Houston Spaceport takes off with second phase of development
ready for liftoff
Since the Houston Spaceport secured the 10th FAA-Licensed commercial spaceport designation in 2015, the development's tenants have gone on to secure billions in NASA contracts. Now, the Houston Spaceport is on to its next phase of growth.
“Reflecting on its meteoric rise, the Spaceport has seen remarkable growth in a short span of time. From concepts on paper to the opening of Axiom Space, Collins Aerospace, and Intuitive Machines, the journey has been nothing short of extraordinary,” says Arturo Machuca, director of Ellington Airport and the Houston Spaceport, in a news release. “These anchor tenants, collectively holding about $5 billion in contracts with NASA and other notable aerospace companies, are not just shaping the future of space exploration but injecting vitality into Houston’s economy.”
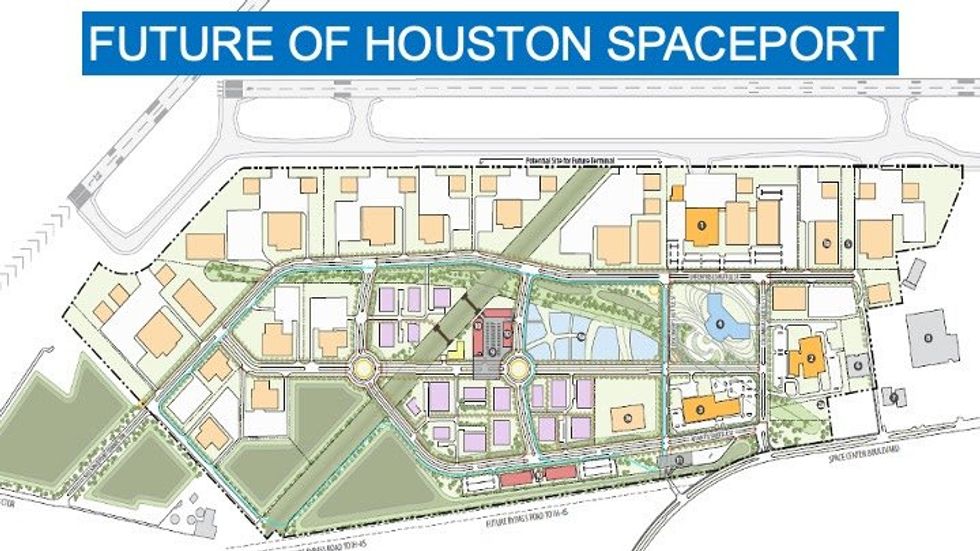
The next phase of development, according to Houston Airports, will include:
- The construction of a taxiway to connect Ellington Airport and the Spaceport
- The construction of a roadway linking Phase 1 infrastructure to Highway 3
- The expansion of the EDGE Center, in partnership with San Jacinto College
The Houston Spaceport's first phase completed in 2019. Over the past few years, tenants delivered on their own buildouts. Last year, Intuitive Machines moved into its new $40 million headquarters and Axiom Space opened its test facility. In 2022, Collins Aerospace cut the ribbon on its new 120,000 square-foot facility.
“The vision for the Houston Spaceport has always been ambitious,” says Jim Szczesniak, director of Aviation for Houston Airports. “Our vision is to create a hub for aviation and aerospace enterprises that will shape the future of commercial spaceflight.”
Educational partners have also revealed new spaces, including San Jacinto College's EDGE Center, which broke ground in July of 2019, finally celebrated its grand opening in 2021. Last year, Texas Southern University got the greenlight to operate an aeronautical training hub on a two-acre site at Ellington Airport.
“By providing the education and training needed to sustain jobs in the rapidly evolving space industry, the Spaceport is not only attracting companies but also nurturing the talent that will drive Houston's aerospace sector forward,” continues Szczesniak in the release.



