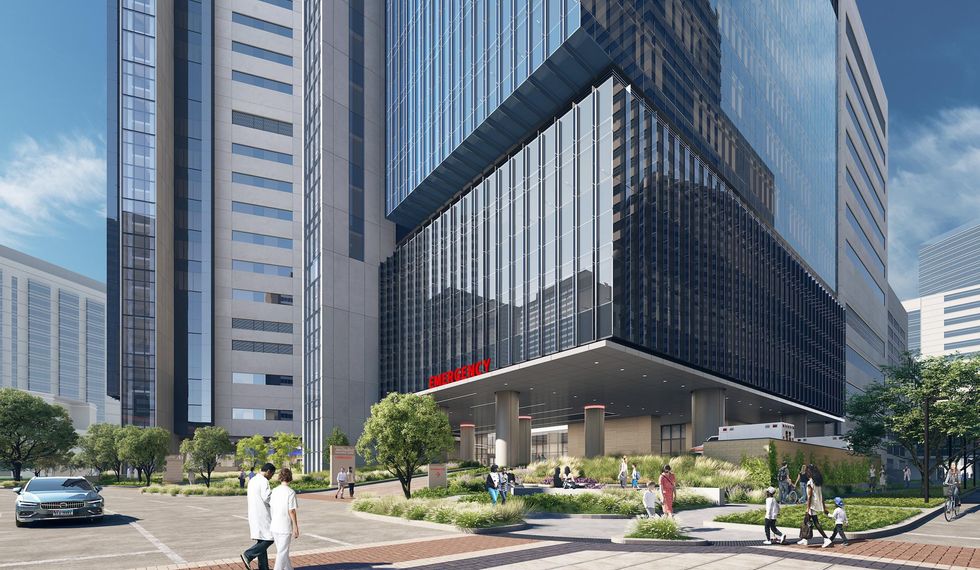
Construction has begun on a $1.4 billion hospital tower at the Texas Medical Center.
Houston Methodist’s 26-story Centennial Tower will be connected to the Paula and Joseph C. “Rusty” Walter III Tower, which opened in 2018. Among other things, the new tower will feature a larger emergency department and hundreds of patient beds. It’s scheduled to open in 2027.
“Together, the towers will add an impressive profile to the Texas Medical Center skyline,” says Dr. Marc Boom, president and CEO of Houston Methodist. “We are building this for our community, showing our commitment to the future of health care at Houston Methodist as we continue leading medicine for decades to come.”
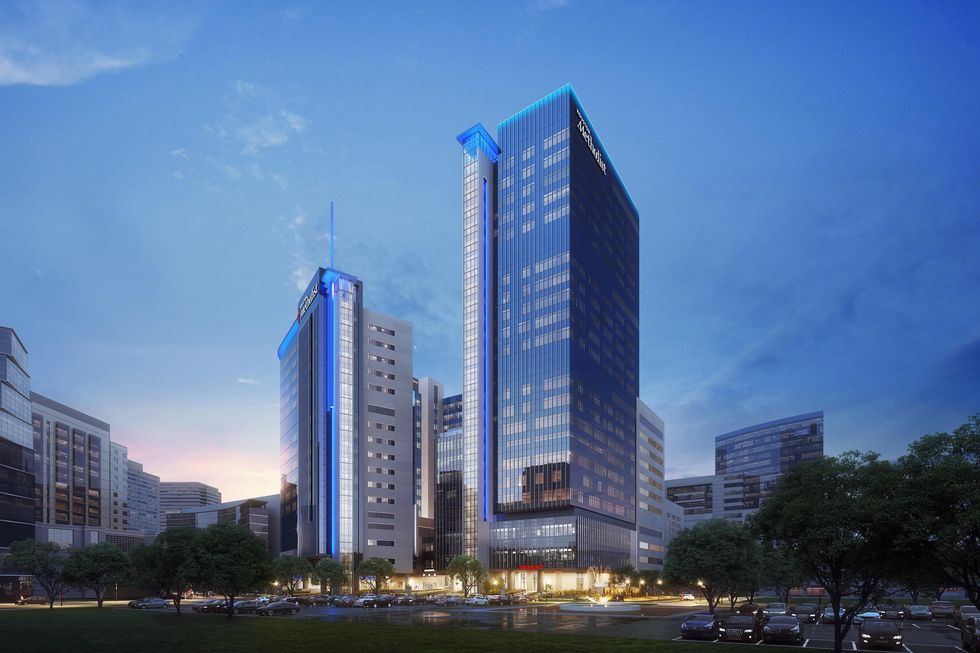

Highlights of Centennial Tower include:
- A new emergency department with 54 beds and additional suites.
