The Liu Idea Lab for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Lilie) has named 11 students and researchers with breakthrough ideas to its 2026 Rice Innovation Fellows cohort.
The program, first launched in 2022, aims to support Rice Ph.D. students and postdocs in turning their research into real-world ventures. Participants receive $10,000 in translational research funding, co-working space and personalized mentorship.
The eleven 2026 Innovation Fellows are:
Ehsan Aalaei, Bioengineering, Ph.D. 2027
Professor Michael King Laboratory
Aalaei is developing new therapies to prevent the spread of cancer.
Matt Lee, Bioengineering, Ph.D. 2027
Professor Caleb Bashor Laboratory
Lee’s work uses AI to design the genetic instructions for more effective therapies.
Thomas Howlett, Bioengineering, Postdoctoral 2028
Professor Kelsey Swingle Laboratory
Howlett is developing a self-administered, nonhormonal treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding.
Jonathan Montes, Bioengineering, Ph.D. 2025
Professor Jessica Butts Laboratory
Montes and his team are developing a fast-acting, long-lasting nasal spray to relieve chronic and acute anxiety.
Siliang Li, BioSciences, Postdoctoral 2025
Professor Caroline Ajo-Franklin Laboratory
Li is developing noninvasive devices that can quickly monitor gut health signals.
Gina Pizzo, Statistics, Lecturer
Pizzo’s research uses data modeling to forecast crop performance and soil health.
Alex Sadamune, Bioengineering, Ph.D. 2027
Professor Chong Xie Laboratory
Sadamune is working to scale the production of high-precision neural implants.
Jaeho Shin, Chemistry, Postdoctoral 2027
Professor James M. Tour Laboratory
Shin is developing next-generation semiconductor and memory technologies to advance computing and AI.
Will Schmid, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Postdoctoral 2025
Professor Alessandro Alabastri Laboratory
Schmid is developing scalable technologies to recover critical minerals from high-salinity resources.
Khadija Zanna, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ph.D. 2026
Professor Akane Sano Laboratory
Zanna is building machine learning tools to help companies deploy advanced AI in compliance with complex global regulations.
Ava Zoba, Materials Science and Nano Engineering, Ph.D. 2029
Professor Christina Tringides Laboratory
Zoba is designing implantable devices to improve the monitoring of brain function following tumor-removal surgery.
According to Rice, its Innovation Fellows have gone on to raise over $30 million and join top programs, including The Activate Fellowship, Chain Reaction Innovations Fellowship, the Texas Medical Center’s Cancer Therapeutics Accelerator and the Rice Biotech Launch Pad. Past participants include ventures like Helix Earth Technologies and HEXASpec.
“These fellows aren’t just advancing science — they’re building the future of industry here at Rice,” Kyle Judah, Lilie’s executive director, said in a news release. “Alongside their faculty members, they’re stepping into the uncertainty of turning research into real-world solutions. That commitment is rare, and it’s exactly why Lilie and Rice are proud to stand shoulder-to-shoulder with them and nurture their ambition to take on civilization-scale problems that truly matter.”
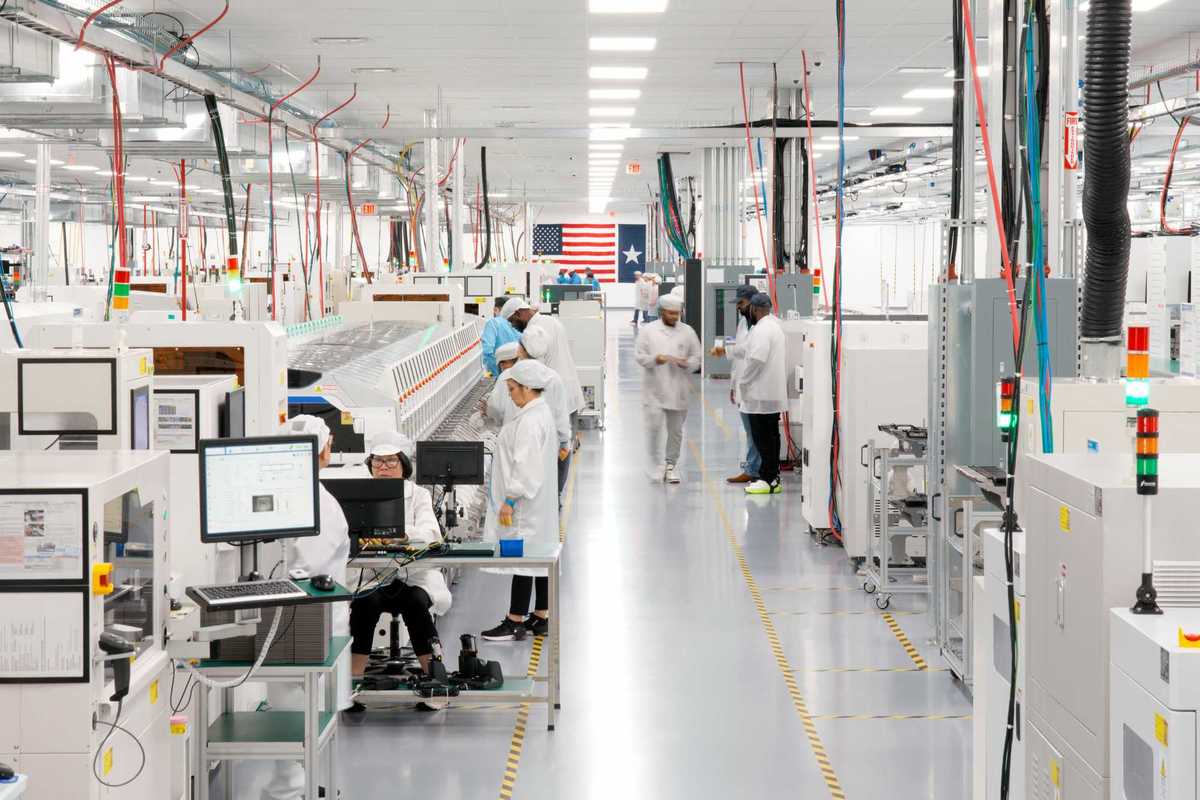


 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.