Finding growing Houston startups is as easy as following the money, and a few local companies are starting 2019 strong with a recent round of funding closed. InnovationMap has rounded up a few recent raises to highlight heading into the new year.
Apartment Butler

Ben Johnson's business idea turned into a growing company making the lives of apartment dwellers easier. Courtesy of Apartment Butler
Apartment Butler closed a $2 million seed funding round in October that was led by Houston-based Mercury Fund. The Houston startup partners with apartment communities to streamline services — like cleaning or dog walking — for residents.
Founder Ben Johnson recently spoke with InnovationMap about his career and the company. He says the company plans to launch in Austin this month and another market in March. Apartment Butler will also expand to microservices — smaller services that have only been available to the rich before.
The funding reportedly is being used to expand the company's footprint as well as make competitive hires.
Data Gumbo

Blockchain-as-a-service company, Data Gumbo, closed its seed fund with more money than it planned for. Getty Images
Data Gumbo, a Houston company that provides blockchain technology as a service, overachieved when it closed its seed round in August 2018. The company closed with $1.35 million, which is $300,000 more than the goal.
Led by CEO Andrew Bruce, Data Gumbo has a viable product and is producing revenue, according to a release. The company launched a full implementation of its technology on a Diamond Offshore rig this fall, which made it the first commercial installation of industrial blockchain technology.
Among the investors was Houston-based Carnrite Ventures and Silicon Valley's Plug and Play, the release notes.
Validere
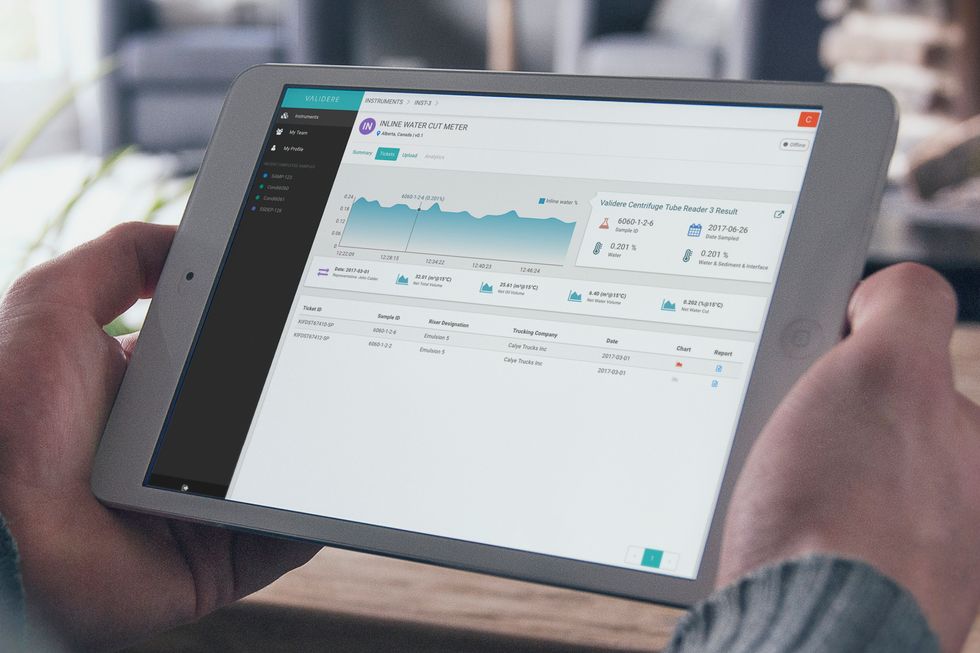
Validere, a Canada-based energy logistics company, is expanding in Houston. Courtesy of Validere
While based in Canada, Validere is using its recent raise to expand into the Houston market. The seed round closed in October with $7 million raised. The company's co-founder, Nouman Ahmad, told InnovationMap in a recent article that they are focusing on expanding the Houston office and are actively hiring.
"The goal in 2019 is to be at the same stage — in terms of customer success — in the U.S. market as we were at the end of 2018 in the Canadian market," Ahmad says.
Intelligent Implants
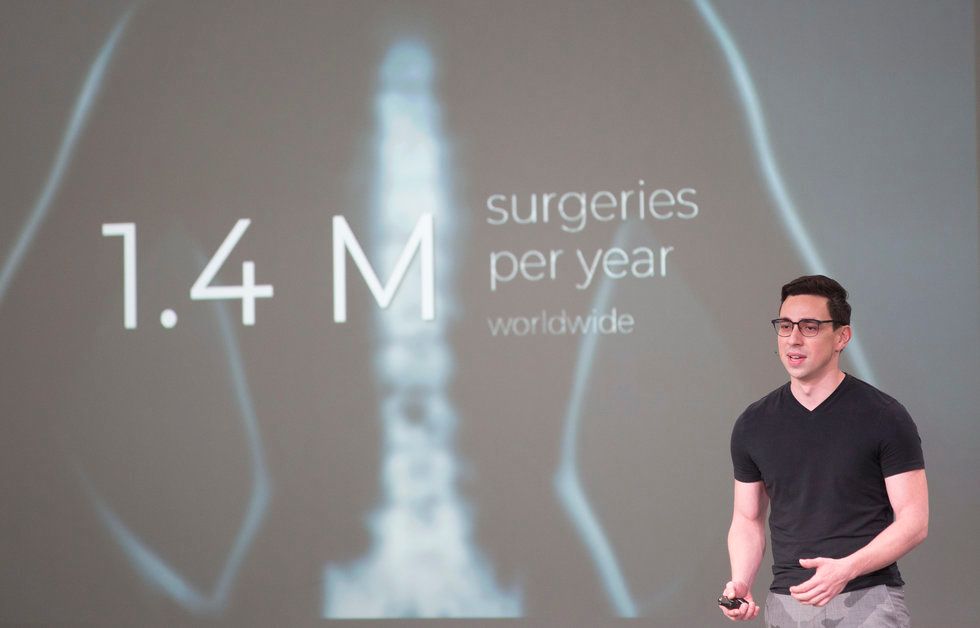
Intelligent Implant's co-founder, Juan Pardo, told the crowd at Demo Day that his company's device allows for 50 percent faster bone growth in patients. Photo by Cody Duty/TMC
Recent graduate of the Texas Medical Center's TMCx medical devices program, Intelligent Implants created a technology that stimulates bone growth following corrective back surgery.
The Houston startup closed a funding round in October with two investors, according to Crunchbase. The total raise was reported as a $1 million Mezzanine round on AngelMD.
Saranas

Saranas Inc. is testing its technology that can detect and track internal bleeding complications. Getty Images
Saranas Inc., a Houston-based medical device company, is currently in its clinical trials thanks to a $2.8 million Series C fund that closed in May 2018. The trials are focused on the company's key device, called the Early Bird Bleed Monitoring System, which is designed to detect and track bleeding complications related to endovascular procedures. These medical procedures treat problems, such as aneurysms, that affect blood vessels.
In a story for InnovationMap, Zaffer Syed, president and CEO of Saranas, says the clinical trials are crucial for receiving approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. That approval is expected this year.
---
Venture adventures will be a regular roundup on InnovationMap. If your company is in the process of closing or recently closed on a round, please email Natalie Harms at natalie@innovationmap.com.


 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.

