At the conclusion of TMCx's recent Digital Health cohort — the most international group to date — there was only one Houston company among the 19. However, most of that group have developed a presence in Houston throughout the program.
Besides just being based here in Houston for four months, TMCx associate director, Lance Black, says the city has a lot to offer these startups.
"Why Houston? Why are these companies coming from everywhere to be here? Three big reasons," he says to the crowd at Demo Day. "The size and scale of the Texas Medical Center, the diversity of Houston, and the willingness and hunger of Houstonians wanting to be involved in innovation."
From pilots and partnerships to funding and mentorship, these TMCx08 companies announced the impact they've made on Houston at the Demo Day on Thursday, June 6. Meanwhile, TMCx had its own announcement that it would create early stage programming for professionals connected to the Texas Medical Center.
"It is the TMC's mission to advance health care, research, and education. It's our mission at the Innovation Institute to bring value back to the med center through health care technology," Black says. "And, through TMCx, we do that through startup companies."
Here are some examples of TMCx companies setting foundations in the Houston ecosystem.
Virti

Photo via virti.com
California-based Virti has developed an extended reality simulation technology for training medical staff. It's a cheaper, more effective way to train personnel, says Alex Young, CEO of the company.
Virti was selected to be in England's National Health Service accelerator — the only evidence-based AR/VR training company ever to be picked for the program, says Young.
With a presence in California and England, Young says he's also planted roots in Texas too, with sales representation based in the TMCx offices.
"In the time that we've been here, we've closed deals in Texas and back in California," Young adds.
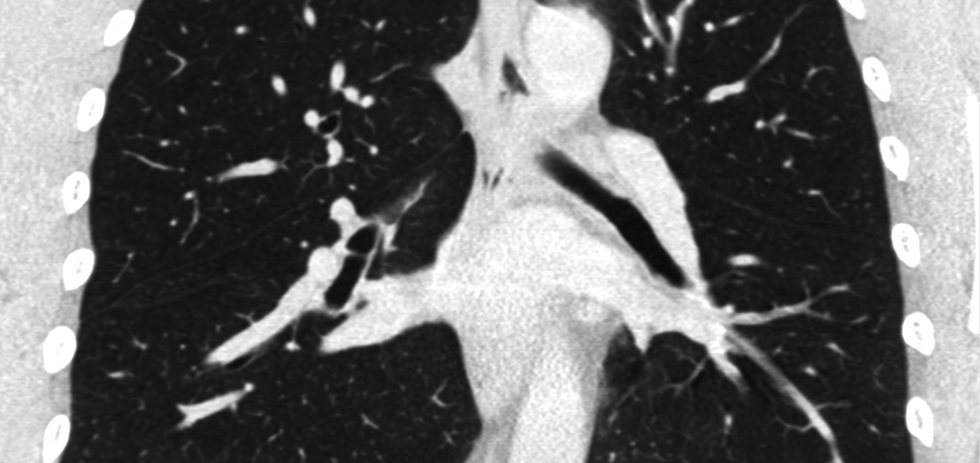
Optellum

Photo via optellum.com
Optellum is changing the way lung cancer is being detected. With the startup's artificial intelligence-enabled detection software, oncologists can better identify at-risk patients, which translates into more treatment for those in need, and less for those who don't.
The company, which is based in the United Kingdom, has raised funds abroad while networking locally.
"TMCx has been amazing for a small British company like us. We have started pilots and trials at four TMC member institutions," says Vaclav Potesil, CEO.
Oncora Medical

