Houston health care expert shares lessons from journey of developing a telehealth MVP
GUEST COLUMN
In the vibrant landscape of startups, the quest to build groundbreaking products can sometimes overshadow the true essence of our existence — to solve problems for our customers.
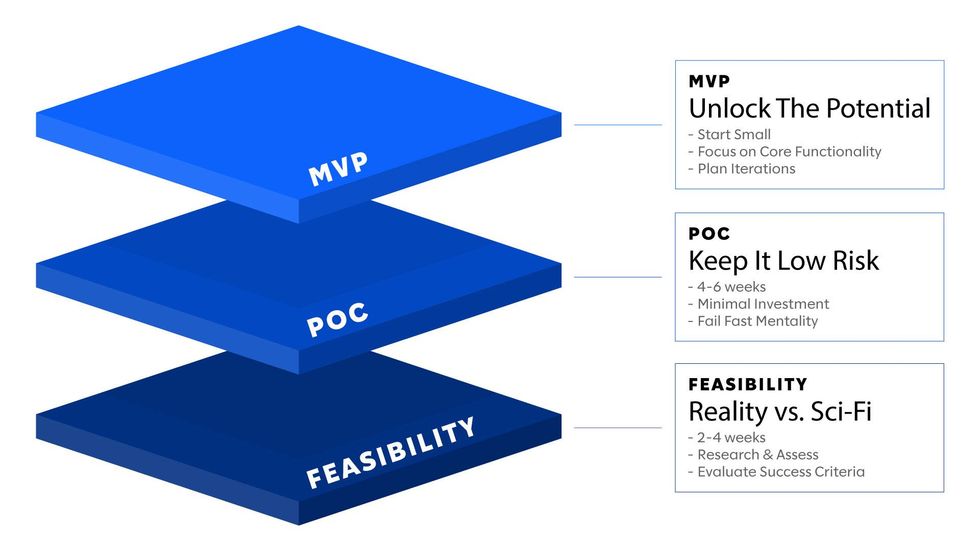
It's a trap many fall into, often leading to two common outcomes: prolonged product launches stretching over years or an unfortunate mismatch between product and market leading to startup death. But a dynamic solution exists, minimum viable products, or MVPs. MVP has propelled startups to unprecedented success.
A real-life testimony: MVP's power
Imagine a health care-focused at-home testing startup partnered with a major player. The aim: a telehealth support system for the at-home colon cancer screening. Unlike traditional telehealth services, this system required guiding members through a complex process of collecting stool samples accurately.
Challenges presented
- Develop a user-friendly telehealth solution in five to six weeks on a limited budget and secure a high-stakes multimillion-dollar deal.
- Carefully integrating telehealth on the existing portal for user-friendly access while aligning seamlessly with user expectations.
- Address the complexities of Telehealth, including clinician staffing and regulatory adherence.
User Insights
User journeys and interviews confirmed the necessity for guided support during test-taking, but users showed reluctance to navigate the process independently and expressed a preference for customer support over a clinician assistant.
Interestingly, telehealth was not instinctively linked to test support, but rather to medical advice.
The birth of an MVP strategy: a catalyst for innovation
Since the main user problem was the guided support during test-taking, we created the following MVP solutions.
- Video call integration: Direct video call button under customer support.
- Guided messaging: Articulate call support purpose.
- Testing guides: Portal's step-by-step guidance with videos.
- Video guide in test kit materials.
Our MVP led us to an excellent NPS score and became a guide for our future roadmap.
Next time you build, remember this and embrace the dynamic MVP strategy — create, learn, and reiterate are the cornerstones of success in digital health product management's journey.
Here are four steps for building a successful MVP in telehealth.
- Identify crucial user problems: Pinpoint your target customers' most pressing issue.
- Solve a small problem simply: Initiate a straightforward solution to address a minor problem.
- Plot the user's journey: Map out the user's path through your solution.
- Prioritize ruthlessly: Discern the key features and prioritize with precision.
Tanu Jain is the founder and CEO of Houston-based Digital Health Innovator, a strategic marketing firm for health care products.