New cancer-fighting nanodrug tops Houston innovation news to know
Trending News
Editor's note: The new year brings big Houston innovation news, from pending retirements to new hires and a cancer-fighting nanodrug. Below are the five most-read InnovationMap stories published January 16-30, 2026:
1. Houston team uses CPRIT funding to develop nanodrug for cancer immunotherapy
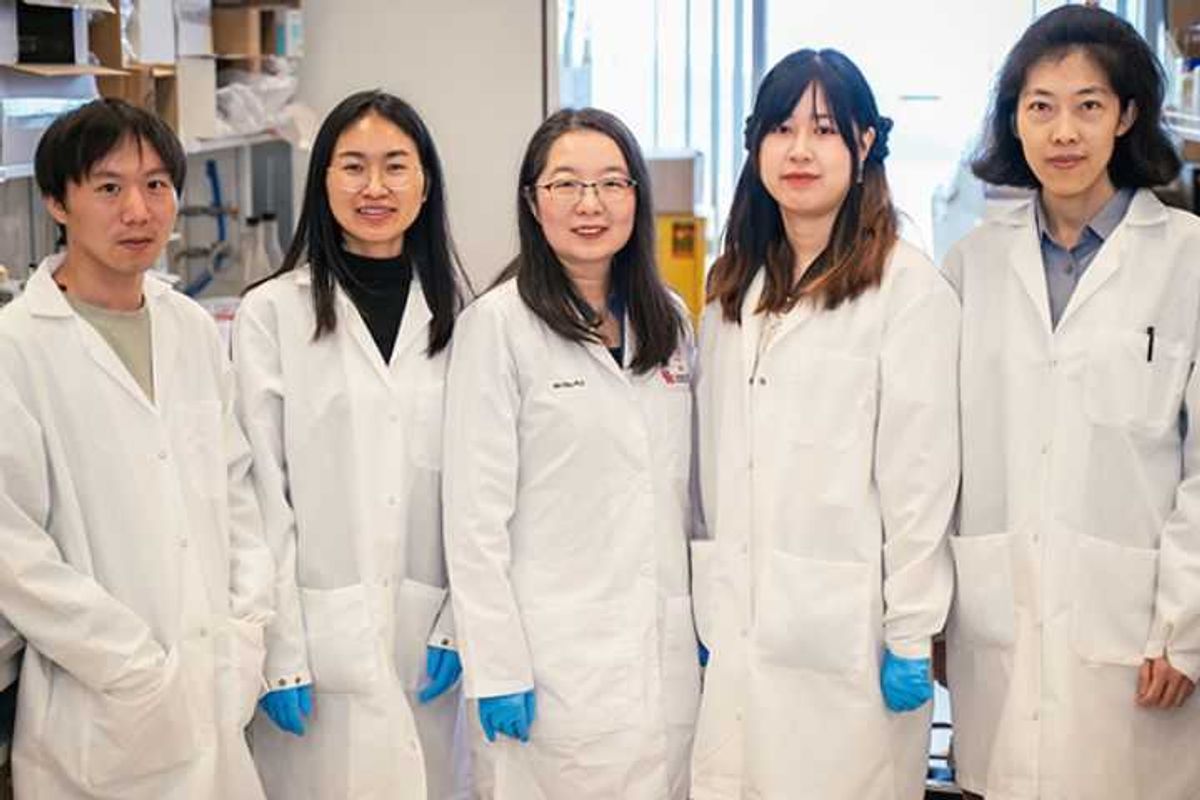
Wei Gao (center), a UH assistant professor of pharmacology, and her team have developed Nano-273, which helps the immune system fight pancreatic and lung cancers. Photo courtesy UH.
With a relative five-year survival rate of 50 percent, pancreatic cancer is a diagnosis nobody wants. At 60 percent, the prognosis for lung cancer isn’t much rosier. That’s because both cancers contain regulatory B cells (Bregs), which block the body’s natural immunity, making it harder to fight the enemies within. Newly popular immunotherapies in a category known as STING agonists may stimulate natural cancer defenses. However, they can also increase Bregs while simultaneously causing significant side effects. But Wei Gao, assistant professor of pharmacology at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy, may have a solution to that conundrum. Continue reading.
