Exclusive: Houston startup rebrands to provide AI chat tool focused on women’s health
meet ema
Amanda Ducach set out to create a platform where mothers could connect with each other socially, but when she launched SocialMama just ahead of a global pandemic, she soon learned there was a bigger market need for access to information surrounding women's health — from fertility to menopause.
After pivoting her femtech platform to include women's health experts, she realized her technology wasn't able to completely support growing user base. The platform, which was called SocialMama, saw users engaging with experts in similar ways — and as Ducach looked into growing the platforms users, she realized that 24/7 access to experts was going to be hard to scale.
"We noticed that most of these conversations were repetitive," Ducach tells InnovationMap. "You had women asking an expert about tracking ovulation a hundred times a day. Having an OBGYN answer that question a hundred times a day was crazy and just not scalable."
Ducach says that about 16 months ago, her team took a step back to recreate the platform incorporating GPT technology. GPT stands for generative pre-trained transformer, and is a family of artificial intelligence language models most recently made popular but ChatGPT developed by OpenAI.
Now, after building out the platform, Ducach's company has rebranded to ema. The AI-based chat tool — named from the three letters in the middle of "female" — is meant to feel like texting "your childhood best friend who became an OBGYN physician," Ducach says. Not only can the chat provide crucial medical information, but it has a memory and can pick up conversations where they left off to be a constant resource to users.
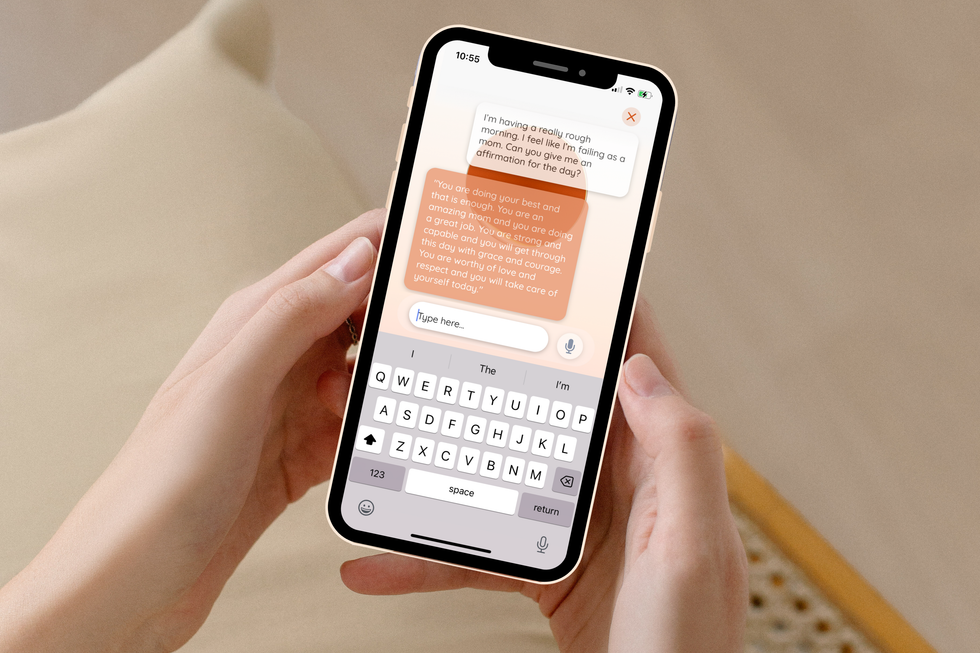
"Ema can answer everything from, 'how do I improve my baby's latch,' to 'how to I get a diabetic-friendly brownie recipe,' to 'give me an affirmation that's spoken like Snoop Dog because I'm feeling sad today,'" Ducach says.
Ducach first described the evolution of the company to AI-based communication last summer on the Houston Innovators Podcast. Now, the platform is gearing up for its launch next month and plans to raise seed funding this year to double her current team of 10 people to support the company's growth. Ducach, who was accepted into the Techstars Austin program in 2021, also says she's looking for more beta users in the meantime, and those interested should reach out to her or her team.
Ultimately, Ducach says the mission of ema is to democratize access to women's health care so that women feel supported and just a few taps away from important information.
"Barriers to care for women who face socioeconomic disparities is where you see the need for change," Ducach says. "For us, it's reducing those barriers of care. Ema is always in your pocket. You have access to her 24/7. The way that ema is really structured and her purpose is to catch red flags so that we can then help the female user get to positive health outcomes."

