Ion expansion, Eli Lilly factory, and more Houston innovation news to know
Trending News
Editor's note: We're looking back at the top Houston innovation news for the second half of September. Catch up on the latest from the Ion District, Oxy, Eli Lilly, and more. Here are the five most-read InnovationMap stories from September 15-30:
1. Houston's Ion District to expand with new research and tech space, The Arc
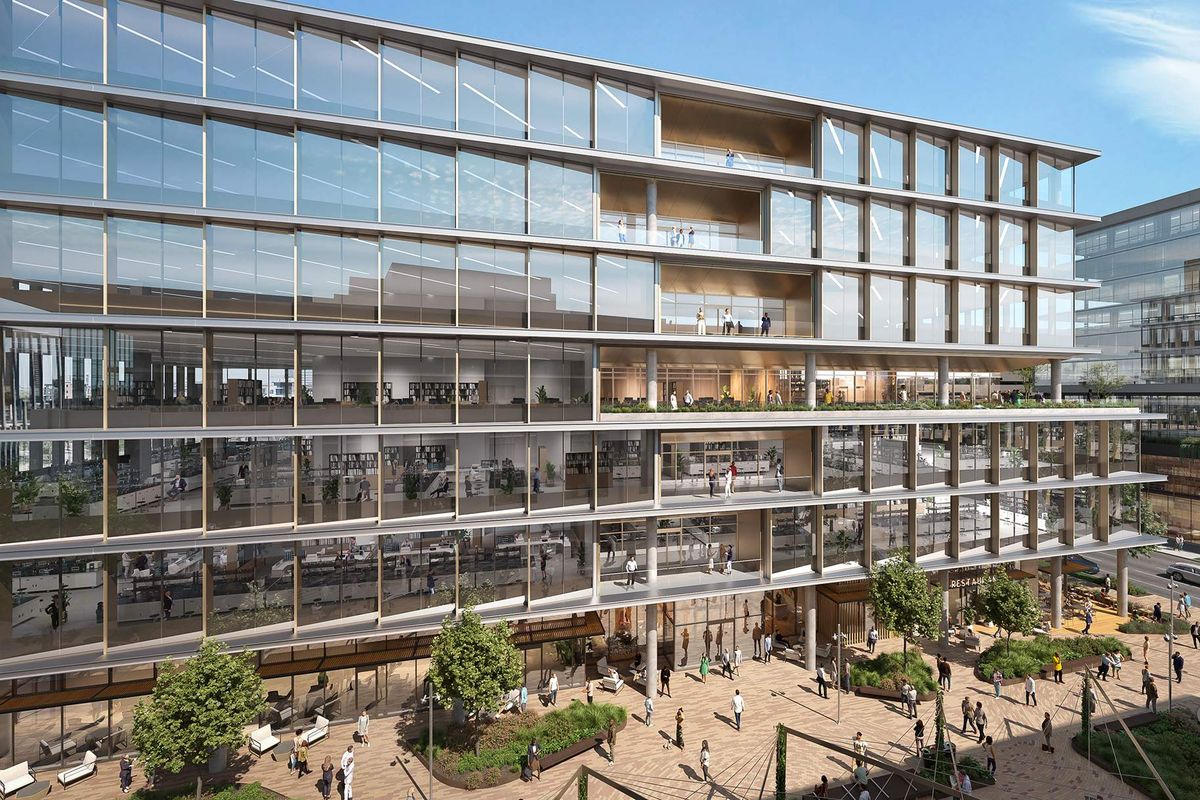

The Arc will feature office and lab space, a gym, an amenity lounge, conference and meeting spaces, outdoor plazas and more. Rendering by Neoscape. Courtesy HKS.
Houston's Ion District is set to expand with the addition of a nearly 200,000-square-foot research and technology facility, The Arc at the Ion District. Rice Real Estate Company and Lincoln Property Company are expected to break ground on the state-of-the-art facility in Q2 2026 with a completion target set for Q1 2028.
