Hardtech startup moves into Houston area with new Conroe facility, eyes tests in space
LEADING TECH
FluxWorks, a hardtech startup, recently opened its new base of operations in Workhub Developments’ Conroe location.
Founded in College Station by CEO Bryton Praslicka, FluxWorks specializes in making contactless magnetic gears for use in extreme conditions. At 9,000 square feet, the new Conroe facility is a result of discussions with Governor Greg Abbott's office and the Greater Houston Partnership, who introduced the company’s leadership to the Conroe Economic Development Council, encouraging their move, Praslicka tells InnovationMap.
“The pieces of the puzzle were all there, and with the support of the local, state, and federal government, we were thrilled to move to Conroe,” Paslicka says.
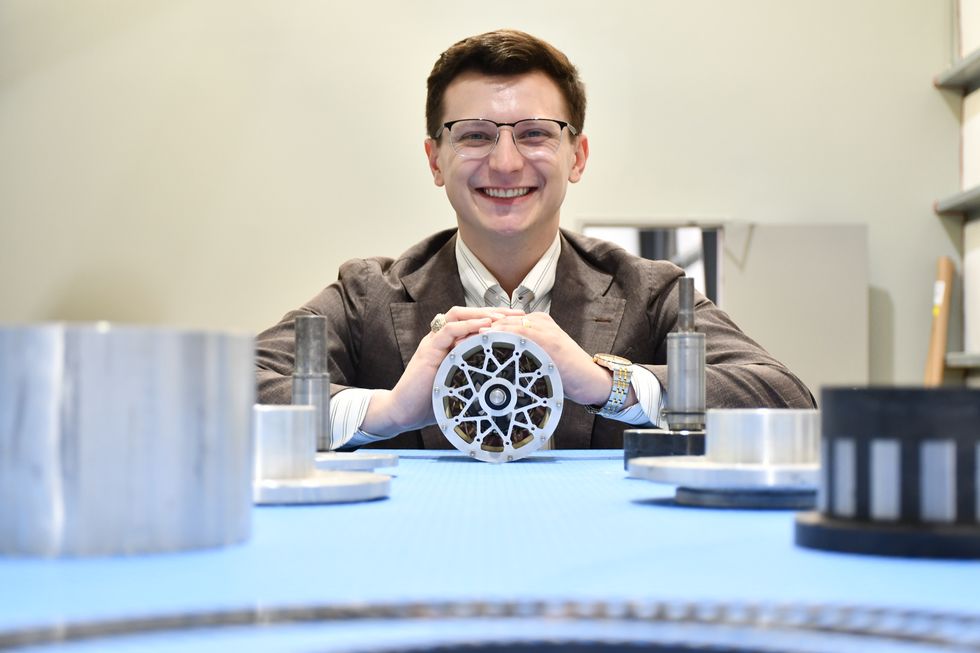
The enterprise recently won the MassChallenge’s technology in space prize, allowing them to test four gears at the International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory in 2026. The prize is funded by Boeing and the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, or CASIS which runs the ISS. Praslicka says their new offices will expand their manufacturing capacity by having all levels of production on-site.
"Since our inception, FluxWorks has been fragmented, having an office in one location, manufacturing in another location, and testing in a third location," Praslicka explains. "This is a new chapter for us to begin having the entire process, from design to testing and validation and then shipping to customers, all under one house.”
The magnetic gears FluxWorks makes are suited to space applications because they do not require lubricants, which can be difficult to control at harsh temperatures and in microgravity, to minimize friction. Through their partnership with the ISS, Praslicka says FluxWorks has strengthened their connections to other space tech companies including Axiom and Boeing, and it's opened the door to collaborations with the new Texas Space Commission.
“Now the NASA Johnson Space Center is even officially supporting our proposal to the Texas Space Commission as a proposed teaming partner,” Praslicka says.
The new facility received special security certification from the National Institute of Standards and Technology, increasing FluxWorks’ opportunities to work with NASA and defense contractors. The Texas Manufacturing Assistance Center awarded FluxWorks for “outstanding innovation” during its recent ribbon cutting ceremony.
The company, named a finalist for the 2024 Houston Innovation Awards, cleaned up in the 2023 Rice Business Plan Competition with a $350,000 investment prize from Houston group, Goose Capital.





