Houston-based medical device companies pitch at TMCx Demo Day
Local legends
Earlier this month, 16 medical device companies wrapped up their time at the Texas Medical Center's accelerator program and pitched their companies to fellow health professionals, guests, and more. While each made important connections in the local ecosystem during the program, a quarter of the entrepreneurs had roots in Houston already.
Four of the 16 TMCx09 companies that are headquartered in Houston. They have built solutions within sepsis, surgery, and transplant spaces in health care. Here's a little more about the homegrown companies that pitched at the event.
CorInnova
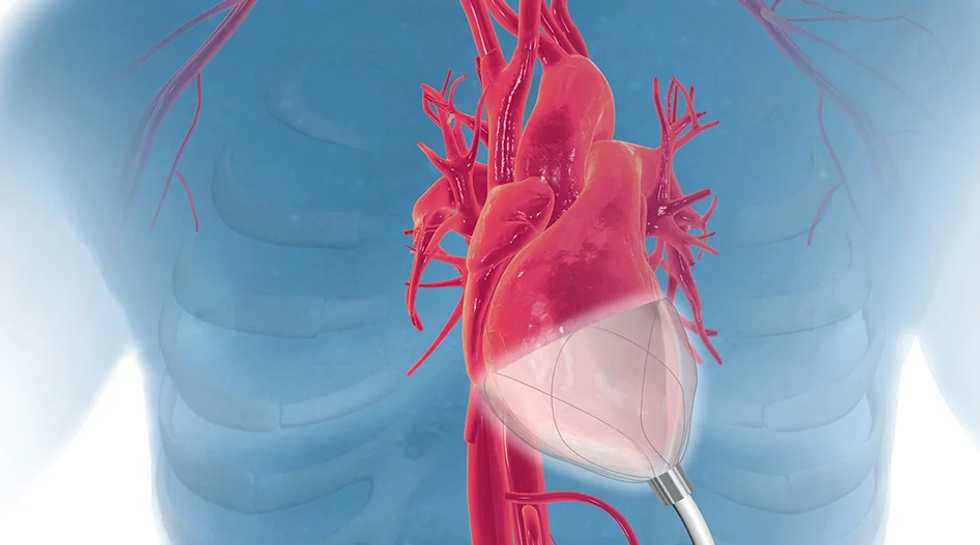
Photo via corinnova.com
The standard practice for acute heart failure patients is very invasive, says William Altman, CEO of CorInnova.
"The problem with existing devices is that they have invasive blood contact," Altman says. "Problem with that is blood contact is bad. It can cause up to 15 percent rate of stroke, which could kill you, and after five to seven days it provides 10 percent rate of blood destruction and has a 47 percent rate of kidney disfunction."
CorInnova's technology features a device that can be easily inserted through a 1-inch incision, and then be used for increase blood pumping by 50 percent.
"Surgeons tell us this is less invasive than minimally invasive aortic valve replacement, which is a widely done surgery, so this promises widespread adoption for our technology as we get it approved," Altman says.
The human prototype is expected to be ready in two years, with the next year being focused on animal studies. CorInnova is raising $12 million to accomplish its goals.
Ictero Medical

Getty Images
An estimated 10 to 15 percent of the United States population will get a gallstone in their lifetime. Should one of those stones cause trouble or blockages, the only solution is to remove the gallbladder completely through surgery. However, Matthew Nojoomi, CEO and co-founder of Ictero Medical, has another idea.
Ictero Medical has created a minimally invasive treatment that uses cryoablation to defunctionize the gallbladder without having to remove it.
"The CholeSafe System not only treats the source of the disease, but it leverages existing clinical workflows that doctors use to access the gallbladder," says Nojoomi, adding that the process only uses mild station and pain control.
The company expects to get to humans in the next two years, and has launched a financing round.
