Houston tech company launches digital product to take the guesswork out of SEO
Meet INK
A Houston company wants to arm content creators and writers with the tools to perfect search engine optimization, and they want to provide these tools for free.
INK, a downloadable writing tool and web app, was created by the brains behind Edgy Labs, a tech company that has been working on dissecting how Google and search engines operate. Edgy's founders — Alexander De Ridder, Michael Umansky, and Gary Haymann — created the content site as a lab to test out their SEO theories and best practices.
"INK is the byproduct of everything we've learned at Edgy Labs that we productized," says Umansky, who serves as CEO. "We think we are on the cusp of leading what we are calling the content performance optimization revolution."
Umansky says that of the 4 million pieces of content created online daily, 94 percent of content gets little to no traffic on Google. And a big reason for content failing is because the writer doesn't fully understand how SEO works — and search engines are always evolving their algorithms.
Despite this huge SEO problem, there weren't any one-stop-shop tools available already.
"What we came to understand was that there's a ton of SEO and CMS products and analytics products, but what there wasn't was a really good way to help writers — who are really the ground zero for where content is created — bridge the gap to understanding what SEO is all about," Umansky says.
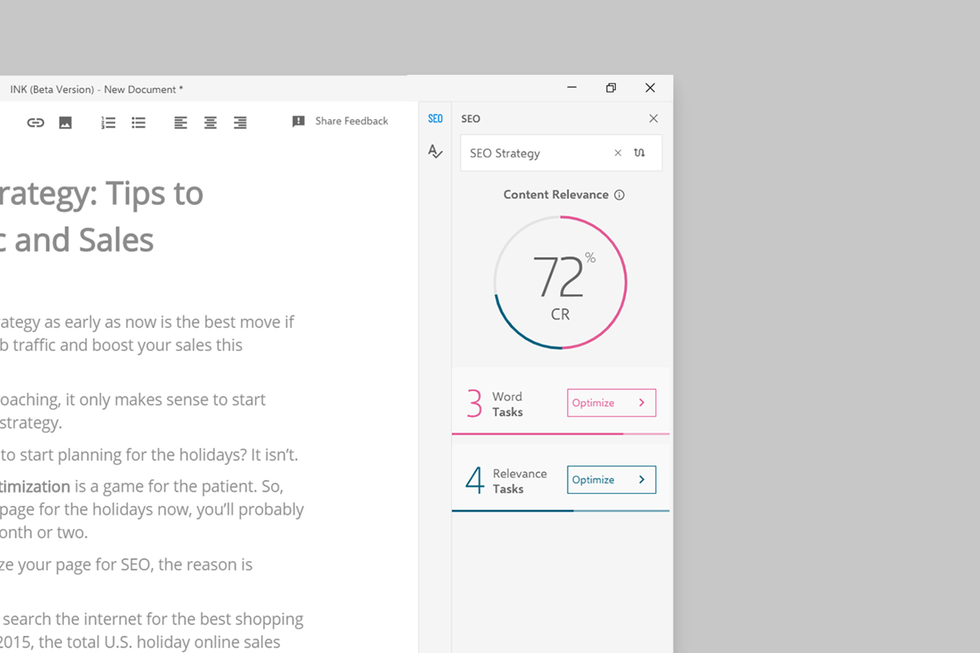
The writing tool allows the user to create content right in the app, and as the writer composes, he or she gets real-time feedback on the content. INK will compare the content to potential competitors' content and analyze and score how it expects the published material to perform. All the while, INK has a customizable interface for users. There are light and dark modes, and even features for writers with dyslexia or color blindness.
Umansky says his team has big plans for growing INK and even introducing more tools and products, and INK's evolution will continue as search engines continue updates and algorithm edits.
"As Google changes, we change with it," Umansky says. "I think last year Google changed something like 3,500 times. It's constant."
He also sees INK being able to provide a headline optimization component, as well as tools for tracking engagement. While perfecting SEO is the first step, Umansky says he also wants to provide products that help optimize writing content for a conversion perspective that would be good for landing pages and digital ads.
INK launched online in early October and was ranked as the product of the week on Product Hunt. For now, the app is completely free to download. Umansky does think the first paid version will be live in the first quarter of 2020.
Ultimately, Umansky says, writers shouldn't also have to be SEO specialists — that's INK's team's job. The product they created will allow for easy content management system integration — it already has an extension in WordPress.
"We envision a world where the content creators can control their own search destiny," Umansky says. "What we want to do is focus on empowering those writers to really take the power of search back into their own hands without having to be SEO experts."