2. Rice Alliance and the Ion leader Brad Burke to retire this summer
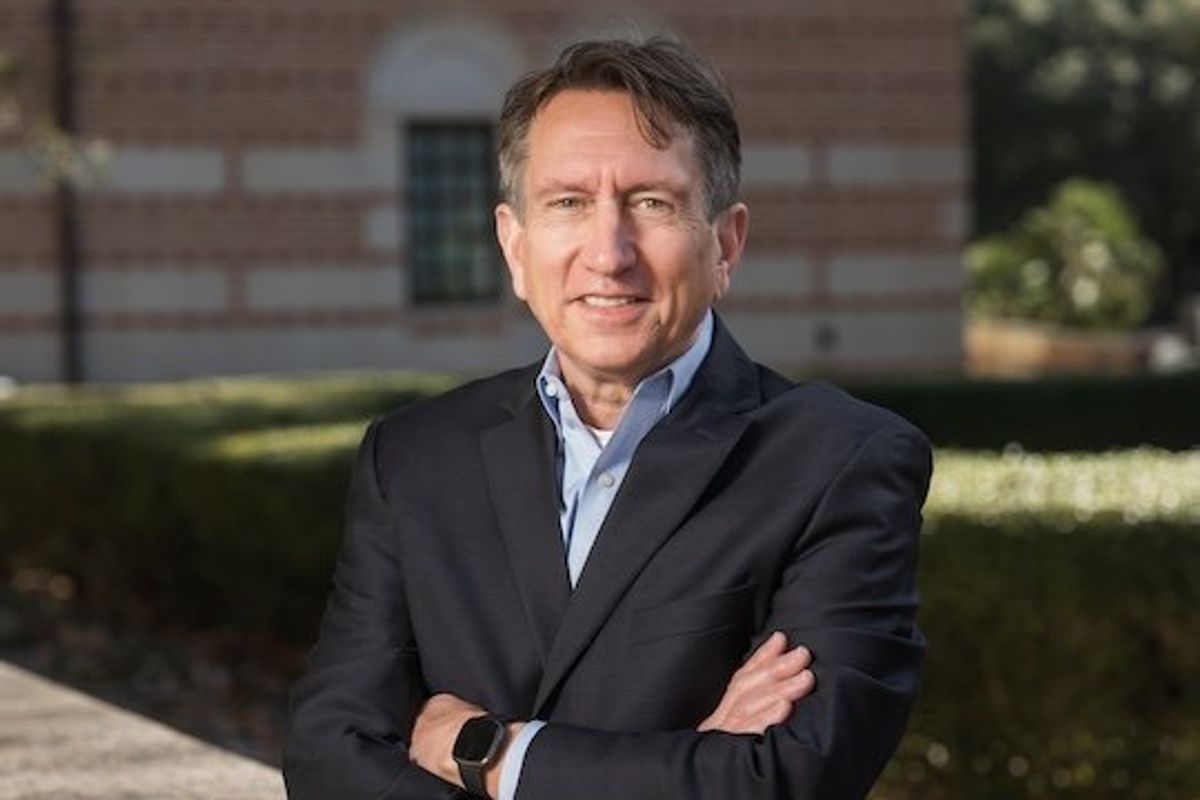

Houston entrepreneurship and innovation leader Brad Burke is set to retire on June 30. Photo by Jeff Fitlow/Rice University
Brad Burke—a Rice University associate vice president who leads the Ion District’s Rice Alliance for Technology and Entrepreneurship and is a prominent figure in Houston’s startup community—is retiring this summer after a 25-year career at the university. Burke will remain at the Rice Alliance as an adviser until his retirement on June 30. Continue reading.
