
"I had that internal founder drive. I was like, 'No, I just need to talk to someone. I'm going to hustle around this.'"
Her request went to the very top, before receiving one final, inarguable "No."
Barreto knows why Apple instituted the new policy — biohackers are the newest cyber threat in the world. But she was being dragged through the ringer while watching her startup slowly slip away, and the anonymous Apple employees on the other end of the phone had no sympathy for her inner turmoil.
"It felt like they just kept reading a script," she says, adding that it was the most painful experience for her. "The insensitivity of the app review people was salt in the wound."
Throwing a Hail Mary
The Pheramor app was still live on Google, Barreto says, but with only 10 percent of the market, and data showing that Android users are historically non-buyers, she knew she had to pivot.
Huang and his team turned around an idea for a couples' compatibility test based on DNA, and WeHaveChemistry.com was born. Barreto tapped an acclaimed relationship expert, Laura Berman, as a strategic adviser. She made a deal with her board — if they could sell 100 of these kits in 60 days, they'll make new goals and keep the testing live.
Barreto says they sold some, but ultimately in June, after not meeting that goal, she suggested to the board the company should sell its assets, if possible, to help pay back her investors.
While the investors of Pheramor's $2.2 million round had pulled out at this point, Pheramor still had $100,000 in the bank. Barreto says she budgeted about $30,000 to legally close the company. At this point, she had laid off her staff, and it was down to the co-founders. Both got new jobs — Huang is now the head data scientist at Houston-based BrainCheck, and Barreto joined Capital Factory as its Houston-based venture associate.
Since Barreto was actively trying to sell the assets, she kept quiet about Pheramor's downfall. While she had some interest, ultimately, people told her the technology was too complicated or that they wouldn't buy unless Barreto came with the company.
"I realized that over the past two years, I had already been ad hoc coaching and mentoring founders and loving it," Barreto says. "Now, I was doing it and getting paid for it, on a bigger scale, and with more resources. I knew it was the journey I wanted to continue down."
Lessons thoroughly learned
Barreto's past six months have been a rollercoaster, to say the least. Losing Pheramor felt like an identity crisis for her.
"I was very personally involved with the brand," she says. "So when Pheramor was gone, it was like, 'Who am I?'"
She had to keep most of her inner turmoil hidden from the startup community, especially since she was trying to sell Pheramor's assets. She battled an eating disorder and lost chunks of her hair, all the while she felt like she had to keep a smile on her face.
"As a female founder, I felt so much pressure to win. It felt like stakes were higher for me," Barreto says. "I felt really nervous to let my insides show."
She did find a few entrepreneurs that helped to guide her with their own perspective and careers, and Barreto says she leaned on her lawyer, Nicole Moss, a Houston-area startup lawyer, to help talk her through things. One surprising confidant was one of her investors, Jack Gill.
Barreto remembers meeting with Gill and thinking she was about to have to apologize for losing a ton of his money, but instead, he hugged her and congratulated on her first failure — that Pheramor's demise made her a real entrepreneur.
"His pride was a big turning point for me. I realized, 'Wow, this is really a jumping off point,'" she says.
This, of course, was directly contrasted by other investor's extreme disappointment. In the end, Barreto paid back investors by about 5 percent. She also realized the difference of working with investors who are new to the process.
"I learned a lesson of taking money from people who are not experienced investors will cause you headaches along the way," she says.
What's next? Funding femtech.
These investor lessons learned are especially important to Barreto, who wants her next startup to be a venture fund focused on empowering the marginalized entrepreneurs — female founders, the LGBT community, minorities, etc.
"I want to be someone of influence for social good," she says. "This crazy idea I had for a dating app was just a way to propel me to becoming that person. I felt like it did that."
Flipping to the other side of the investor table is appealing to Barreto, because she feels like she's able to make more of an impact.
"What I learned from Pheramor is I put all my eggs in one basket, and something happened and all my eggs broke," she says. "As a VC, you put your eggs in lots of baskets. If I want to make big change, I can probably do that more effectively if I'm empowering 20 different companies instead of doing only one thing."
Her idea is to raise a femtech fund that invests in startups and entrepreneurs with products or services within women's health.
"For me, as long as you're working on a technology that improves women's health and wellness, I want to invest in you," she says.
It's taken her a long time to get to this point, but ultimately, Barreto has realized that she did everything she could do, and she's better for this journey — no matter how rough it is. More importantly to Barreto, she sees this as an opportunity to share her story of failure — though, she wishes there were a better word for it — so that other entrepreneurs don't feel so alone in the process. She hopes that Pheramor's legacy can fill that need.
"We need to get comfortable with failure and support each other in the journey," she says.