- Nearly 400 patient beds, including 175 new beds and 207 beds to replace those in Houston Methodist’s Main building. That building and the West Pavilion eventually will be torn down.
- New space for transplant medicine, intermediate care, and surgical intensive care.
- Nine operating rooms, including two new operating rooms.
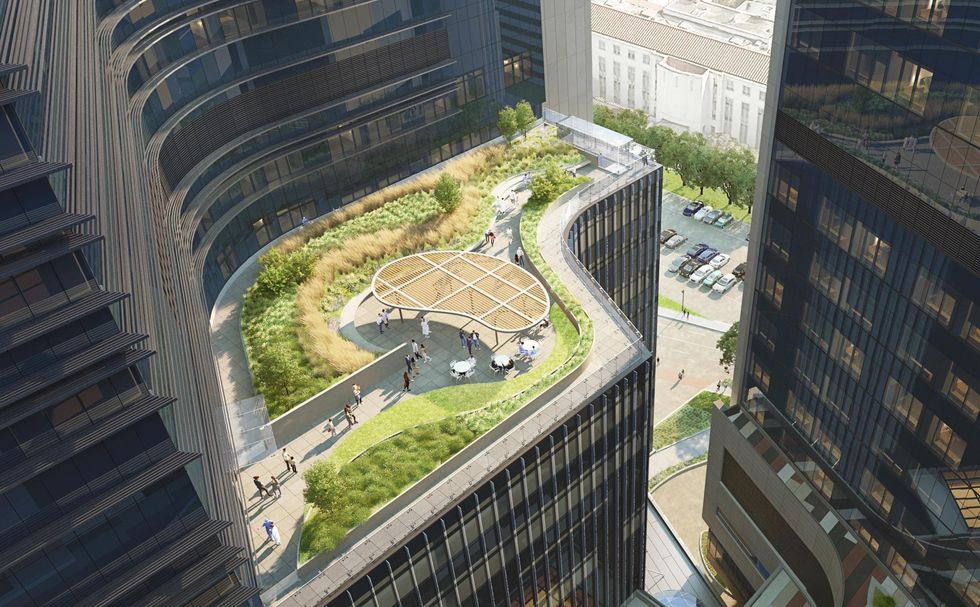
- A 14th-floor rooftop garden.
The adjacent Paula and Joseph C. “Rusty” Walter III Tower houses the Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center and the Houston Methodist Neurological Institute.
Albany, New York-based design firm EYP is Centennial Tower’s architect, and Houston-based Vaughn Construction is the general contractor.

EYP recently filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. In connection with the voluntary bankruptcy filing, Tampa, Florida-based Ault Alliance has agreed to buy the majority of EYP’s assets (including customer contracts) for $67.7 million, plus the assumption of “significant” liabilities. Ault plans to retain EYP’s staff. If the deal goes through, EYP would operate under its current brand name.
“EYP is a good candidate to use the protections that a Chapter 11 process provides,” says Kefalari Maso, interim CEO of EYP. “Our business is as strong as it has ever been, and the advantages … are that it allows us to continue doing the work we love while quickly moving through a sale process that further strengthens our financial position, allowing us to shape a future that matches our success over the last few years.”