Houston's top innovators and startups for 2025 and more news to know
Trending news
Editor's note: We're looking back at the top Houston innovation news for the first half of October 2025, including the big reveal of our 2025 Houston Innovation Awards finalists. Here are the five most-read InnovationMap stories from Oct. 1-15, 2025:
1. Announcing the 2025 Houston Innovation Awards finalists

Meet the finalists for the Houston Innovation Awards, taking place Nov. 13. Graphic via Gow Media
InnovationMap is proud to reveal the finalists for the 2025 Houston Innovation Awards. Taking place on November 13 at Greentown Labs, the fifth annual Houston Innovation Awards will honor the best of Houston's innovation ecosystem, including startups, entrepreneurs, mentors, and more. This year's finalists were determined by our esteemed panel of judges, comprised of past award winners and InnovationMap editorial leadership. Continue reading.
2. 5 minority-founded Houston startups shine as Innovation Awards finalists

These five minority-founded businesses stood out to the judges for the 2025 Houston Innovation Awards. Photo via marsmaterials.tech
Houston is one of the most diverse cities in the nation, and that trend carries over into its innovation and startup ecosystem. As part of the 2025 Houston Innovation Awards, our Minority-founded Businesses category will honor an innovative Houston startup founded or co-founded by BIPOC or LGBTQ+ representation. Five minority-founded businesses have been named finalists for the 2025 award. The finalists range from a wearable health tech device company to a clean chemical manufacturing business to a startup with a lunar mission. Continue reading.
3. 2 UH projects named finalists for $50M fund to shape future of Gulf Coast
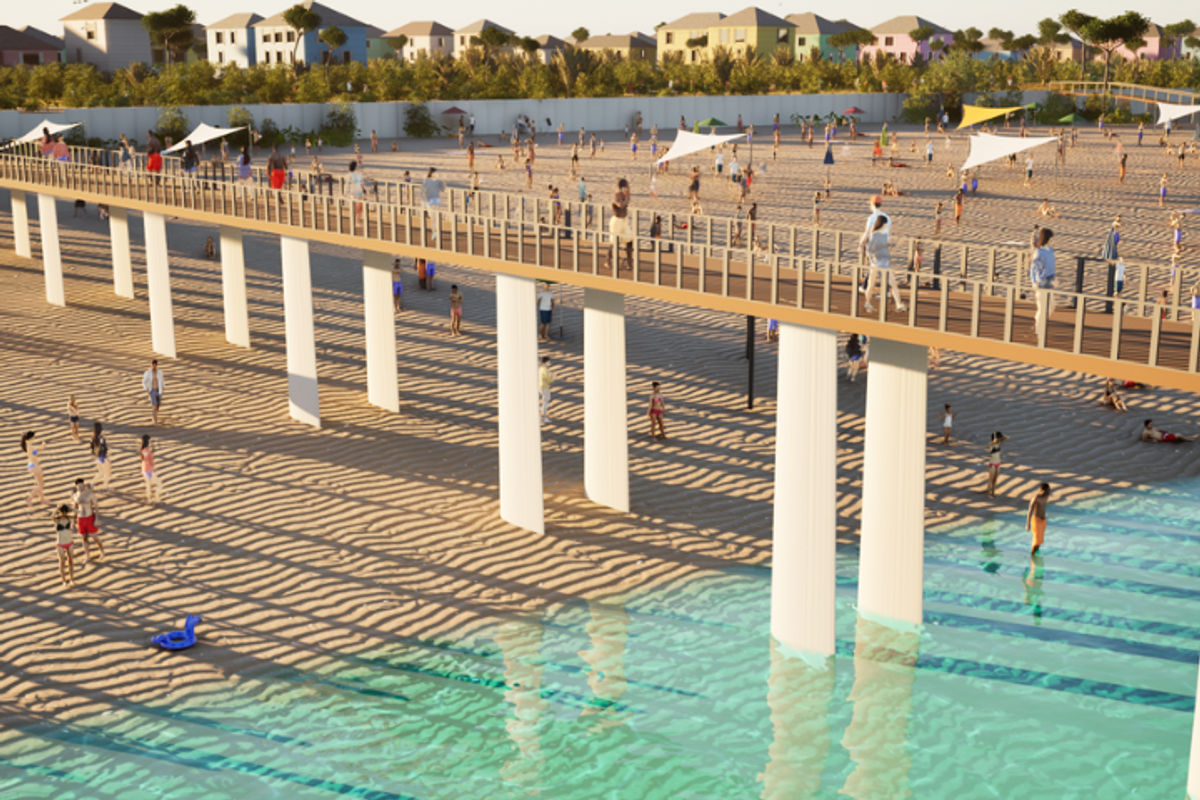

One project involves the innovative recycling of wind turbines into seawall and coastal habitats. Courtesy rendering
Two University of Houston science projects have been selected as finalists for the Gulf Futures Challenge, which will award a total of $50 million to develop ideas that help benefit the Gulf Coast. Sponsored by the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine’s Gulf Coast Research Program and Lever for Change, the competition is designed to spark innovation around problems in the Gulf Coast, such as rising sea levels, pollution, energy security, and community resiliency. The two UH projects beat out 162 entries from organizations based in Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas. Continue reading.
4. 3 Houston-area companies appear on Fortune’s inaugural AI ranking

Spring-based ExxonMobil ranks within the top 10 on the new Fortune AIQ 50 ranking. Photo via Getty Images.
Three companies based in the Houston area appear on Fortune’s inaugural list of the top adopters of AI among Fortune 500 companies. The Fortune AIQ 50 ranking is based on ServiceNow’s Enterprise AI Maturity Index, an annual measurement of how prepared organizations are to adopt and scale AI. To evaluate how Fortune 500 companies are rolling out AI and how much they value AI investments, Fortune teamed up with Enterprise Technology Research. The results went into computing an AIQ score for each company. Continue reading.
5. 10+ can't-miss Houston business and innovation events for October

From the fourth annual Tejano Tech Summit to the first-ever Ion Family Tech Festival, here's what not to miss this month. Image courtesy the Ion
Houston's October calendar is packed with informative and impactful events—plus a few fun ones, too. From the fourth annual Tejano Tech Summit to the first-ever Ion Family Tech Festival, here's what not to miss and how to register.Continue reading.
















 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.





