Houston mobile vet company plans to roll out services statewide
pet care delivered
It's safe to say that the real winners of work-from-home trends that sparked due to the pandemic are our pets. Dogs and cats that were used to not seeing their owners for eight hours every work day now have 24-hour access to attention, treats, and ear scratches.
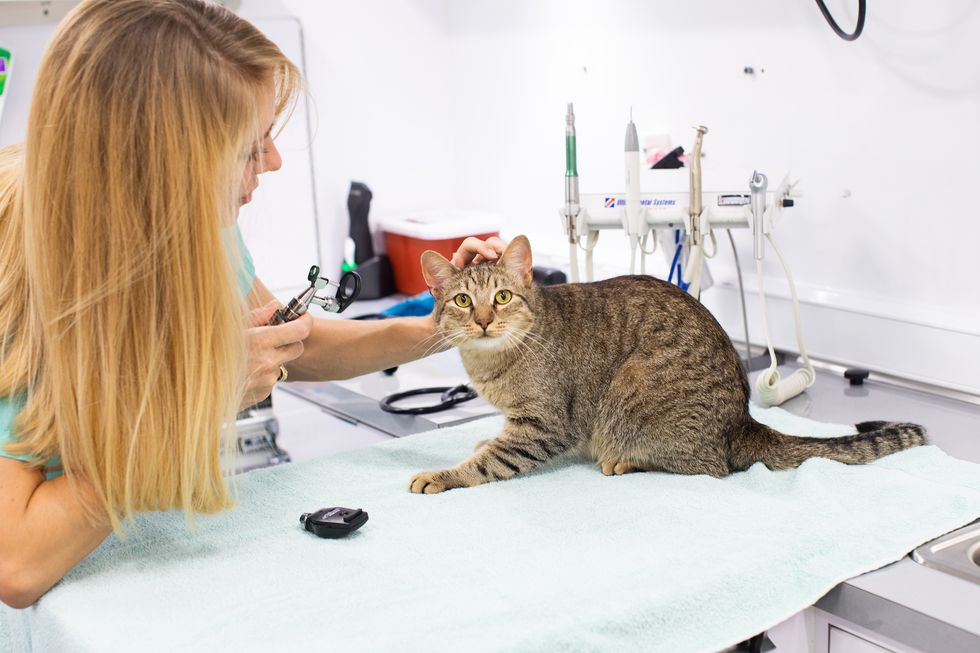
This increased attention pets are getting from their owners has also meant an increased awareness of pet health, says Katie Eick, founder of Houston-based Rollin' Vets, a startup that has mobilized veterinary services.
"People are home and observing their animals more. They're seeing and recognizing things they might not have if they were at work all day," Eick says.
That's, of course, not the only way the pandemic has affected business for Eick. She founded her company in 2016 and was seeing steady growth as delivery and on-demand services like Uber, DoorDash, etc. increased in use and awareness.
"We were continuously growing slowly — then COVID hit. It really cemented that … all the convenience services are in the forefront of people's minds." Eick tells InnovationMap. "COVID made it clear that this was a necessary service."
Like a lot of businesses, vet clinics closed to the public and only accept drop-off patients. This new way of seeing pets coupled with the fact that most people are working remotely from home also played to the advantage Rollin' Vets — why drive your pet to drop off at a clinic when the vet can come to your driveway?
COVID-19 closures and social distancing practices also called for a rise in veterinary telemedicine — something that Eick says has been challenging for her to utilize both due to the board of medicine having strict regulations in place as well as the challenges trying to provide virtual animal care poses.

"Humans can get on and tell you their symptoms, where they hurt, and how they are feeling. Animals can't do that," Eick says.
Earlier in the pandemic, she did provide some telemedicine visits. The board, which bans telemedicine care for pets not previously seen by a vet or pets that haven't been seen in over a year, loosened the regulations to allow for virtual care of pets if the vet has ever seen the animal. This was helpful for providing refill medications, for instance.