Rice University, the new facility's lead tenant, will occupy almost 30,000 square feet of office and lab space in The Arc, which will share a plaza with the Ion and is intended to "extend the district’s success as a hub for innovative ideas and collaboration." Continue reading.
2. Eli Lilly to build $6.5B pharmaceutical factory at Generation Park

Eli Lilly is expected to bring a $6.5 billion manufacturing facility to Houston by 2030. Rendering courtesy Greater Houston Partnership.
Pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly and Co. plans to build a $6.5 billion manufacturing plant at Houston’s Generation Park. More than 300 locations in the U.S. competed for the factory.
The Houston site will be the first major pharmaceutical manufacturing plant in Texas, according to the Greater Houston Partnership. Lilly said it plans to hire 615 full-time workers for the 236-acre plant, including engineers, scientists and lab technicians. The company will collaborate with local colleges and universities to help build its talent pipeline. Continue reading.
3. Oxy's $1.3B Texas carbon capture facility on track to launch this year
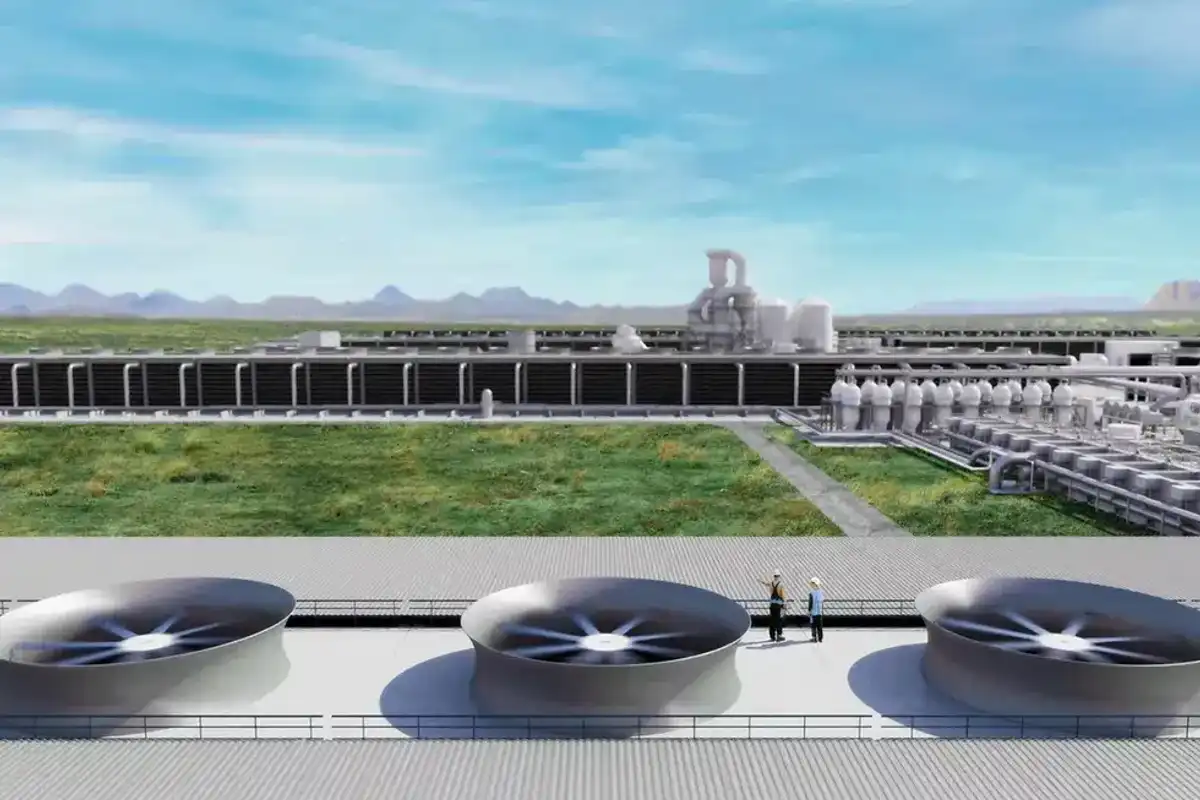
Vicki Hollub, president and CEO of Occidental, said the company's Stratos DAC project is on track to begin capturing CO2 later this year. Photo via 1pointfive.com
Houston-based Occidental Petroleum is gearing up to start removing CO2 from the atmosphere at its $1.3 billion direct air capture (DAC) project in the Midland-Odessa area.
