Early-stage cancer-fighting startup raises pre-seed, launches under Houston life science leader
ready to grow
Fannin Partners has done it again. The Houston-based life science development group behind medtech companies Procyrion and Allterum Therapeutics announced yesterday that it has launched Radiomer Therapeutics. With an undisclosed amount of pre-seed funding, Radiomer joins the $242 million-strong Fannin portfolio.
Radiomer uses Fannin’s proprietary Raptamer platform to target vectors and ligands for theranostic application. The cancer-fighting technology is a targeting agent that can address serious maladies including breast, lung, colorectal, prostate, and head and neck cancers.
And with Radiomer’s launch, Fannin is moving with its trademark aggressiveness. Lead programs expected to complete Phase 0 imaging/dosimetry trial(s) in cancer patients in the first quarter of next year. Those will be closely followed by therapeutic programs.
“Raptamers combine antibody level affinities with desirable physical and pharmacokinetic properties, and a rapid path to clinic,” Dr. Atul Varadhachary, CEO of Radiomer Therapeutics and Fannin managing partner, says in a press release. “We are deploying this unique platform to develop novel therapies against attractive first-in-class oncology targets.”
Varadhachary has operated Radiomer in stealth mode since its 2023 inception. However, Raptamer has been in the company’s portfolio since 2019. The new company has been using the platform to generate data with the rights to radiopharmaceutical applications for the past year.
“Our lead programs include Radiomers targeting both well-established and first-in-class cancer targets,” adds Dr. Phil Breitfeld, Radiomer’s chief medical officer. “Our imaging/dosimetry trials are designed to provide clinical evidence of tumor targeting and biodistribution information, positioning us to rapidly initiate a therapeutic program(s) if successful.”
For over a decade, Fannin has developed and supported promising life science innovations by garnering grant funding and using its team of expert product developers to build out the technology or treatment. The life science innovation timeline is very different from a software startup's, which can get to an early prototype in less than a year.
"In biotech, to get to that minimally viable product, it can take a decade and tens of millions of dollars," Varadhachary said on the Houston Innovators Podcast earlier this year.
- Dallas law firm targets Texas innovation hubs with expansion to Houston, Austin ›
- Houston startup scores $12M grant to support clinical evaluation of cancer-fighting drug ›
- Houston medical device company secures $57.7M to fund journey to FDA approval, commercialization ›
- Houston biotech commercialization company tapped for prestigious federal program ›

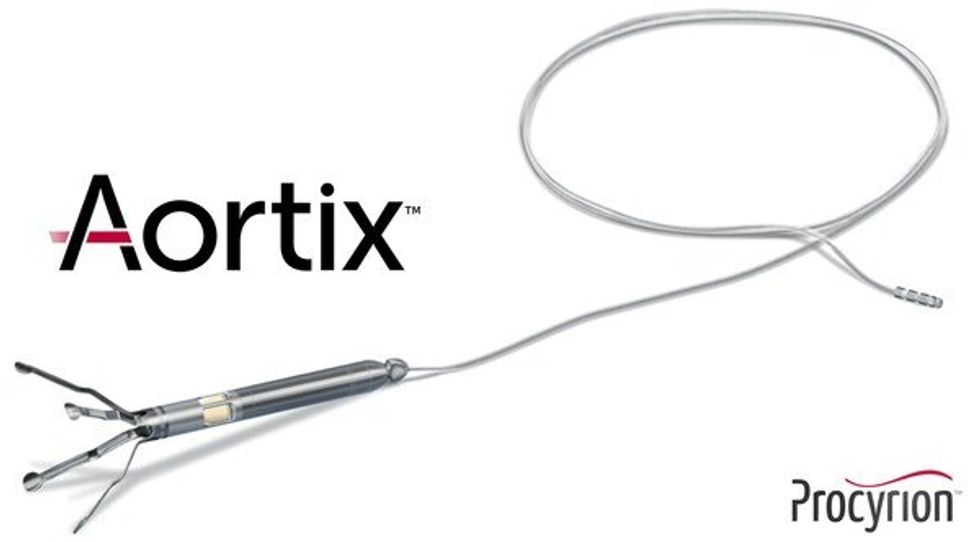 Aortix is a pump designed to be placed in the descending thoracic aorta of heart failure patients. Photo via Procyrion
Aortix is a pump designed to be placed in the descending thoracic aorta of heart failure patients. Photo via Procyrion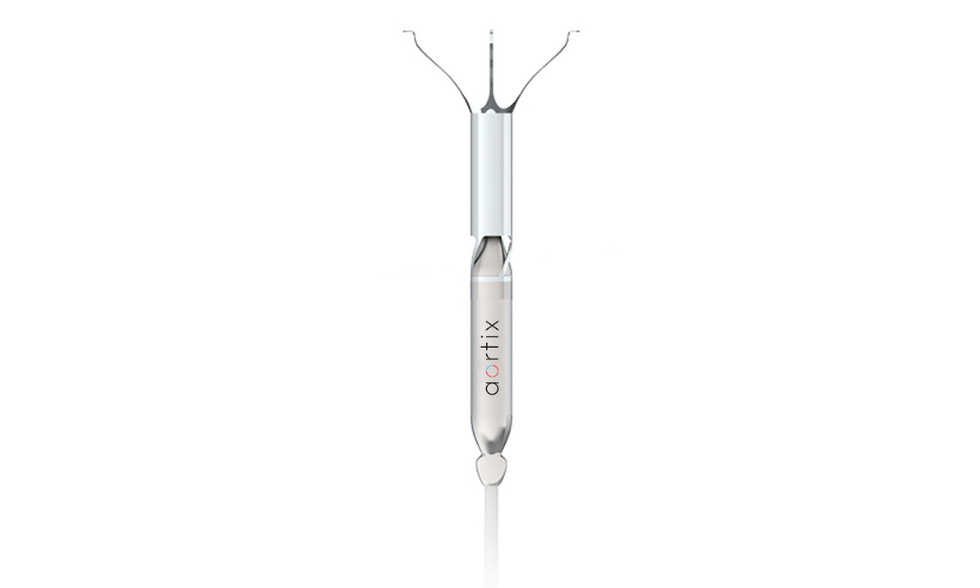 The device is thinner than a pencil and can be inserted in less than 10 minutes. Photo via procyrion.com
The device is thinner than a pencil and can be inserted in less than 10 minutes. Photo via procyrion.com