3. 5+ must-know application deadlines for Houston innovators
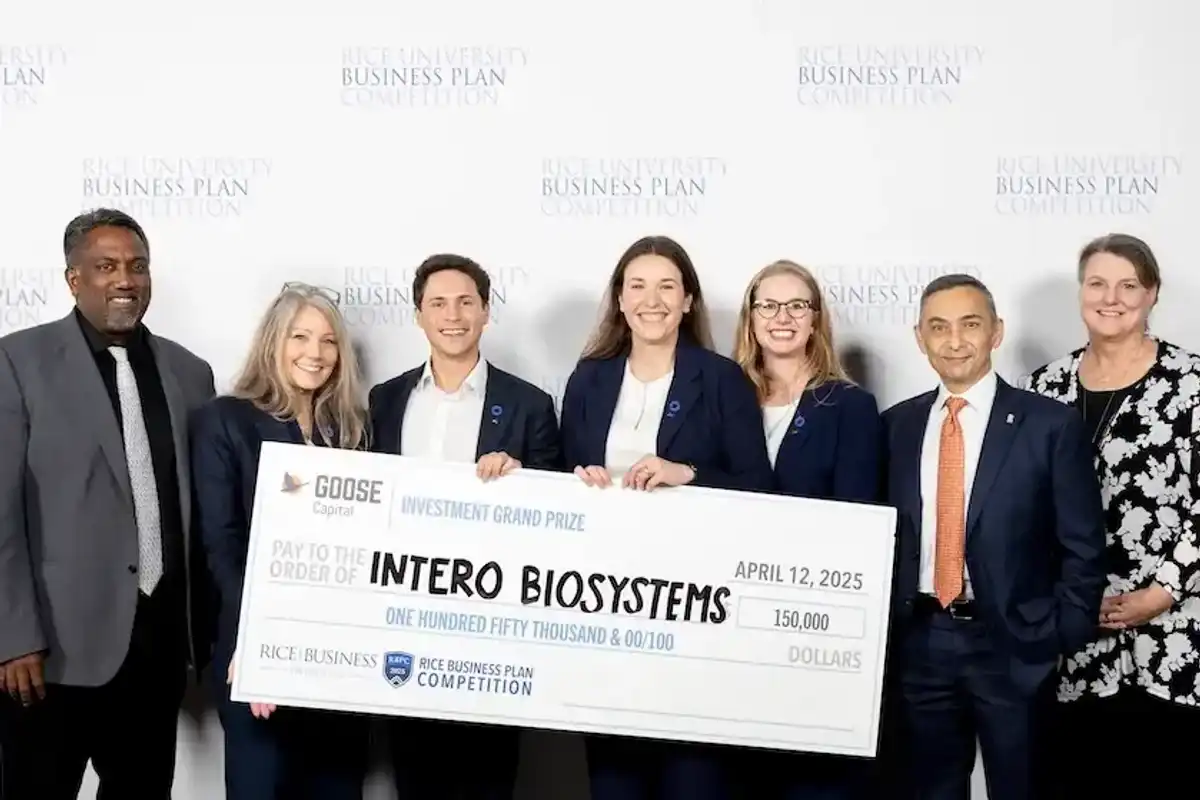

The University of Michigan's Intero Biosystems earned a top-place finish and the largest total investment from the 2025 Rice Business Plan Competition. Photo courtesy Rice University.
As 2026 ramps up, the Houston innovation scene is looking for the latest groups of innovative startups that'll make an impact. A number of accelerators and competitions have opened applications. See which might be a good fit for you or your venture, and take careful note of the deadlines. Continue reading.
4. Houston startups closed $1.75 billion in 2025 VC funding, says report

Local startups collected $1.75 billion in venture capital in 2025. Photo via Pexels.
Going against national trends, Houston-area startups raised 7 percent less venture capital last year than they did in 2024, according to the PitchBook-NVCA Venture