Vicki Hollub, president and CEO of Occidental, said the Stratos project — being developed by carbon capture and sequestration subsidiary 1PointFive — is on track to begin capturing CO2 later this year. Continue reading.
4. Houston autonomous trucking co. completes first test run without human intervention
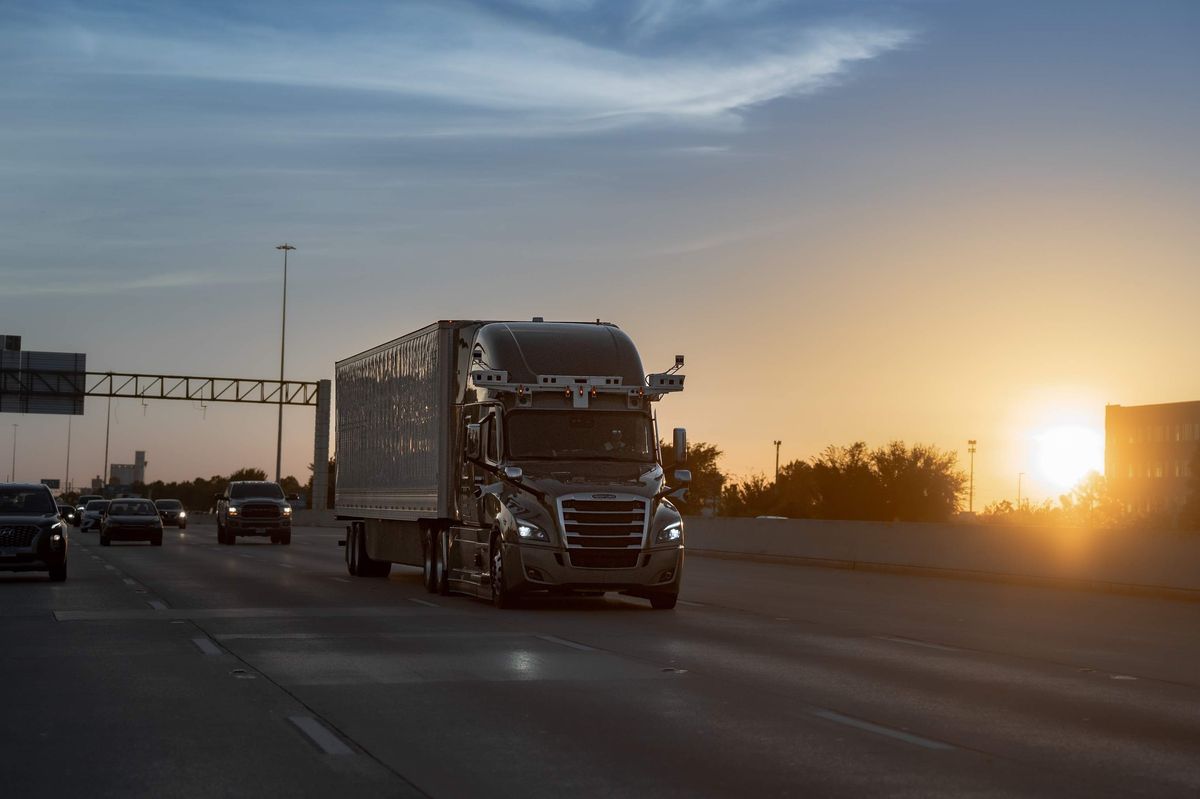

Bot Auto completed its first test run without human assistance in Houston. Photo courtesy Bot Auto.
Houston-based Bot Auto, an autonomous trucking company, has completed its first test run without human assistance. Bot Auto conducted the test in Houston.
“The truck operated seamlessly within its defined operational domain with no one in the cab or remote assistance, navigating real-world traffic conditions,” the company said . “The run was executed at sunset, successfully navigating day and night operations.” Continue reading.