Then, Eick had an appointment with a four-year-old French bulldog that changed her mindset on telemedicine. The dog had some stomach issues when his owner made an appointment with Eick. By the time she got to the dog, he had more or less seemed fine — he was eating again and didn't seem despondent in any way. But when Eick performed his exam, she found a mass.
"If I would have just looked at that dog over a video chat, he would have died," Eick says, adding that she got the dog right into surgery at a nearby facility.
In this case, telemedicine wouldn't have provided a solution for the animal, but Eick hasn't ruled virtual care out in general.
"I do think there's place for it, but we have to be really careful," she says.
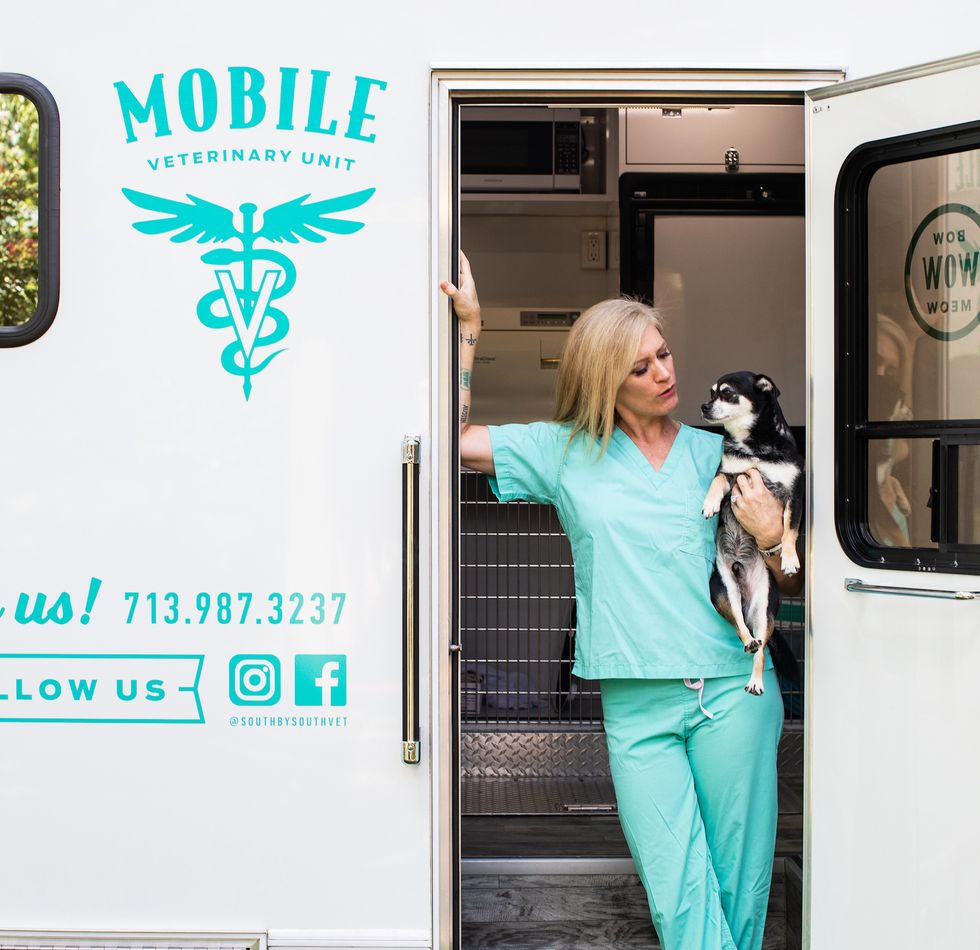
At this point, Eick has more than proven her value proposition for her company. She has four mobile units with a team of four vets, six technicians, and four receptionists. As far as funding goes, she's pitched to the Houston Angel Network and is looking for angel investors. She's also planning on looking into crowdfunding as an option.
She's planning for growth — starting with Dallas and San Antonio — and sees the company adopting a franchise model that will eventually take Rollin' Vets out of state.
"We're aiming to be a nationwide brand," Eick says.