5 Texas companies present the future of health care at TMCx's Demo Day
Homegrown heroes
After four months of product design, networking with medical professionals, pitching to investors, and more, 23 startup leaders had just a few minutes to show the medical community what they've achieved and where they're going next.
Over 700 attendees made it to TMCx's 7th Demo Day or tuned in online to see the results of Houston's award-winning medical devices accelerator program.
"It's really the draw of the experts within our 23 hospitals and clinics that really makes us quite special in our ecosystem compared to the East and West coasts," Texas Medical Center CEO Bill McKeon says. "We're proud to call ourselves the Third Coast of the life sciences."
The cohort, which is the most international to date with nine international companies, has already raised $73 million and confirmed 108 signed agreements for medical professional partnerships.
"The thing that cracks me up from time to time," says Erik Halvorsen, director of the TMC Innovation Institute, "is when you see these talks that say, 'what can the Houston ecosystem learn from Silicon Valley.' Well you know what, I think we're ready to flip that, and say, 'here's what can Silicon Valley learn from us here in Houston — what we've built and where we're headed.'"
From a wearable device that reduces back pain to a new technology that reduces suicidal thoughts, the cohort's presentations didn't disappoint. While all the cohorts made business connections to Houston in the months they were at TMCx, five of the 23 companies are based in Texas. Here are the companies with Lone Star State roots.
Articulate Labs
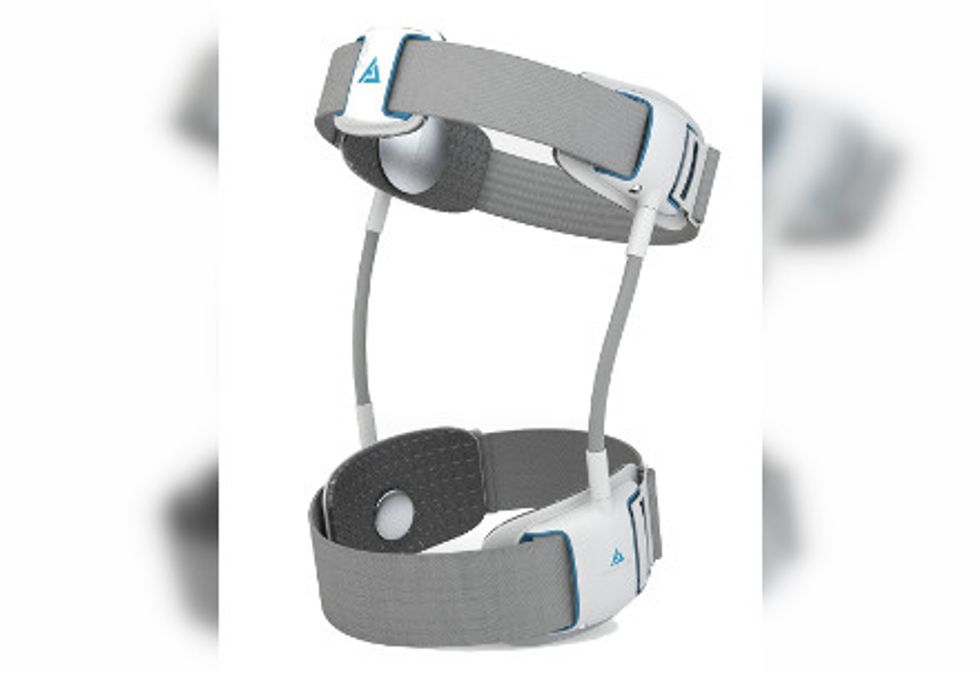

Articulate Labs' KneeStim allows for everyday activities to be muscle-building exercises.
Photo via articulatelabs.com
Herbie Kirn, co-founder and chief scientific officer of Articulate Labs, lost his leg from the knee down in a motorcycle accident and quickly wore through his other knee's cartilage. If he didn't do sufficient rehabilitation and physical therapy, he would lose function of that leg too.
Over 14 million people in the United States individuals suffer from chronic knee problems; however, whether it be due to time or cost, over 70 percent of those affected cannot attend the prescribed physical therapy.
Dallas-based Articulate Labs has a solution. The KneeStim device allows the patient to turn daily activities into rehabilitation exercises.
The company has raised a little over $500,000 already, but looks to raise $1 million with its next round of funding. Articulate Labs is also looking for more scientific and strategic partners.