Photo via oncoramedical.com
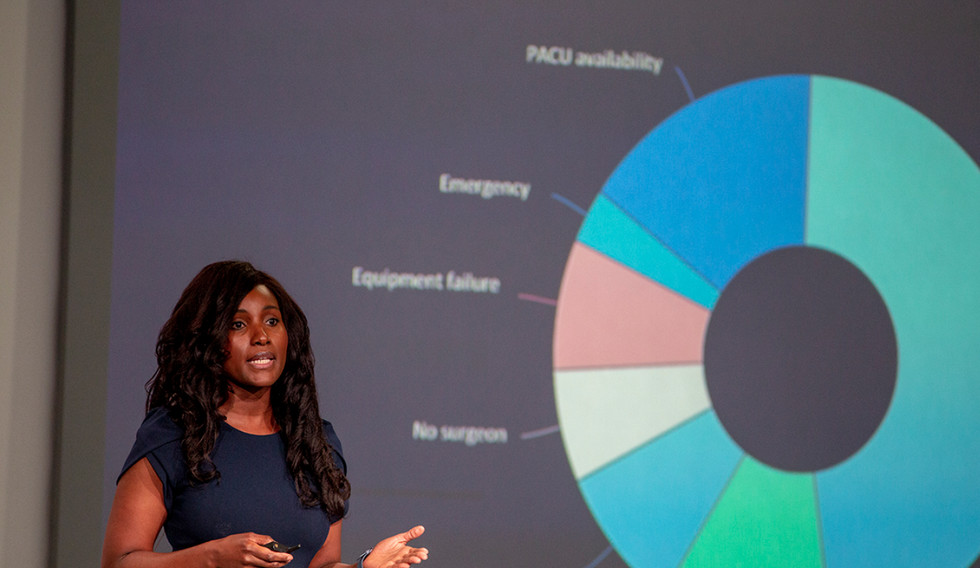
Angela Holmes, the director of product and customer solutions of Oncora Medical, sets the stage at her company's Demo Day pitch by telling a story of her friend's daughter who was diagnosed with cancer. She was forced to pick between two treatment options. She had no data or insights to help.
Oncora Medical's mission is to help fight cancer using data. Though based in Philadelphia, Oncora has Houston ties, since it formed a partnership with MD Anderson Cancer Center in April of 2017.
"We are so honored and gratified to be in a strategic, multi-year collaboration with MD Anderson to build this software system to save the world," Holmes says.
PreOp MD

Cody Duty/TMC
Within health care, the projected annual aggregate surgical expenditure by 2025 is expected to be $912 billion, says Christiana Obi, founder and CEO of PreOp MD, and a Houston-based anesthesiologist. She sees lack of information causing wasted surgical resources regularly.
PreOp MD — the only Houston-based TMCx company this cohort — has an app that allows for pre-procedure education, communication, and more that aims to prevent surgical delays.
While based here, PreOp is truly rooted in Houston, and even more so with their latest news.
"We are happy and excited to say that we have landed our first medical pilot at an medical right here in town," Obi says.
RoundTrip

