Houston-area college breaks ground on new biotechnology program, launches curriculum
coming soon
San Jacinto College and McCord Development Inc. broke ground on the new Center for Biotechnology at the Generation Park Campus in Northeast Houston.
The 4,000-square-foot, state-of-the-art facility is slated to allow for more hands-on training within simulated environments and will allow students to earn associate of applied science degrees in biomanufacturing technology, as well as credentials for those already in the workforce. It's scheduled to be completed in the first quarter of 2025.
“The Center and the overall components of the Biotechnology program will play a vital role in meeting the growing demand for skilled professionals in the biotechnology sector,” Brenda Hellyer, chancellor of San Jacinto College, says in a statement.
“We are committed to equipping our students with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in the dynamic biopharmaceutical industry," she continues. "Our vision is to not only meet the workforce needs of today but will also shape the future of biotechnology education and training in our region.”
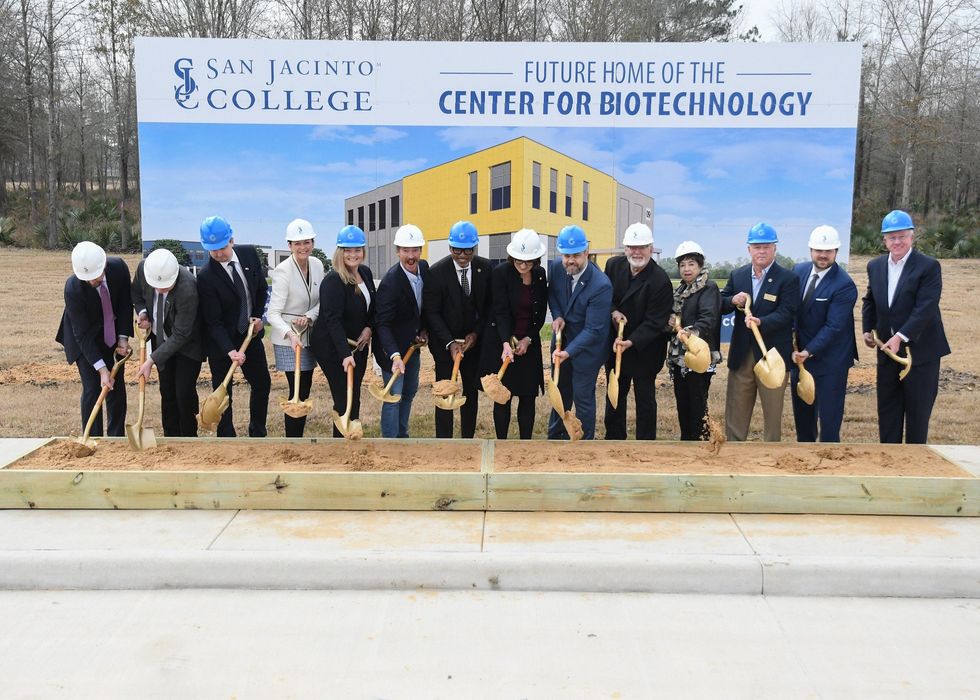

The new Center for Biotechnology curriculum is in partnership with the Ireland-based National Institute for Bioprocessing Research and Training. It is the only NIBRT-licensed training in the Southwest and Southeast region.
At the groundbreaking, San Jacinto College celebrated the ribbon-cutting for the Biomanufacturing Training Program at the South Campus, the first of the college's comprehensive biotechnology offerings.
The Biomanufacturing Training Program will be a customizable two-week hybrid program that combines theoretical teachings with hands-on experience.
“This program is designed to provide a seamless entry into the field for new professionals, with a focus on practical experience and exposure to industry practices,” Christopher Wild, executive director of San Jacinto College Center for Biotechnology, added in a statement.
The new center is part of Generation Park, a 4,300-acre master-planned development in Northeast Houston. In late 2022, San Jac and McCord, which is developing Generation Park, shared that they had signed a memorandum of understanding with the NIBRT to launch the program and center.
At the time, San Jacinto College was slated to be the institute’s sixth global partner and second U.S. partner.
Last summer, McCord also revealed plans for its 45-acre biomanufacturing campus at Generation Park.
 Photo via fly2houston.com
Photo via fly2houston.com