Intelligent Implants
Intelligent Implant's co-founder, Juan Pardo, told the crowd at Demo Day that his company's device allows for 50 percent faster bone growth in patients.
Photo by Cody Duty/TMC
Chronic lower back pain can result in a need for spinal fusion surgery — and 40 percent of those surgeries fail, says Juan Pardo, co-founder of Intelligent Implants, which has an office in Houston. Pardo and his team have come up with an implant that tracks post-op healing and introduces electronic stimulation wirelessly.
The device is the same size and shape as the spacer that surgeons currently use, but contains a technology that can deliver electronic stimulation therapy and monitor progress without needing batteries. The doctor is able to adjust treatment remotely, and the device can heal the patient 50 percent faster than the standard care.
Intelligent Implants was announced as the first in-residence company at the Center for Device Innovation by Johnson and Johnson and also launched its large animal studies. The company has a goal to raise $1.6 million, and has already secured $900,000 — $250,000 of which came from the new TMC Venture Fund.
Noleus Technologies
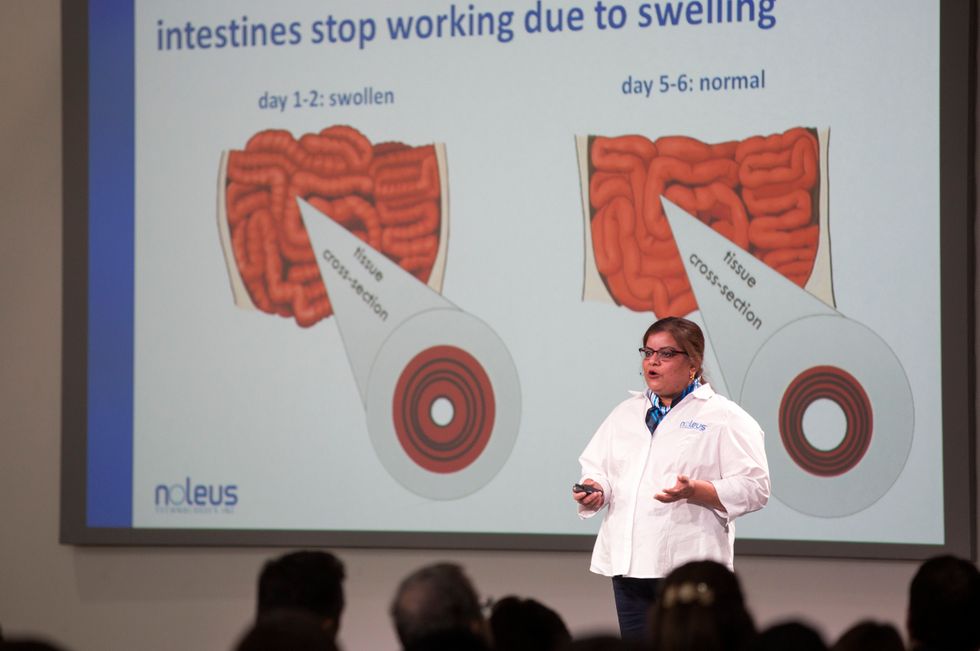

Swarna Balasubramaniam, an experienced surgeon, created a device that heal gastrointestinal surgery patients faster.
Photo by Cody Duty/TMC
Swarna Balasubramaniam watched helplessly as her mom slowly healed from gastrointestinal surgery. She couldn't eat and had trouble sleeping — both of which hindered her ability to heal quickly.
Balasubramaniam, founder of Houston-based Noleus Technologies, created a solution that reduces swelling in the bowels after operation. The disposable device is inserted into the abdomen at the time of surgery, and folds up like a fan to be removed without another surgery.
The invention is attractive to all parties involved. Patients are able to heal quicker, and surgeons are able to provide better care for their patients. Additionally, hospitals, which have bundled reimbursement for surgeries like this, are able to shorten the recovery time for patients thus reducing the costs spent on caring for the patient. Balasubramaniam says she estimates the device saving hospitals $4,000 per patient.
