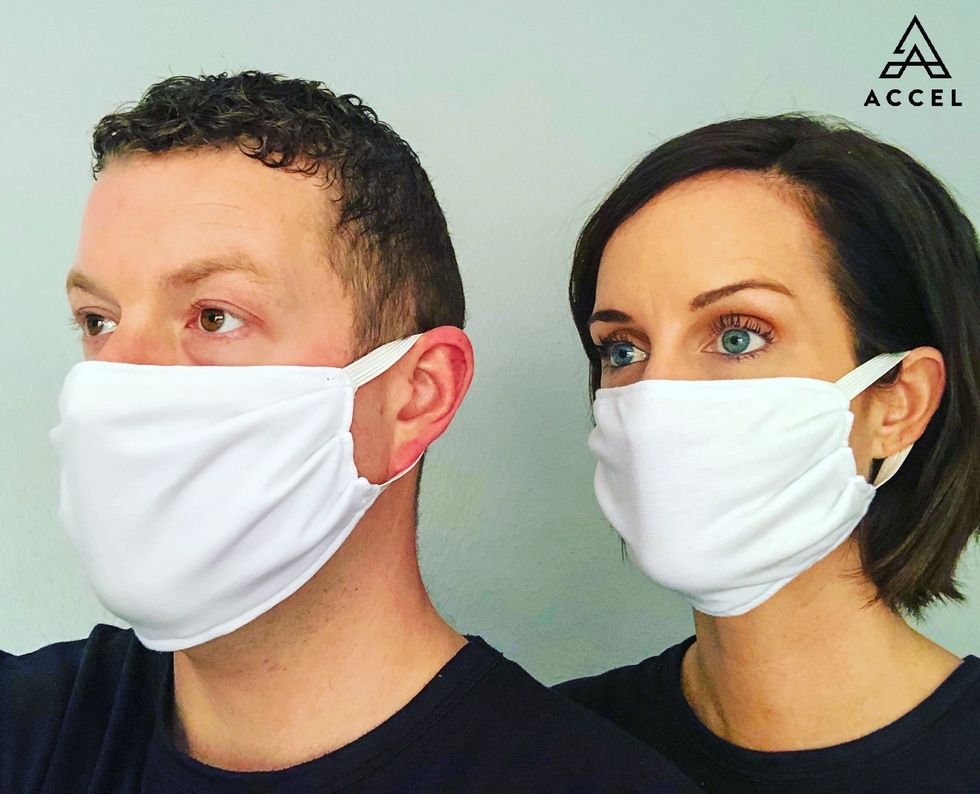
Designers and entrepreneurs fashion face masks for medical professionals in Houston
ready and resourceful
The coronavirus is sweeping the globe and creating new challenges. Notably, companies are not able to keep up with the demand for the N95 masks needed to keep the health care workers safe. Now, Houston's fashion industry is stepping up.
Megan Eddings, founder of Accel Lifestyle, says an article she read about the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advising health care professionals to wear homemade masks or bandanas due to the shortage of the N95 masks inspired her. She was compelled to help combat the COVID-19 pandemic locally and nationwide.
"Accel's Prema fabric was created to prevent the growth of bacteria," Eddings tells CultureMap. "The fabric can be washed up to 100 times and it will still be 99.99-percent anti-bacteria."
Eddings says it dawned on her that she has over 500 shirts made, here in Houston, that could easily be recreated into masks. Her supply chain team consists of 20 sewers and she notes that number can quickly double.
"We have enough supplies here to make 9,000 masks and I have 2,800 yards of fabric sitting at my factory in California," she says. "That's enough fabric to make more than 100,000 masks."
Eddings and her team also tell CultureMap that 47,000 yards of elastic is en route to the Bayou City this week.
"I knew this was serious when the president of MD Anderson responded to my Saturday morning email within three minutes of sending," she says. "He's interested, and they want the infection control team to analyze the fabric."
Other local hospitals interested in Accel Lifestyle's masks are Methodist, Texas Children's, Baylor, and Memorial Hermann. The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City has also shown interest as well as Yale's New Haven Hospital in New Haven, Connecticut.
When Chloe Dao made the decision to temporarily close her Rice Village boutique last Tuesday, offering shopping requests by appointment only, she posted a video to her Instagram account the following day about the emotional roller coaster she's been on surrounding the COVID-19 outbreak.
In the video, Dao says she wanted to play a role in helping her community by creating a pattern and hand sewing 100 washable face masks with pockets. She noted in the caption that the pocket allows for extra filtration but that because it's a fabric mask, it does not stop the spread of the virus. Dao also recommends washing the mask before wearing it.
With production underway since her initial 100 masks, available in small/medium and medium/large, Dao and her team have produced close to 1,000 masks for Houstonians who reached out via social media.
"The requests are overwhelming," a representative for the label tells CultureMap. "We're now shifting our focus to help those on the front line of the coronavirus outbreak; the doctors, nurses, family members of doctors and nurses."
For those who would like to donate to Dao's efforts to continue producing these washable masks, click here.
Houston-based, internationally recognized nonprofit design house, Magpies & Peacocks, and Inclán Studio, a local women's ready-to-wear fashion label, are upcycling together to create nonwoven polypropylene masks, which will be distributed to Houston-area hospitals.
Founder and CEO, Sarah-Jayne Smith and vice president and director of communications/PR, Ahshia Berry, tells CultureMap that partnering together was never a question for either of our brands but more "how can we pull our resources together and help during these trying times."
Clarence Lee, a designer at Inclán Studio, tells CultureMap he searched the studio to find elastic cording that didn't get used in past collections.
"Waste as a resource and upcycling material for good use has never been more important than it is right now," Magpies & Peacocks writes on an Instagram post.
Houston Arts Alliance and Visit Houston donated excess promotional products and now, are deconstructed to reuse the material for these masks.
"It's actually a spun plastic, not a fabric, so it works effectively as a filter, and is more moisture resistant," Magpies & Peacocks tells CultureMap. "It's more compliant and efficient for the current exposure to the service industry in the midst of the crisis."
Lee, who is also a lead designer for Magpies & Peacocks, and serves as an executive board member for the nation's exclusive nonprofit design house, tells CultureMap that for them, it simply boils down to help in any capacity, especially after seeing what's happening across the country with the shortage of supplies.
He notes that they may not have all the supplies, but they do have the capability and time to sew to help those that are on the frontline, fighting and sacrificing everything they have.
"[Houston] is our home, and we all have a part to play in helping fight this," he says. "The [fashion] industry has a major role, and now is definitely the time to show how valuable it can be."
Magpies & Peacocks and Inclán Studio aim to produce 500-600 masks, and hopefully more, should they come across more materials, Lee tells CultureMap. Seven volunteers are helping to sew these nonwoven polypropylene masks.
------
This article originally ran on CultureMap.