Editor's note: In this week's roundup of Houston innovators to know, I'm introducing you to over a dozen local innovators across industries — from cognitive tech to mobile ordering — recently making headlines in Houston innovation. That's right it's a special edition of this Monday feature. Scroll to see the 11 honorees from the Houston Innovation Awards Gala.
Betsy Furler, co-founder and CEO of For All Abilities

Betsy Furler, co-founder and CEO of For All Abilities, joins this week's Houston Innovators Podcast. Photo courtesy of For All Abilities
The fact that people's cognitive abilities differ widely is not exactly new information, but with new technologies and information about the subject, communities are able to learn better and more efficient ways of coping with neurodiversity — especially in the workplace. Betsy Furler, founder and CEO of Houston-based For All Abilities, is working on a unique approach to these challenges.
After its initial assessment, For All Abilities, which operates as a subscription software model for businesses, provides employees with curated low or no-cost apps and efficiency tools. While her work is mission-driven, Furler says on the show she was very intentional on starting her organization as a for-profit tech startup.
"It really makes sense from a business perspective to support your employees this way," she says. Click here to read more.
Marshall Law and Aaron Knape of Rivalry Technologies

Rivalry Tech's co-founders — Marshall Law and Aaron Knape — share news of the company's latest round of investment. Photo courtesy of Rivalry Tech
Rivalry Tech, originally founded as sEATz and tackling mobile ordering in sports venues, has raised $3.5 million following expanding with a new product, myEATz, that targets the health care, leisure, and business industries. The round was led by Houston-based Sightcast, with participation from Houston-based Softeq Venture Studio, Rice University’s Valhalla Investment Group, and more.
Co-Founders Aaron Knape, Marshall Law, and Craig Ceccanti launched the company in 2018. The idea came to Law after he missed catching a home run ball in the 2017 World Series because he was stuck in a long line waiting for concessions.
“We have built an amazing mobile ordering platform over the last four years for some of the best teams in professional and collegiate sports. It is exciting to see our success in sports and entertainment translate into opportunities in other industries. People want the best mobile ordering experience no matter where they are. That is exactly what we provide,” says Law. Click here to read more.
Meet the startup founders, mentors, investors, and other innovation leaders honored at the Houston Innovation Awards Gala
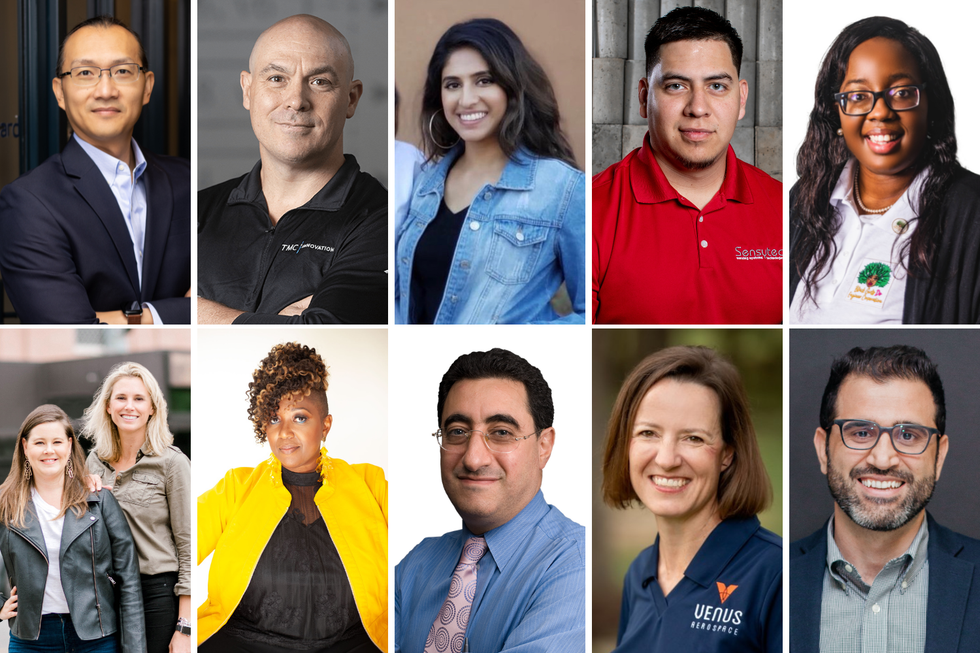

The 2022 Houston Innovation Awards revealed its big winners across 11 categories. Photos courtesy
Last Wednesday, InnovationMap and Houston Exponential announced the winners of the 2022 Houston Innovation Awards Gala. Eleven founders, mentors, investors, and more took home wins. Click here to read more.
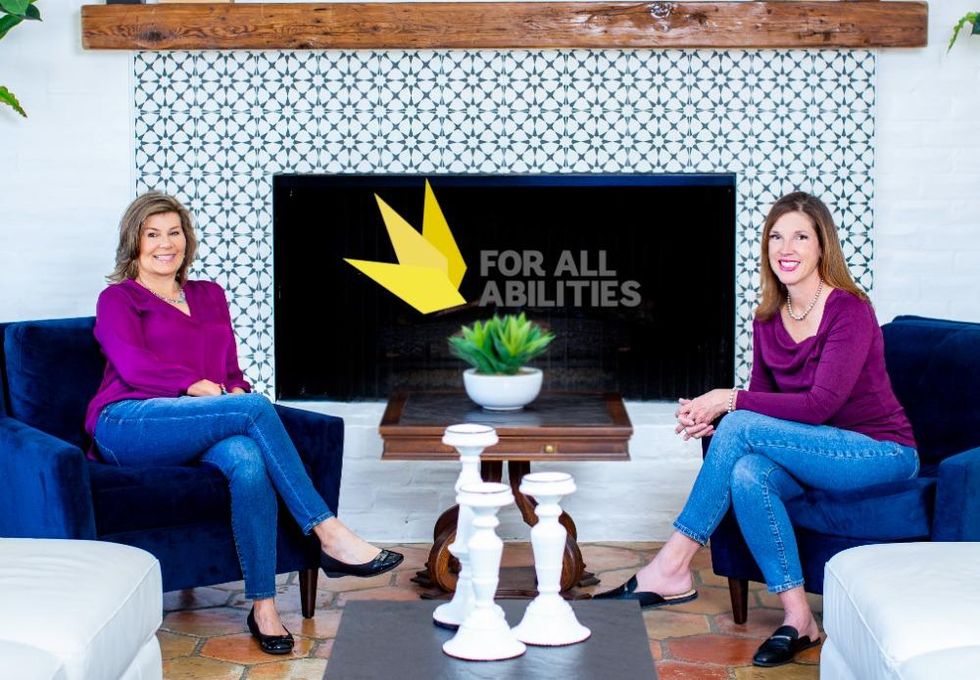
 Montie Krumnow (left) recently joined Betsy Furler as co-founder and COO of For All Abilities. Photo courtesy of For All Abilities
Montie Krumnow (left) recently joined Betsy Furler as co-founder and COO of For All Abilities. Photo courtesy of For All Abilities