Editor's note: Every week, I introduce you to a handful of Houston innovators to know recently making headlines with news of innovative technology, investment activity, and more. This week's batch includes a podcast with the CEO of a community-focused coworking space, a professor joining a major health care research project, and a guest columnist with advice on navigating the energy transition.
Jon Lambert, CEO of The Cannon
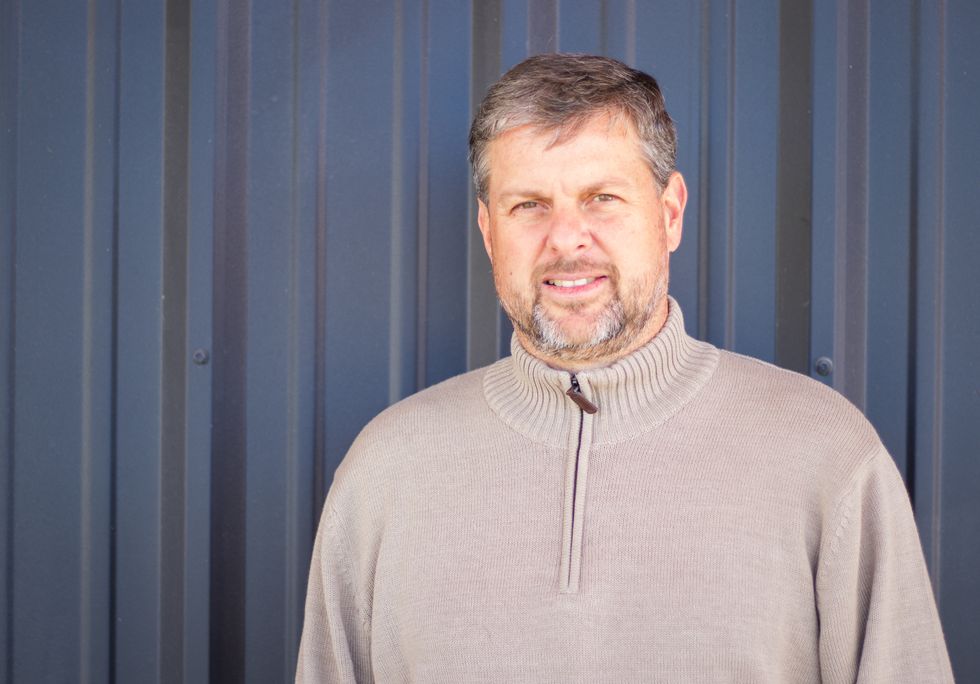

Jon Lambert, CEO of The Cannon, joins the Houston Innovators Podcast to discuss the growth of The Cannon, including its newest location. Photo courtesy of The Cannon
For the past five years as CEO, Jon Lambert has faced some challenges leading The Cannon — from navigating a global pandemic to the subsequent evolved real estate market. But now, the coworking and community building company is poised for even more growth — especially with its ninth location opening up this month — thanks to its community-driven mission.
The Cannon Memorial opens its doors on Monday, May 13, with a week of free coworking and events. And while the new space, developed in partnership with MetroNational, is open for leasing, Lambert says on the Houston Innovators Podcast the first and foremost, The Cannon is a community.
"The Cannon wasn't created as a real estate play — we got into coworking because as we started supporting the community and asking the question of, 'what can we do for you?,' one of the highlights was, 'hey, we need space to work,'" he says on the show. "For us, we were going to provide space because that's one of the key needs of this community.
"Our measurement of success is not the buildings we have or the occupancy even — it's what's the success of the companies that are part of the community," he continues. Click here to read more.
Ken Cowan, senior vice president of Enchanted Rock
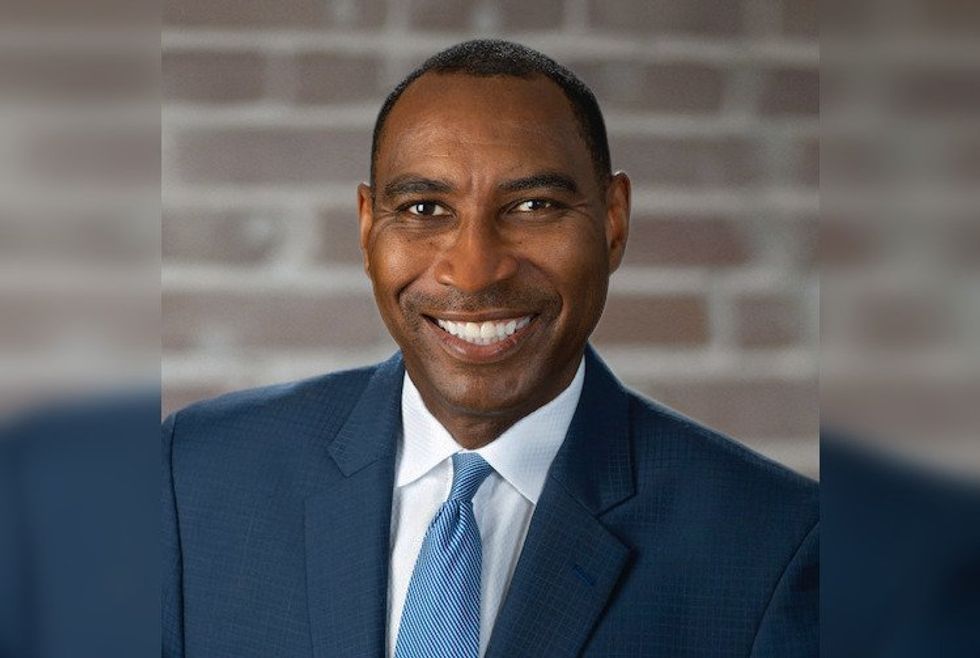

Ken Cowan writes a guest column for InnovationMap. Photo courtesy
As senior vice president of Enchanted Rock, a Houston-based provider of microgrid technology, Ken Cowan has seen how energy resilience has emerged as a key strategy for businesses across industries, as he writes in a guest column for InnovationMap.
