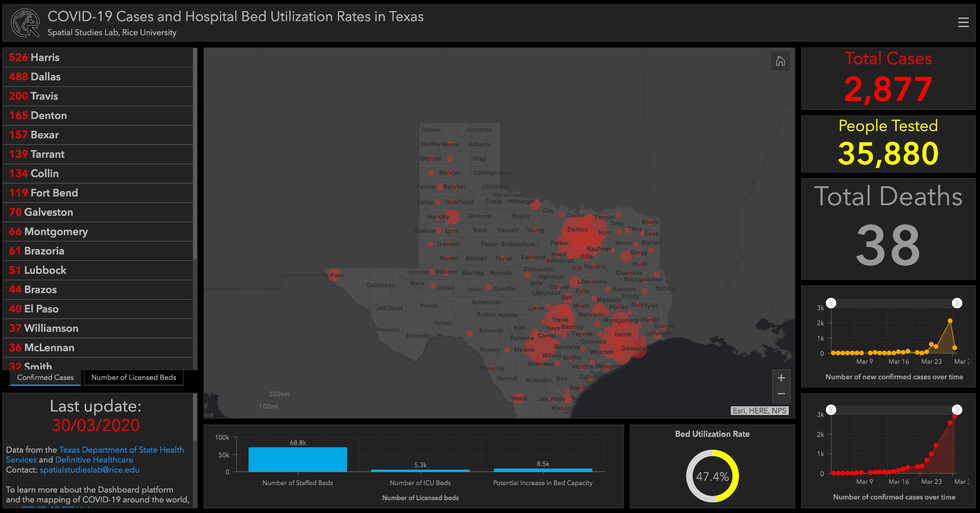
6 Houston-area inventors named fellows in prestigious program
best in class
The National Academy of Inventors has announced its annual set of NAI Fellows — and six Houstonians make the list of the 164 honorees from 116 research institutions worldwide.
The NAI Fellows Program honors academic inventors "who have demonstrated a spirit of innovation in creating or facilitating outstanding inventions that have made a tangible impact on the quality of life, economic development, and the welfare of society," according to a news release. The appointment is the highest professional distinction for inventors within academia.
The six Houstonians on the list join a group that hold more than 48,000 U.S. patents, which have generated over 13,000 licensed technologies and companies, and created more than one million jobs, per the release. Additionally, $3 trillion in revenue has been generated based on NAI Fellow discoveries.
These are the scientists from Houston organizations:
- Zhiqiang An, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston: An is the director of the Texas Therapeutics Institute, a drug discovery program operated by the John P. and Kathrine G. McGovern Medical School at Houston. He's also a professor of molecular medicine and holder of the Robert A. Welch Distinguished University Chair in Chemistry at UTHealth.
- Alex Ignatiev, University of Houston: Ignatiev served as director of two NASA-supported research and technology development centers at the University of Houston and as Lillie Cranz and Hugh Roy Cullen Professor of Physics, Chemistry, and Electrical and Computer Engineering.
- David Jaffray, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center: Jaffray was appointed MD Anderson's first-ever chief technology and digital officer in 2019. He oversees MD Anderson’s Information Services division and Information Security department and is a professor of Radiation Physics with a joint appointment in Imaging Physics.
- Pei-Yong Shi,The University of Texas Medical Branch: Pei-Yong Shi is a professor and John Sealy Distinguished Chair in Innovations in Molecular Biology Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology;. He's also the Vice Chair for Innovation and Commercialization.
- Ganesh Thakur, University of Houston: Thakur is a pioneer in carbon capture, utilization and storage and has a patent on forecasting performance of water injection and enhanced oil recovery. His team is continuing to push the research envelope for CCUS employing world-class lab research, simulation, machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- Darren Woodside, Texas Heart Institute: Woodside is the Vice President for Research and Director of the Flow Cytometry and Imaging Core at the Texas Heart Institute. His research centers around the role that cell adhesion plays in cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases, and the development of novel means to identify and treat these diseases.
- Sanjay Banerjee, The University of Texas at Austin
- Thomas Boland, The University of Texas at El Paso
- Joan Brennecke, The University of Texas at Austin
- Gerard Cote, Texas A&M University
- Ananth Dodabalapur, The University of Texas at Austin
- Holloway (Holly) H. Frost Jr., The University of Texas at Arlington
- James E. Hubbard, Texas A&M University
- Yi Lu, University of Texas at Austin
- Samuel Prien, Texas Tech University
- Earl E. Swartzlander Jr., The University of Texas at Austin
"The caliber of this year's class of NAI Fellows is outstanding. Each of these individuals are highly-regarded in their respective fields," says Paul R. Sanberg, president of NAI's board of directors, in the release. "The breadth and scope of their discovery is truly staggering. I'm excited not only see their work continue, but also to see their knowledge influence a new era of science, technology, and innovation worldwide."

 Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)
Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)