Vax-Immune Diagnostics
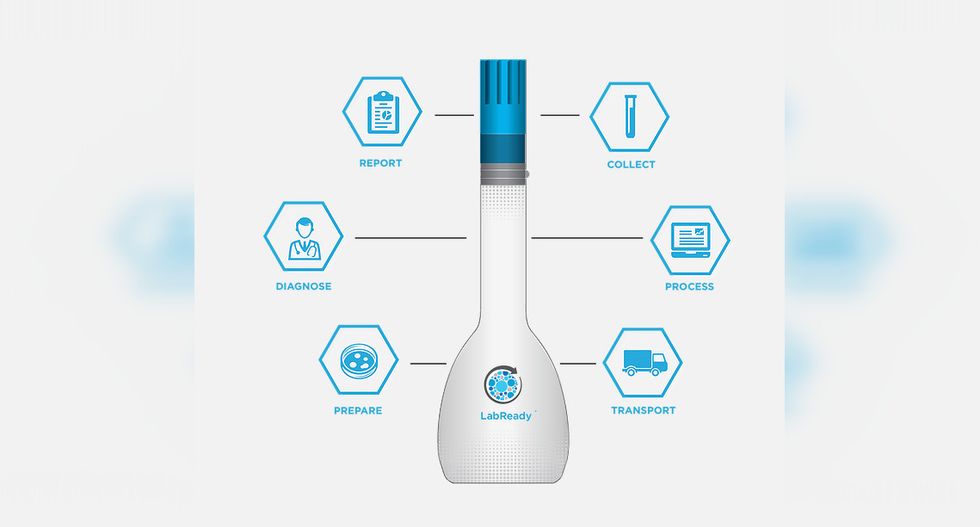

LabReady ensures samples make it from the patient to the lab without compromising the quality of the sample.
Photo via vaximmune.com
Over 70 percent of care decisions come from lab results, but more than 20 percent of microbiology lab tests are inaccurate due to problems in transport from the patient to the lab. Leonard Weisman, founder and chief technology officer of Houston-based Vax-Immune Diagnostics, invented Lab Ready — a tool for protecting the quality of the sample for testing.
The device is easy for patients to use at home and send to the lab directly, and the device is likewise easy to use by lab technicians.
Lab Ready is prepared to launch in 2019, immediately following FDA approval. Vax-Immune is on track to meet its funding goal of $5 million in the first quarter of 2019.
VenoStent
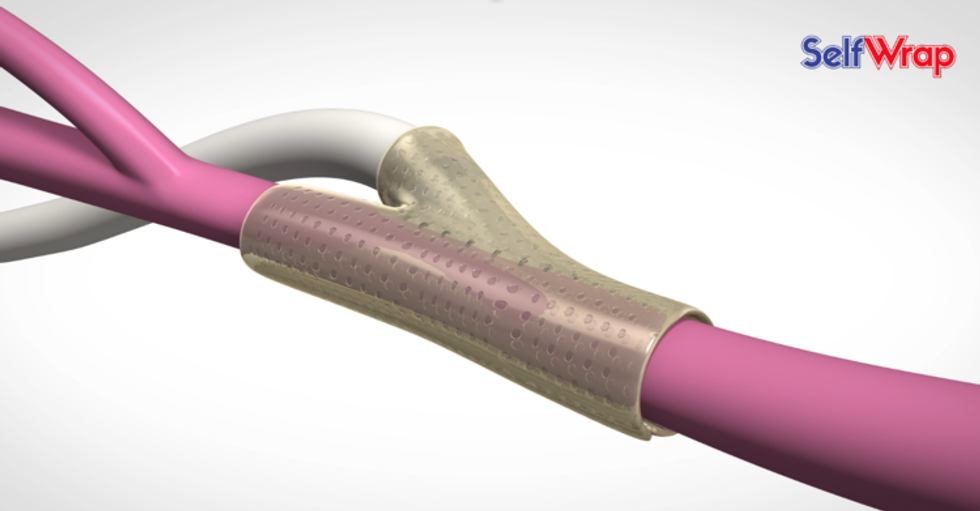
VenoStent wants every external stent procedure is successful on its first try.
Photo via venostent.com
Patients with kidney disease or diabetes have four chances to get an external stent successfully inserted into their arms for dialysis treatment, and the current standard of care results in a failure in half of these access sites, says Tim Biore, founder of Houston-based VenoStent.
It was Biore's vision to create a device that allows a successful stent implementation on the first try. VenoStent's SelfWrap is made from a shape-memory polymer that uses body heat to mold the stent into the vein-artery junction.
One in eight people suffer from kidney disease, and Biore says SelfWrap would save Medicare upwards of $200 million annually, while improving the success rate by 20 to 30 percent.
VenoStent has seven signed agreements from partners as a result of the accelerator program. The company is seeking $2.4 million to continue manufacturing as they await FDA clearance — expected in early 2022.