5. Houston team develops low-cost device to treat infants with life-threatening birth defect
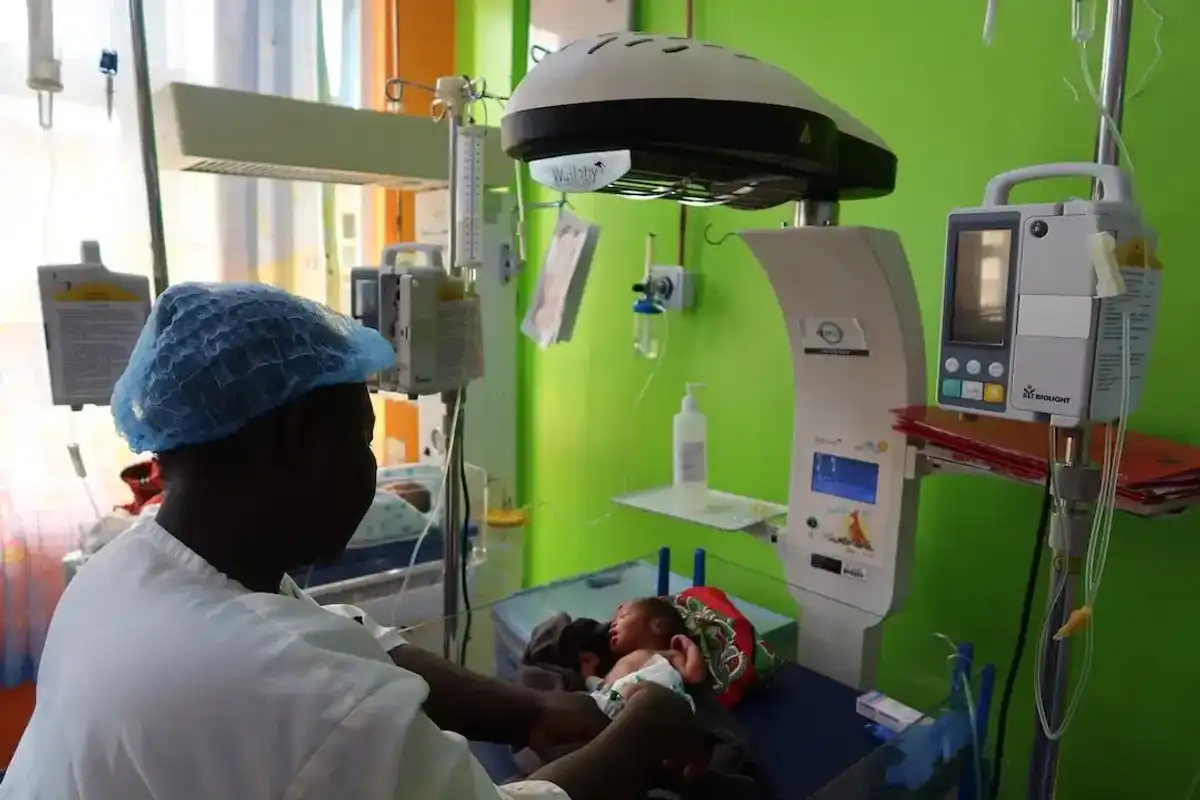
SimpleSilo, created at Rice360, offers a low-cost, easy-to-source solution for infants born with gastroschisis. Photo courtesy Rice University
A team of engineers and pediatric surgeons led by Rice University’s Rice360 Institute for Global Health Technologies has developed a cost-effective treatment for infants born with gastroschisis, a congenital condition in which intestines and other organs are developed outside of the body.
The condition can be life-threatening in economically disadvantaged regions without access to equipment.
The Rice-developed device, known as SimpleSilo, is “simple, low-cost and locally manufacturable,” according to the university. It consists of a saline bag, oxygen tubing and a commercially available heat sealer, while mimicking the function of commercial silo bags, which are used in high-income countries to protect exposed organs and gently return them into the abdominal cavity gradually. Continue reading.