Monitor report. The report shows local startups collected $1.75 billion in venture capital in 2025, down from $1.89 billion the previous year. Continue reading.
5. Baylor College of Medicine names Minnesota med school dean as new president, CEO
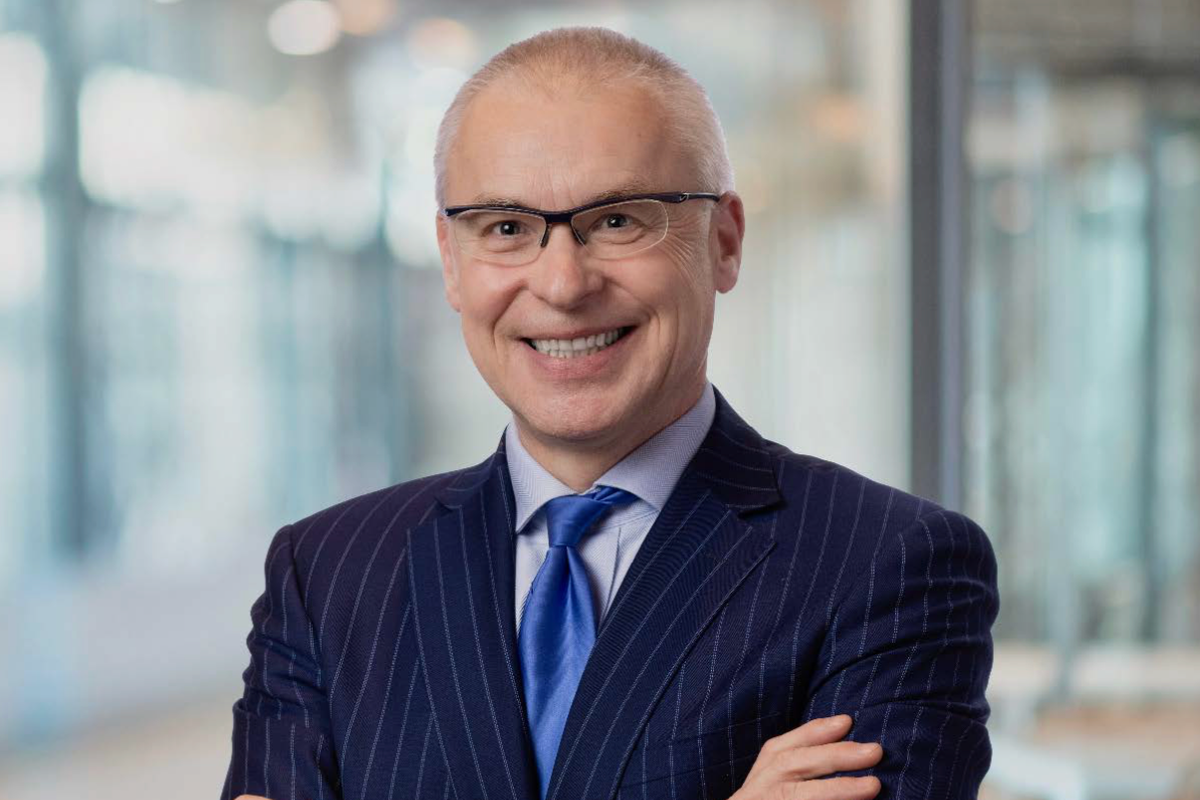

Baylor College of Medicine has named Dr. Jakub Tolar as its new president, CEO and executive dean. Photo courtesy of Mendel Lectures.
Dr. Jakub Tolar, dean of the University of Minnesota Medical School, is taking over as president, CEO and executive dean of Houston’s Baylor College of Medicine on July 1. Tolar—who’s also vice president for clinical affairs at the University of Minnesota and a university professor—will succeed Dr. Paul Klotman as head of BCM. Klotman is retiring June 30 after leading Texas’ top-ranked medical school since 2010. Continue reading.
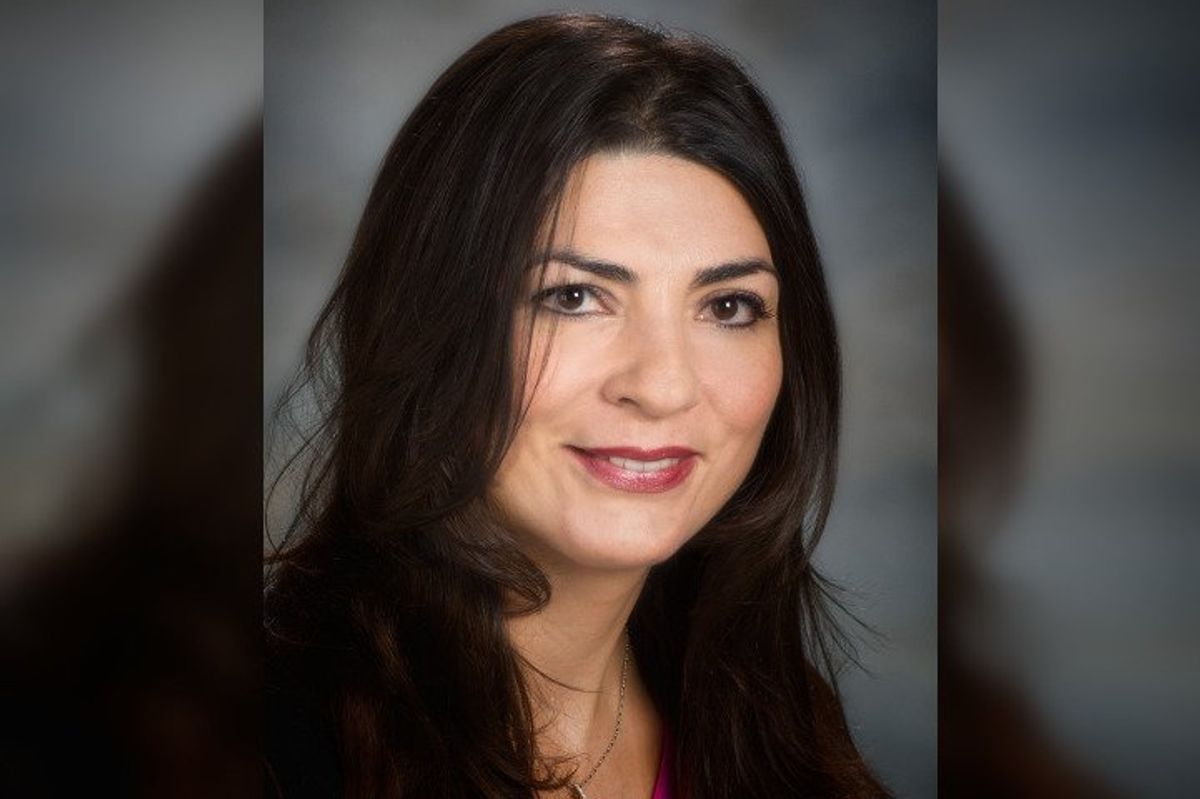
