Houston Food Bank launches app to better connect the city's food insecure residents to resources
Food for thought
In many ways, it was a perfect storm. Pariveda Solutions, a Dallas-based management consulting firm that specialized in helping its client maximize performance, reached out to the Houston Food Bank about offering some of its interns for a project. The Food Bank, long a pioneer and foot soldier in the fight to end food insecurity and hunger for the region's residents, had been considering ways to harness technology to better serve the needs of its clients.
"It was a fantastic opportunity for us," says Casey Ferrell, the Houston Food Bank's director of information technology, about the opportunity. "And we thought an app would be the best thing for the intern team to work on."
Five Pariveda interns worked over the summer on the app, which taps into Amazon Web Services, which the Food Bank was already using.
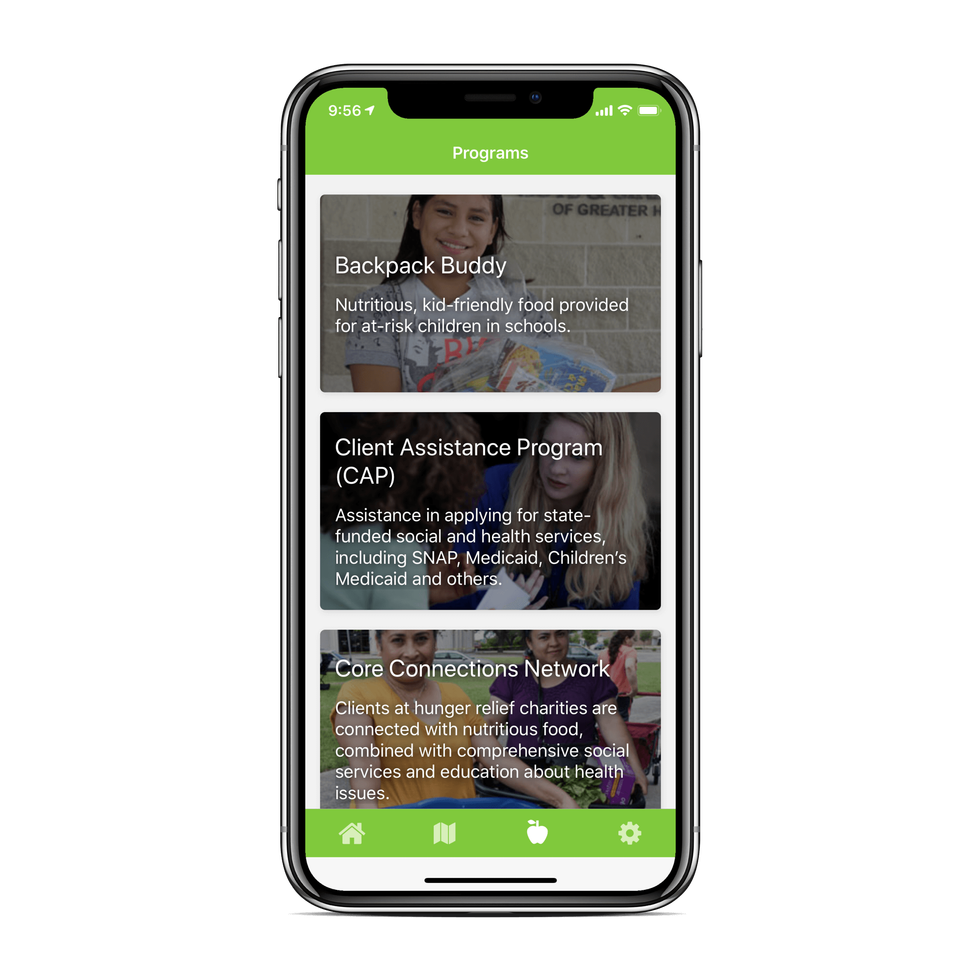
"Since the Houston Food Bank was already using AWS, this fit into where they wanted to go," explains Kevin Moorman, principal consultant for Pariveda. "The app uses GPS location services to help connect people who need the Food Bank's services with the closest location that can help them."
Across the Houston region, more than one million people are food insecure, lacking reliable access to nutritious food. Through its network of more than 1,500 community partners, the Houston Food Bank leads the fight against hunger by providing food assistance across its 18-county coverage area in southeast Texas. The Food Bank partners with thousands of entities, from soup kitchen to meal sites to shelters. Every year, the Houston Food Bank helps feed 800,000 individuals. There is a lot of need, and there are a lot of sites around the region that can aid people lacking food.
The app, in addition to pinpointing locations that can provide food for those in need, also allows people to make appointment with Food Bank staff. Currently, those appointments are on a walk-in basis, and clients are seen on a first-come, first served basis. With the launch of the app earlier this month, Ferrell says the organization has launched a pilot program with its Portwall location to allow clients to make appointments via the app. In the future, they should be able to make appointments all more Houston Food Bank locations.
"We actually did a soft launch back in October, says Ferrell. "And now, we have more than 3,000 downloads and 2,500 monthly users. The app lets them see open times for appointments, as well as contact information for locations."
Ferrell says the feedback from users has been positive. In particular, they enjoy the ability to receive updates about their appointments. But the app also provides for a greater user experience, allowing clients the chance to set things up as it makes sense for them and their daily schedules.
"We've also heard from other food banks who are looking to do something similar," says Ferrell. "So, we're looking forward to sharing our experiences with them."
Pariveda Solutions' 11-week internship program, offered each summer, is focused on making an impact to the community. The app last summer's intern cohort created is a first because it integrates with the database housed on AWS and reaches new communities.
"Working with Houston Food Bank gave us the opportunity to impact the Houston community at a large scale," says Allison Esenkova, Houston vice president for Pariveda Solutions in a press release announcing the app. "It provided a platform for our interns to learn the world of consulting while giving back in a way that impacts the Houston community to reduce hunger."
The internship was also an important opportunity for students to get hands-on experience not only in building an app, but also to get experience working with a client, listening to feedback and coming up with solutions to challenges.
"We want our interns to have as much real-world experience as possible," says Moormann. "This not only provided that, but has wonderful value for the end user. The app makes the process of finding services much smoother for those who need them."
Ferrell says that as the app is updated, the Houston Food Bank hopes to be able to use it to engage volunteers, as well as provide places where clients can rate their experiences at various food pantries.
"This has been a great value to us," says Ferrell. "And it allows us to provide better services to our clients."