"Executives must recognize the strategic imperative of investing in resilient energy infrastructure like microgrid systems, which can provide a competitive advantage against organizations that do not have similar measures in place," he writes. "In doing so, they can navigate uncertainty with confidence, set their business up for future success, and emerge stronger and more resilient than ever before."
In the piece, he explores the value proposition and other benefits to making these changes. Click here to read more.
Richard Willson, Huffington-Woestemeyer Professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at the University of Houston
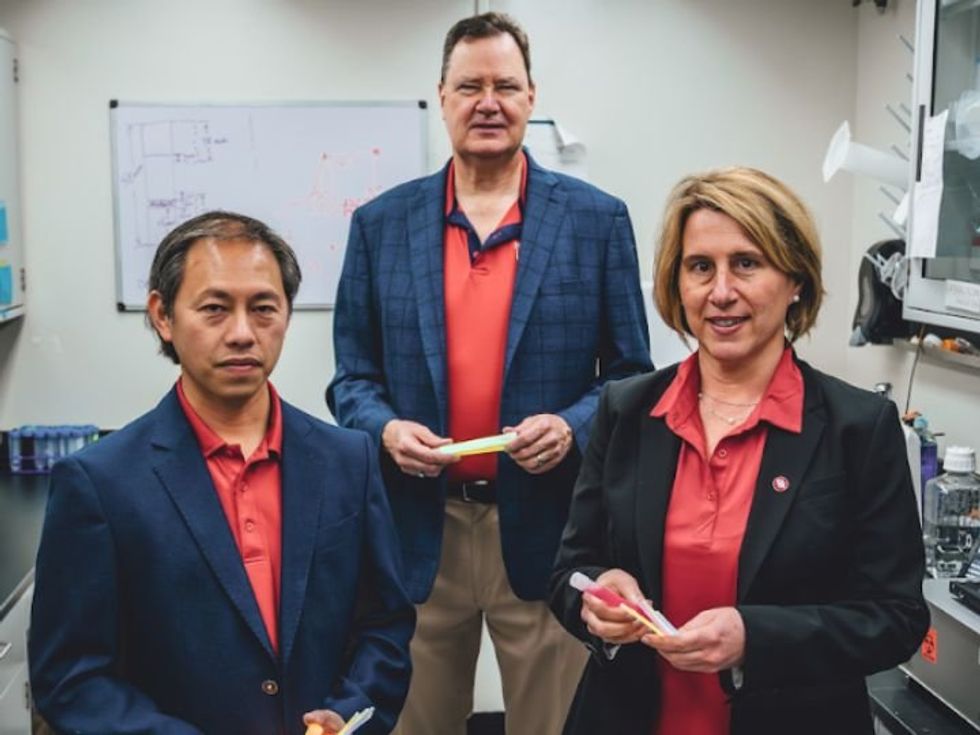

Richard Willson (center) and his team are working to develop a mix-and-read antibody measurement system that uses fluorescent materials to determine the amount of antibody present in a sample. Photo via UH.edu
An engineering project at the University of Houston has been selected to join a $10 million effort to bring biopharmaceutical manufacturing into the future. The National Institute for Innovation in Manufacturing Biopharmaceuticals (NIIMBL) chose the lab of Richard Willson, Huffington-Woestemeyer Professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at UH, as one of eight development projects that it will fund.
Willson and his team are working to develop a mix-and-read antibody measurement system that uses fluorescent materials to determine the amount of antibody present in a sample. The funding for this project is $200,000. This is the first grant UH has received from NIIMBL.
“In the course of the manufacturing processes, it's important to know the concentration of antibody in your sample and this measurement needs to be made many times in a typical manufacturing process,” said Willson in a press release. In the realm of fluorescents, he is also working to pioneer the use of glow sticks to detect biothreats for the U.S. Navy. His discoveries include a fluorescent material that emits one color of light when excited with another color of light. Click here to read more.

