Houston startup founder is reinventing medical devices by thinking outside the pillbox
What's Poppin'
One day in college on her way to lunch with some friends, Regina Vatterott fainted on the sidewalk. It wasn't anything serious, but she had a few vitamin deficiencies and hadn't eaten in a while. After that, she started taking her daily supplements more seriously.
She tried using the traditional pillbox, but it would take her forever to organize. And she hated how her friends would call it, in a loving, playful way, her "old people pillbox."
She joined forces with a few like-minded individuals at her school to create a health and wellness accessory, rather than a medical device. They bought craft supplies and hand-glued LED lights to the first prototype of what would become EllieGrid, a smart pillbox that syncs with an app on your phone so that you can easily program your medicinal schedule and receive alerts of when to take what.
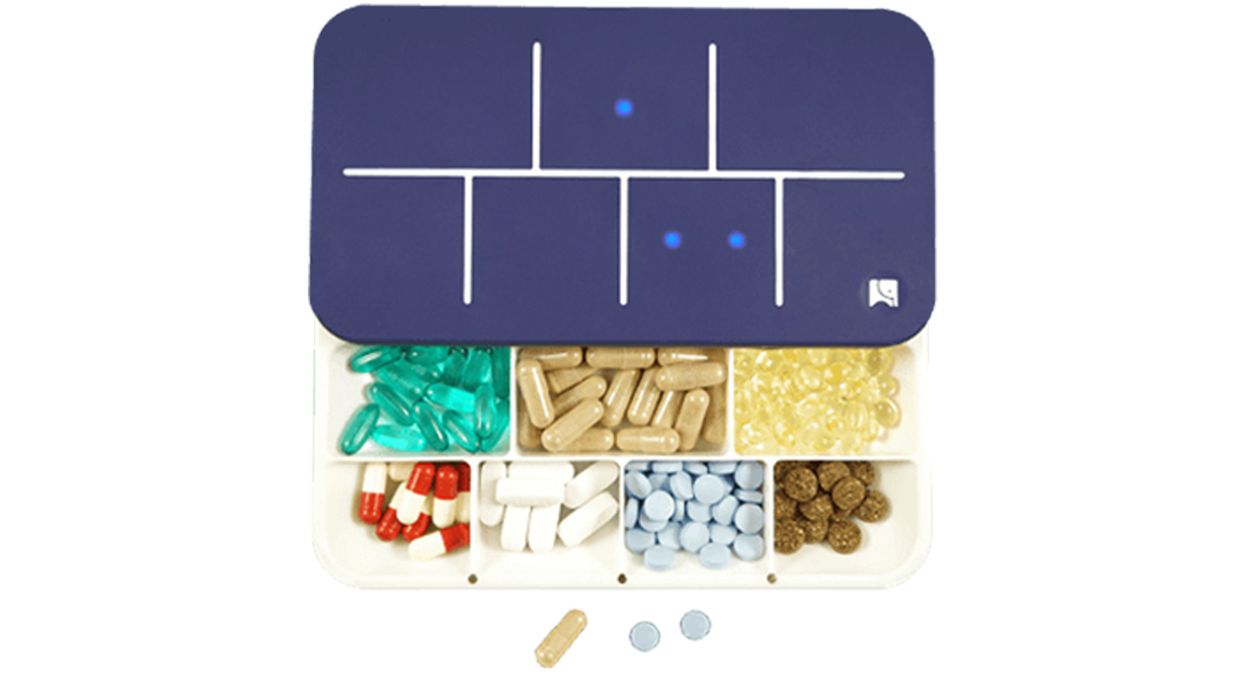

Vatterott, who was interning at a company that did social media marketing for independent pharmacies nationwide, saw an underserved market of adults who have a need for a product like this. EllieGrid targets the Baby Boomer age and younger, usually between ages 35 and 55.
Now, EllieGrid is growing from its initial presale phase to setting a system in place where Houstonians can find EllieGrid in stores or online.
InnovationMap: You and your team were only college students when you started. How did you get funding?
Regina Vatterott: We started pitching business plan competitions all over the country — even as far as Barcelona. We raised money — and some of it wasn't even money, but resources, like access to 3D printers or free office space. It was an amazing tool for us, and it helped validate us and helped us perfect our business plan. We ended up raising like $200,000 just in business plan competitions.
After that, we knew we had to prove it in market. Last year, we ran a crowdfunding campaign on IndieGoGo. Our goal was to raise $40,000, and we raised around $167,000. In January of this year, we shipped all the products that were preordered on IndieGoGo to 37 different countries.
IM: What's been the biggest challenge?
RV: The very beginning, the challenge was affording our legal fees — it's not something you want to skimp on, but was incredibly expensive. After that, it was simply manufacturing. It's never easy. It's always going to cost three times as much and take three times as long as you expect. With our plastics, we use a process called injection molding, and if the temperature is off, the plastics will dry in a different way and the pieces won't fit together. It's an obnoxious challenge that we're still facing today.
IM: What's next for you or your company?
RV: Right now, we are making that transition from pre-selling products to just regular sales. It's easier said than done because we are making sure that supply chain is efficient and on time. We are finishing up a batch of 1,000 units to work with that we'll just sell on our website. Once we have information on how we can sell these units, we want to work with distributors, so we are working on creating those relationships now.
IM: How has being headquartered in Houston been?
RV: This is a very affordable place and has a lot of resources for startups. I will say our one struggle is there's not a lot of funding for hardware startups — especially for consumers — like ours. That's more in California or New York.
IM: Thinking more long term, what do you have in mind for EllieGrid and your team?
RV: For EllieGrid, we want to implement artificial intelligence. We want to be able to take the data of how the user is interacting with the device and be able to predict when people will forget to take their meds to prevent any issues with medication.
For us, Ellie is just the start. We want to develop more health and wellness accessories that are traditionally known to be medical devices. One example we give is how eyeglasses used to be medical devices, and now glasses are a fashion accessory. We want to do more and more with medical devices because we think that people are always people before they are patients.
IM: What's the worst piece of advice you've received?
RV: In the beginning when we'd pitch this idea to doctors, they would tell us we were wasting our time because patients don't care what a product looks like as long as it works. I don't really get that anymore, because we're proving that wrong now.
---
Portions of this interview have been edited.