Cody Duty/TMC
RoundTrip has a solution to 3.6 million missed or postponed medical visits that happen annually that are inconvenient to hospitals and a major health risk to the population: Ride sharing.
The Philadelphia-based company enables all forms of transportation and puts the power in the hands of the medical institution. From ambulances to other medical vehicles, the company can optimize utilization of all vehicles to get patients to their appointments and even has a partnership with Lyft.
While completing the TMCx program, RoundTrip closed its Series A round of $5.14 million led by Virginia-based Motley Fool Ventures in April. The funds will be used for expansion.
"Now we have all this new money to expand really rapidly. Texas, we're coming for you, whether you're ready or not," says Jackson Steeger, account supervisor.
Meru Health
![]()
Photos via meruhealth.com
Meru Health is also one of the 2019 TMCx Digital Health companies that has raised money while in the program. Palo Alto, California-based Meru completed a $4.2M raise in April 2019. The round was led by San Francisco-based Freestyle Capital.
Access to mental health professionals is increasingly more difficult, so Meru Health has created a low-cost digital clinic that offers an app-based treatment program from licensed therapists. Kristian Ranta, CEO and founder, while not yet providing specifics, that they aren't done in Texas.
"I'm happy to say there's some good stuff brewing here in Texas for us. More to follow," says Ranta.
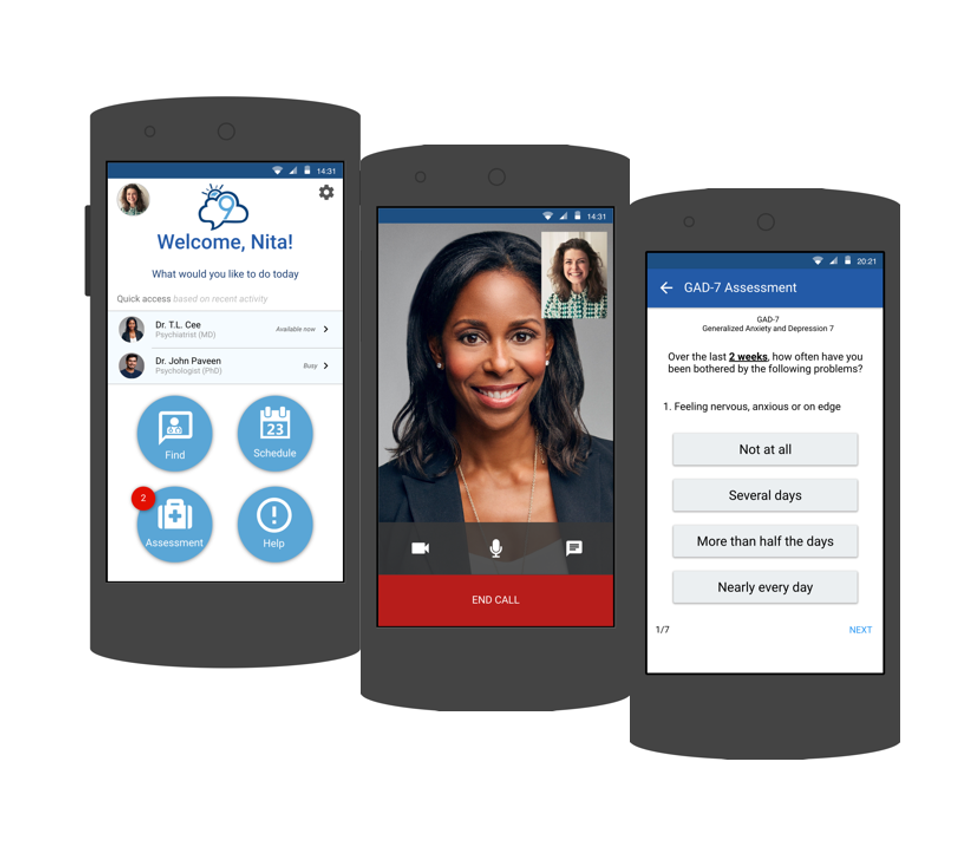
Cloud 9

Photo via cloud9psych.com
Mental health is a key contributing factor in the legal system cycle, but it doesn't have to be Liz Truong, co-founder of Cloud 9. Better educating officers and providing them with mental health resources is the best way to get them out of the hospitals and court rooms and back out in the field to protect the city.
While some police departments have instituted ride-along programs with mental health professionals that have showed success, it's expensive for the police department and risky for those professionals. Cloud 9 has created a digital solution.
"We proved this works in the Harris County Sheriff's office right here in Houston," says Truong. "Officers reported that 97 percent of Cloud 9 care was superior or equal to their current program and showed an immediate 632 percent return on investment for our customers in the same budget cycle compared to what they were already spending."
Truong also says they have other local customers they are working with, including the Harris County Health Department.
Axem Neurotechnology

Photos via axemneuro.com
Recovering stroke patients need rehabilitation to get back to 100 percent, but getting patients into the facility is challenging and at-home compliance is hard to track.
Canadian company Axem Neurotechnology has a solution. With their external device and mobile application, physical therapists can track progress and communicate with patients remotely.
"When we talk to rehab professionals, they are excited about what we're doing," says Tony Ingram, CEO and co-founder. "That's why we have leading institutions in both Canada and the U.S. onboard for clinical trials — this includes TMC's own TIRR, which is consistently ranked in the top five rehab centers in the U.S. We're collecting core baseline data in the most diverse city in the country."
Correction: A previous version of this article said Oncora's partnership with MD Anderson was formed during the TMCx program, when the partnership began in 2017.