PATH EX

Photo via tmc.com
Currently, sepsis is hard to identify in patience. Even if a patient is in a hospital, and that hospital knows the patient has sepsis, the individual still has a 38 percent chance of dying, says Sinead Miller, CEO of PATH EX.
"Right now the problems associated with sepsis are very clear," she says. "It's the leading cause of death in our ICUs, and it's also associated with the highest hospital cost and readmission rates."
PATH EX's technology allows medical professionals to better diagnose and treat sepsis. The PATH EX therapeutic device can be hooked up to a patient and flow his or her blood through the machine to capture bacteria, clean and recirculate the blood, and faster diagnose what sort of bacteria the patient has attracted. The device technology is similar to hemo hemodialysis, Miller explains.
The Houston company, which recently won big at the Ignite Healthcare Network's Fire Pitch Competition, was named an honoree within the Johnson and Johnson Breakthrough Medical Technologies Quickfire Challenge.
The company was recently received clearance from the Food and Drug Administration as a breakthrough device technology. PATH EX closed its $615,000 seed round — with plans for a series A next year — and has received $1 million in SBIR grant funding. The company was founded two years ago, and relocated to call Houston HQ this year.
Volumetric
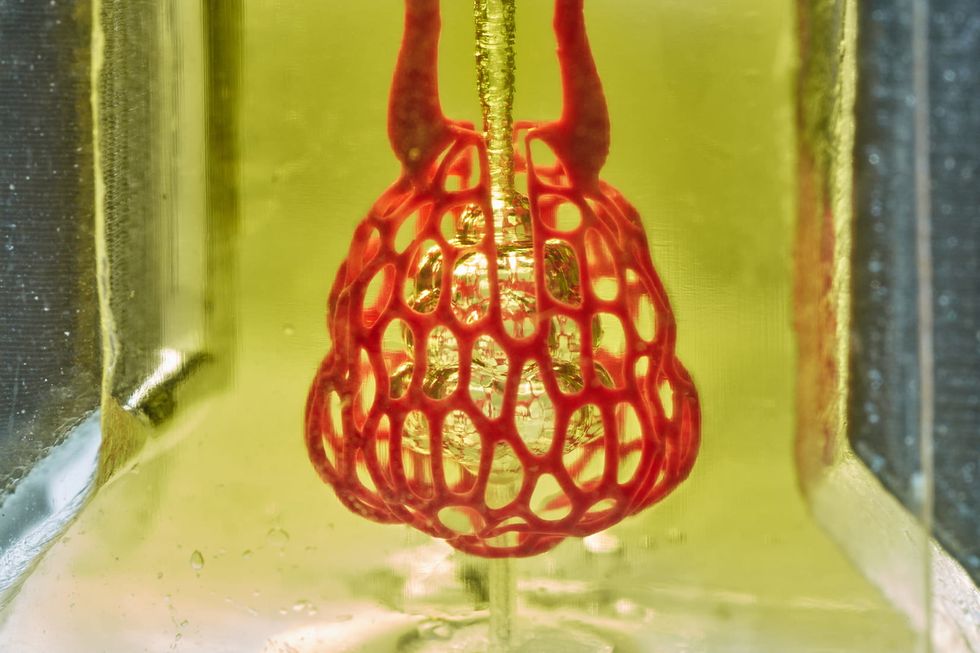
Jordan Miller/Rice University
Volumetric is banking on their technology being among the inventions that will lead the medical industry into the future. The human tissue-printing technology company has created the 3D printer and the "ink" that can create whole organs for transplant.
"We can create complicated vascular architectures inside of soft water-based gels, in this case, mimicking the structure and function of human lung tissue," says Jordan Miller, CEO. "We can oxygenate red blood cells."
The company is commercializing its technology and has three streams of revenue, which as generated almost $1 million in revenue in Volumetric's second year. The company is also in the process of closing its seed round of fundraising.
Earlier this year, the startup, which works out of Rice University, was featured on the cover of Science magazine.
