Houston expert: New technologies are improving lives of those living with type 1 diabetes
Guest column
Texas Chapter has some examples of how technology is helping people with type 1 diabetes. Photo courtesy of JDRF
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease where insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are mistakenly destroyed by the body's immune system. Insulin is vital in controlling blood-sugar or glucose levels. Not only do you need proper blood-sugar levels for day-to-day energy, but when blood-sugar levels get too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia), it can cause serious problems and even death. Because of this, those with T1D are dependent on injections or pumps to survive.
The causes of T1D are not fully known, and there is currently no cure; however, advancing technologies are making it easier to live with T1D.
Monitoring
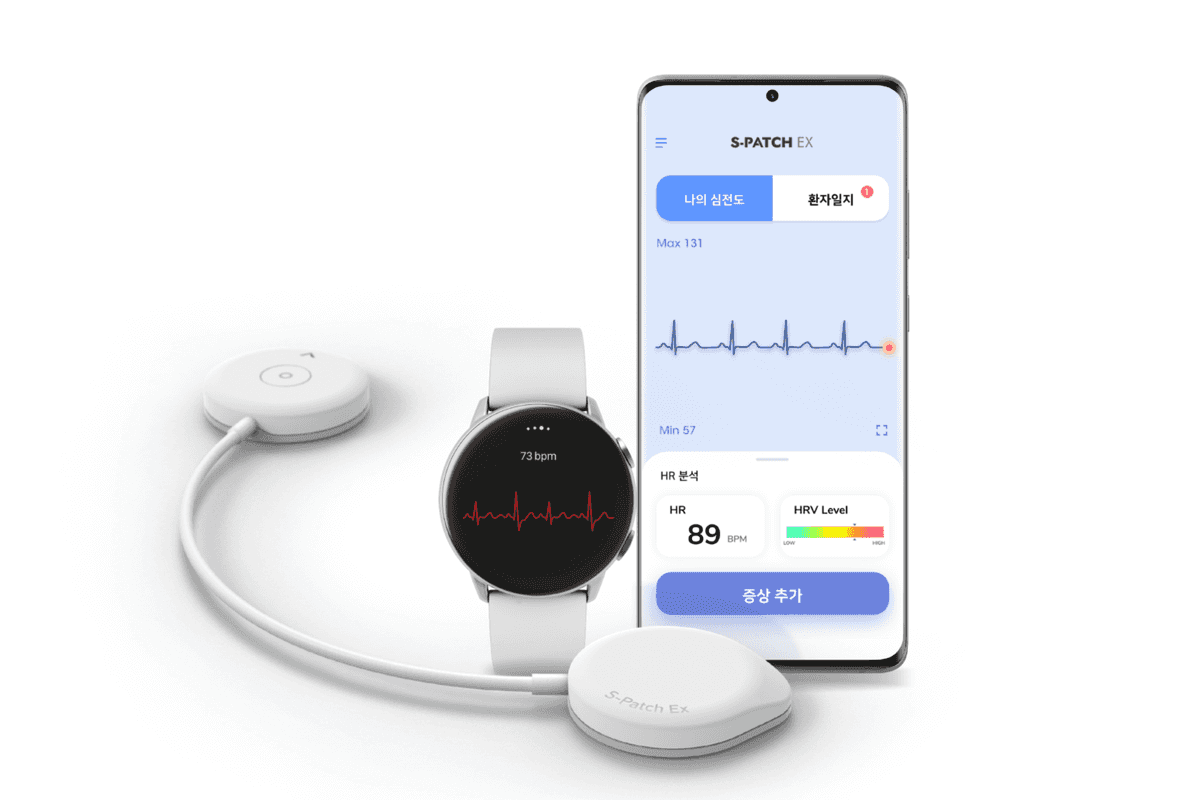
Those who have had T1D for decades might recall having to pee into a vial and test reagent strips in order to check their blood-sugar levels. Thankfully, this evolved into glucometers, or glucose meters. With a glucometer, those with T1D prick their finger and place a drop on the edge of the test strip, which is connected to the monitor that displays their results. Nowadays, glucometers, much like most T1D tech, can be Bluetooth enabled and sync with a smartphone.
From there, scientists have developed the continuous glucose monitor (CGM) so that those with T1D can monitor their blood sugar 24/7. All you need to do is insert a small sensor under the skin. The sensor then measures glucose levels every few minutes, and that information can then be transmitted to smartphones, computers and even smart watches.
Monitoring blood-sugar levels is vital for those with T1D, particularly because it helps them stay more aware of their body, know what to do and even what to expect, but they also have to actively control those levels by injecting insulin. Think of a monitor as the "check engine" light. It can tell you that there may be a problem, but it won't fix it for you. To fix it, you would need an injection or a pump.
Pumps and artificial pancreas
The development of insulin pumps has made a huge impact on the lives of those with T1D and parents of children with T1D by making it easier to manage their blood-sugar levels. 50 years ago, the prototype of the insulin pump was so large, it had to be a backpack, but with today's technology, it is about the size of a smartphone. The pump is worn on the outside of the body, and it delivers insulin through a tube which is placed under the skin. Insulin pumps mimic the way a pancreas works by sending out small doses of insulin that are short acting. A pump can also be manipulated depending on each person's needs. For example, you can press a button to deliver a dose with meals and snacks, you can remove it or reduce it when active and it can be programmed to deliver more at certain times or suspend delivery if necessary.
One of the most recent and trending developments in T1D research is the artificial pancreas, or more formally referred to as the automated insulin delivery (AID) systems. Essentially, the artificial pancreas is an insulin pump that works with a CGM. The CGM notifies the insulin pump of your blood-sugar reading, which acts accordingly to restore your blood sugar to the target level. The artificial pancreas allows those with T1D to be even more hands off, as it does essentially everything: It continuously monitors blood-sugar levels, calculates how much insulin you would need, which can be done through smart devices, and automatically delivers insulin through the pump.
Living with T1D is a 24/7/365 battle; however, the advances in technology make it easier and safer to live with the disease. Organizations like JDRF play a huge role in investing in research, advocating for government support and more.
November was National Diabetes Awareness Month, and this year is particularly special for JDRF, as it is the 50th year of the organization. JDRF was founded in 1970 by two moms. The community grew to include scientists, lobbyists, celebrities and children—all determined to improve lives and find cures.
Bound by a will stronger than the disease, this year during National Diabetes Awareness Month (NDAM), JDRF celebrates "The Power of Us." We are reflecting on the power of our community and reminding ourselves and the public of how far we've come in the fight against T1D.
------
Rick Byrd is the executive director of the JDRF Southern Texas Chapter.