Extended reality will have a big impact on business, this Houston expert says
guest column
What does your reality look like? Look around you. What do you see? It would be safe to say (almost guarantee) that you are looking at a screen right now, correct? We are consumers of information and use screens to access, view, and create information.
But why are we spending so much of our time looking at screens?
One poll stated that the average adult will spend 34 years of their lives looking at screens. It almost feels that screens (TV, laptop, or phone) have become so ubiquitous in everyday life that they have blended into our reality and are just ‘there’. Do you think the inventor of the TV, John Logie Baird, ever fully grasped how much the fabric of society would revolve around his invention? Time and time again, incredible disruptions have always come from breaking the ‘norm’ and given the vast level of integration of screens into our everyday reality, this ‘norm’ feels long overdue for innovation. This is where the world of augmented reality and spatial computing comes into play.
The COVID-19 pandemic saw an unprecedented shift to even more screen time and interactions using remote video communication platforms. It was also around this time that wireless virtual reality headsets were, for the first time ever, economically accessible to the consumer due to the large push of one multinational corporation. Fast forward to 2023, there are even more companies beginning to enter the market with new extended reality (XR) headsets (i.e. virtual, mixed, and augmented reality) that offer spatial computing – the ability for computers to blend into the physical worlds (amongst other things).
Some of our innovation engineering activities at the Houston Methodist Institute for Technology, Innovation, and Education (MITIE) have focused on specific use cases of XR in surgical education and training. One of our projects, the MITIEverse, is a VR-based platform focused on creating the first-ever metaverse for medical innovation. It is a fully immersive VR environment that allows the user to view 3D-rendered patient anatomies whilst watching the actual patient procedure, even offering the ability to meet the surgeon who performed the operation. It also affords the ability to give a ‘Grand Rounds’ style presentation to an audience of 50 participants.
We have looked at using augmented reality to control robotic-assisted surgery platforms. In our proof-of-concept prototype, we successfully demonstrated the manipulation of guide wires and catheters using nothing more than an augmented reality headset, illustrating the possibility of surgeons performing surgery at a distance. Houston Methodist is dedicated to transforming healthcare using the latest innovative technology including XR. The question we now need to ask – is society ready and willing to replace screens with XR headsets?
To learn more about our XR initiatives and other Houston’s cross-industry innovation collaborations, attend Pumps & Pipes Annual Event 2023, Problem Xchange: Where Solutions Converge next month at The Ion.
------
Stuart Corr is the director of Innovation Systems Engineering at Houston Methodist and executive director of Pumps & Pipes.

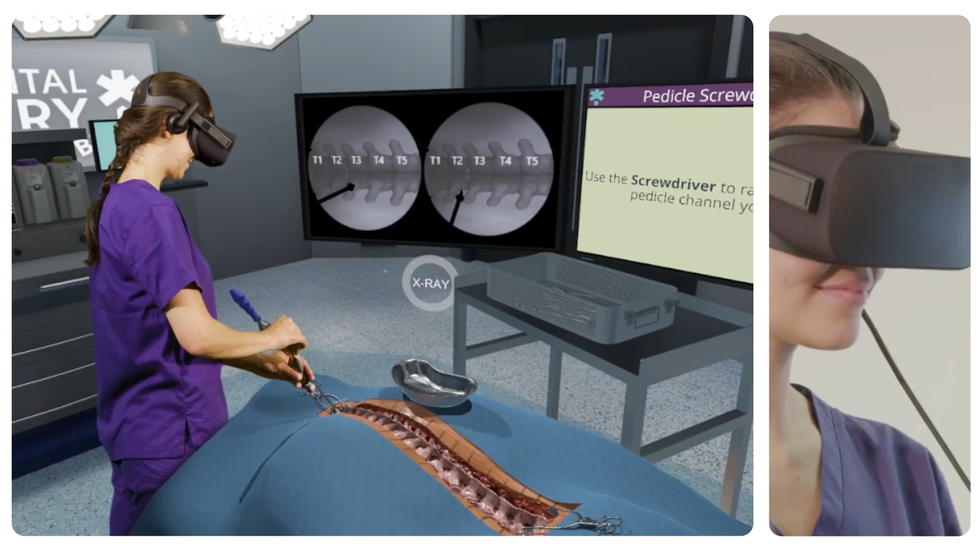 Image courtesy of Houston Methodist
Image courtesy of Houston Methodist Image courtesy of Houston Methodist
Image courtesy of Houston Methodist