New health-focused generative AI company emerges from stealth with Houston office, $4M in funding
eyes on ai
A new scalable biodata foundry startup has emerged from stealth with $4 million in investment funding and two new health care artificial intelligence tools. The company is co-located in Houston and Palo Alto, California.
Biostate AI was co-founded by former Rice Professor David Zhang, who serves as the company's CEO, in 2023. With the launch, the company announced two service products: Total RNA sequencing and Copilot for RNAseq data analysis, Biostate reveals in a press release.
"The successful training of any AI well requires large quantities of relevant and high-quality data," Zhang says in the release. "Biostate AI has developed the instrumental technologies to facilitate the collection of more biological data at lower costs. We are pleased to offer these capabilities to academic and industry partners and collaborators."
The company has raised more than $4 million in venture funding. Matter Venture Partners led the initial round, with participation from Vision Plus Capital, Catapult VC, and the California Institute of Technology through the Caltech Seed Fund. Additional investors included Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic; Joris Poort, CEO of Rescale; Michael Schnall-Levin, CTO of 10X Genomics; and Emily Leproust, CEO of Twist Bioscience.
"AI is the next frontier and AI needs data, and biological data is a lot harder to get than text or images. We are excited about the potential for Biostate's technology to dramatically lower the cost of collecting RNAseq datasets," adds Haomiao Huang, founding partner at Matter Venture Partners, in the release. "As a US company, Biostate's affordable AI-embedded CRO services are much needed today as the supply of preclinical research services shrinks due to geopolitical tensions."
With an ultimate goal of designing AI products to predict human and animal health changes, Biostate AI is looking to partner with academic researchers, hospital biorepositories, and pharma and other biotech companies.
In addition to its two launched products, Biostate AI has filed nine pending patents on its technologies and is collaborating with Twist Bioscience and California Institute of Technology.
With its official launch, Biostate AI also debut OmicsWeb Copilot, a conversational AI that aids biologists in and visualizing data. Using large-language models, the platform provides access to over 1000 unique RNAseq datasets collected by the Biostate team.
"Bioinformatic analysis of RNAseq and other omics data is a highly complex, multi-step process that currently takes many hours of dedicated specialized programming," explains Ashwin Gopinath, co-founder and CTO of Biostate AI, in the release. "As we scaled up our RNAseq data collection in the past year, we started building OmicsWeb Copilot as an internal tool to help our scientists make sense of the data. And then we realized other people may also find this tool useful, so we're opening it up to the general public for free."
Biostate is asking those interested in collaboration to reach out at partnerships@biostate.ai.
- Seattle biotech co. to move to Houston thanks to $13.3M grant from Texas organization ›
- Houston-founded startup raises $1.1M seed to fuel growth in bioeconomy ›
- Houston biotech company closes IPO in $15.25M deal ›
- Houston biotech commercialization company tapped for prestigious federal program ›
- Houston-area college breaks ground on new biotechnology program, launches curriculum ›
- California-founded biotech startup relocates to join Houston's emerging bioeconomy ›
- New biotech training center to rise in Northeast Houston ›
- New biotech lab, accelerator emerges in Houston to speed up commercialization of life-saving cures ›
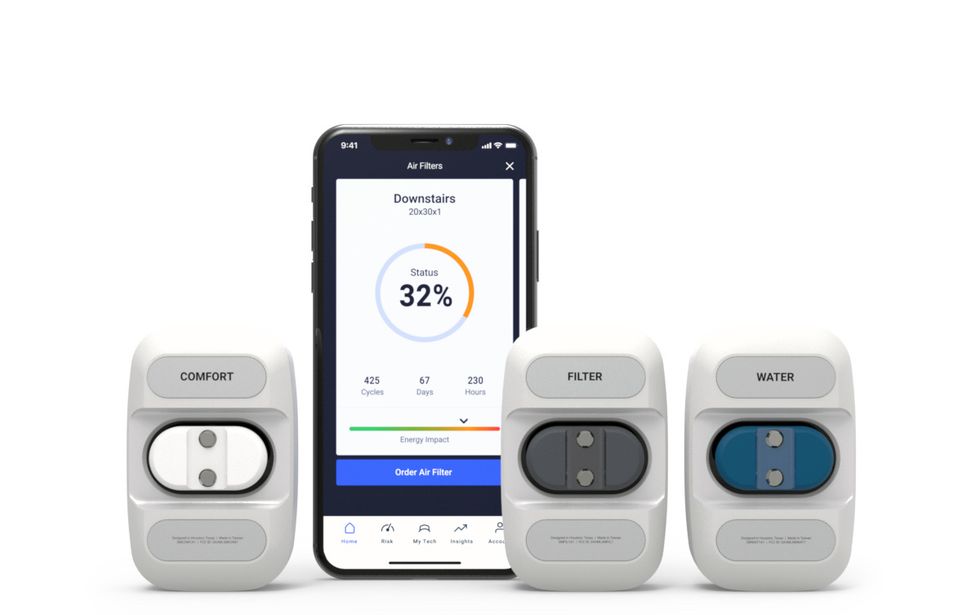
 The three SmartAC.com sensors are magnetic and easy to install. Photo courtesy of SmartAC.com
The three SmartAC.com sensors are magnetic and easy to install. Photo courtesy of SmartAC.com The data from the sensors is analyzed and sent to users via the smart phone app. Photo courtesy of SmartAC.com
The data from the sensors is analyzed and sent to users via the smart phone app. Photo courtesy of SmartAC.com