 Dr. Katy Rezvani is a professor of stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy and the force behind MD Anderson’s Rezvani Lab, which is focused on harnessing natural killer cells to combat cancer. Photo via mdanderson.org
Dr. Katy Rezvani is a professor of stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy and the force behind MD Anderson’s Rezvani Lab, which is focused on harnessing natural killer cells to combat cancer. Photo via mdanderson.org
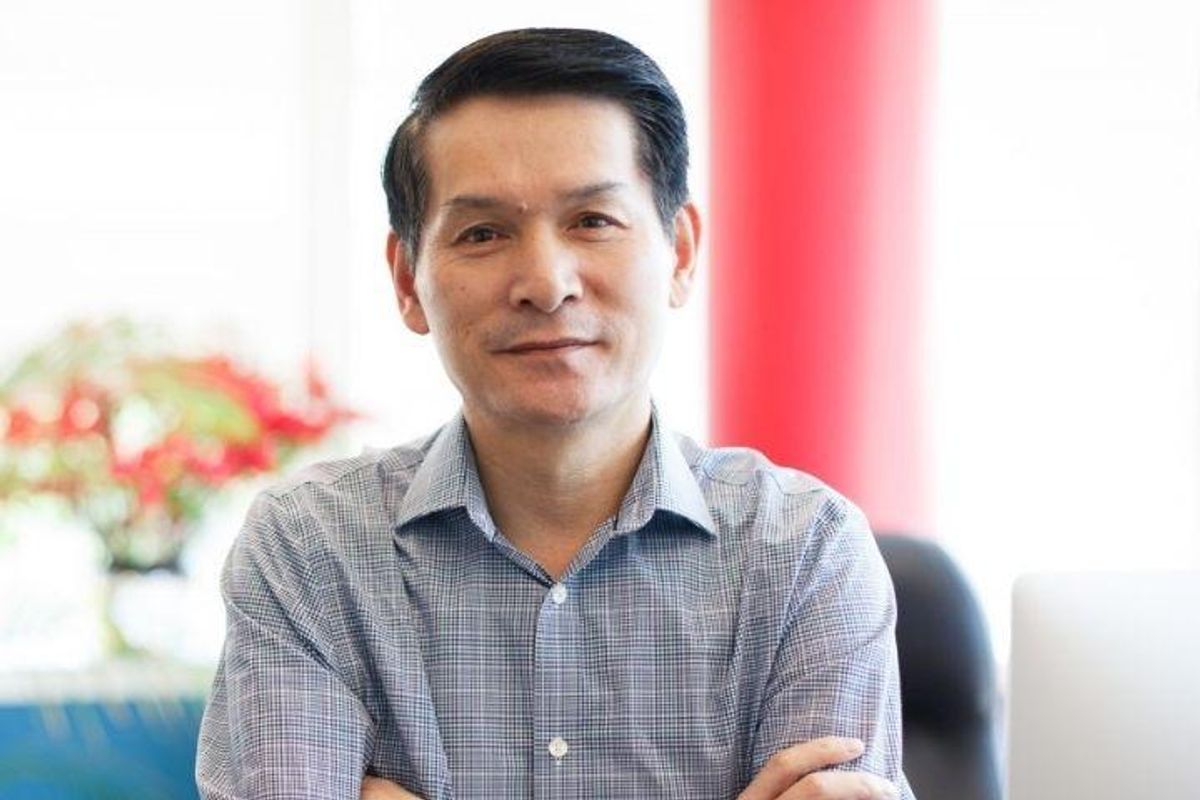 Shaun Zhang is the director of the Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling at the University of Houston and M.D. Anderson professor in the Department of Biology & Biochemistry. Image via UH.edu
Shaun Zhang is the director of the Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling at the University of Houston and M.D. Anderson professor in the Department of Biology & Biochemistry. Image via UH.edu