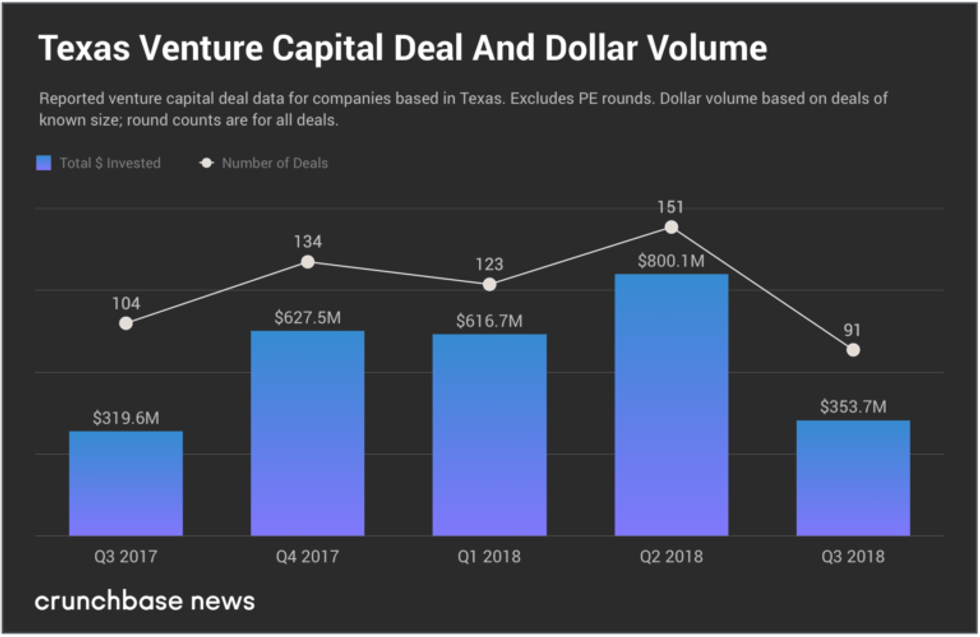 Chart courtesy of
Chart courtesy of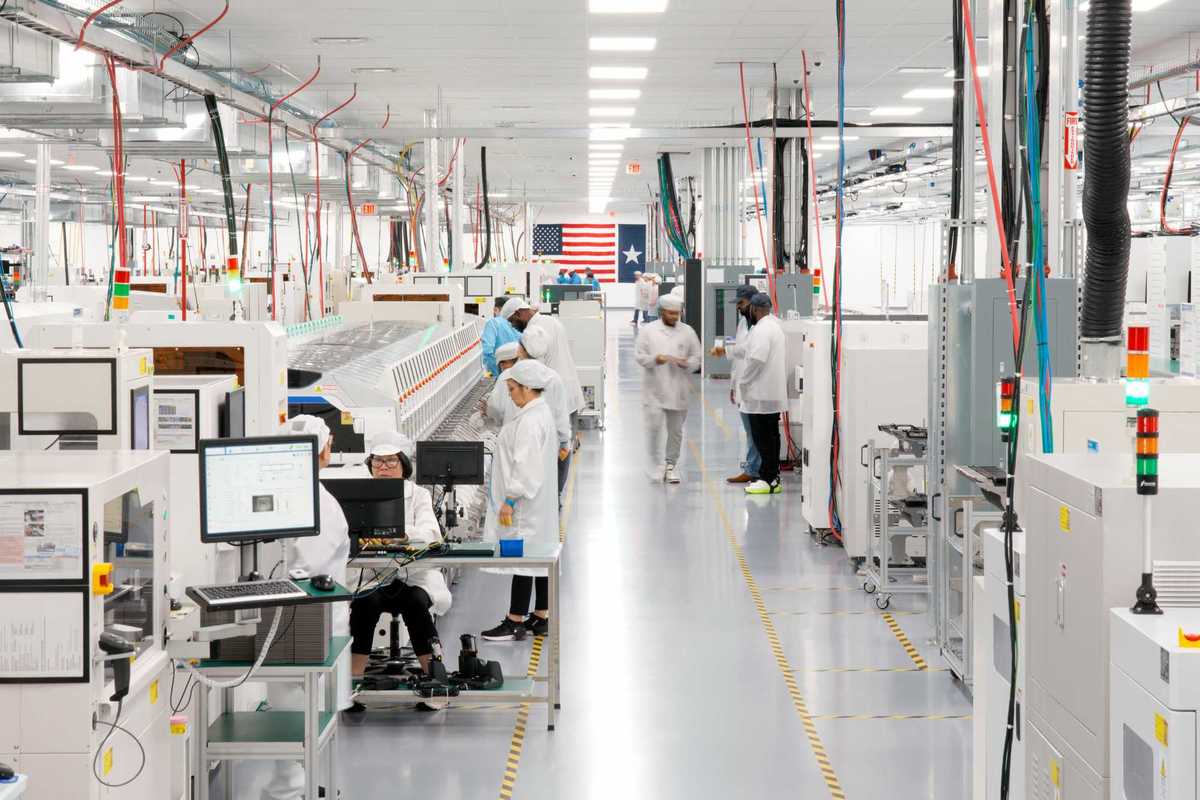  Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training center Photo courtesy Apple.