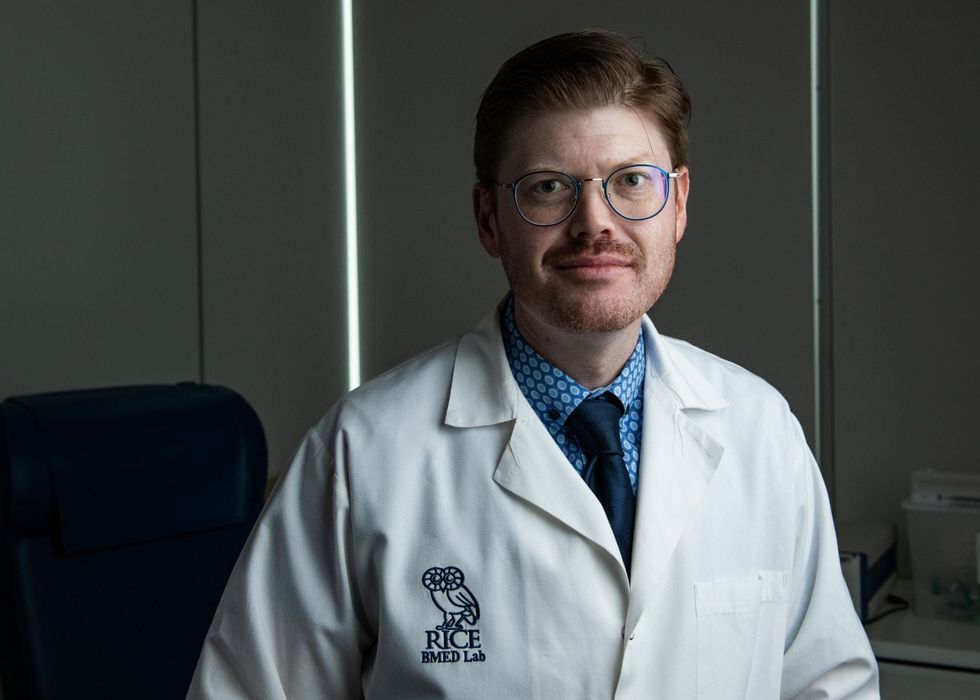
The Rice Biotech Launch Pad, which is focused on expediting the translation of Rice University’s health and medical technology discoveries into cures, has named Amanda Nash and Kelsey L. Swingle to its leadership team.
Both are assistant professors in Rice’s Department of Bioengineering and will bring “valuable perspective” to the Houston-based accelerator, according to Rice.
“Their deep understanding of both the scientific rigor required for successful innovation and the commercial strategies necessary to bring these technologies to market will be invaluable as we continue to build our portfolio of lifesaving medical technologies,” Omid Veiseh, faculty director of the Launch Pad, said in a news release.
Amanda Nash
Nash leads a research program focused on developing cell communication technologies to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases and aging. She previously trained as a management consultant at McKinsey & Co., where she specialized in business development, portfolio strategy and operational excellence for pharmaceutical and medtech companies. She earned her doctorate in bioengineering from Rice and helped develop implantable cytokine factories for the treatment of ovarian cancer. She holds a bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering from the University of Houston.
“Returning to Rice represents a full-circle moment in my career, from conducting my doctoral research here to gaining strategic insights at McKinsey and now bringing that combined perspective back to advance Houston’s biotech ecosystem,” Nash said in the release. “The Launch Pad represents exactly the kind of translational bridge our industry needs. I look forward to helping researchers navigate the complex path from discovery to commercialization.”
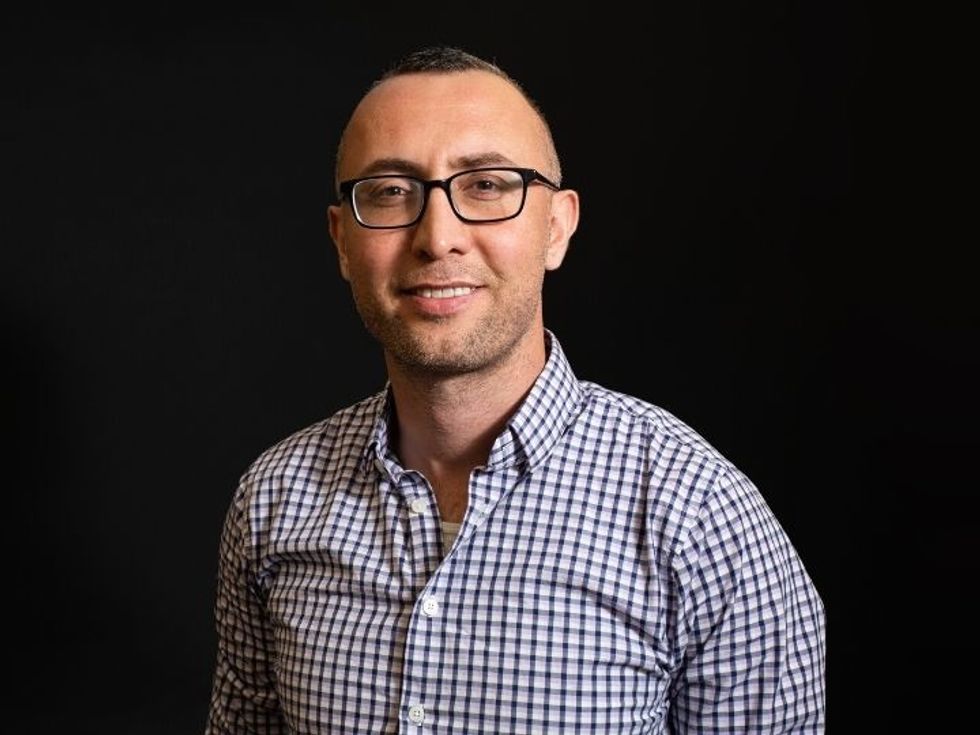
Kelsey L. Swingle
Swingle’s research focuses on engineering lipid-based nanoparticle technologies for drug delivery to reproductive tissues, which includes the placenta. She completed her doctorate in bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, where she developed novel mRNA lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of preeclampsia. She received her bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering from Case Western Reserve University and is a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellow.
“What draws me to the Rice Biotech Launch Pad is its commitment to addressing the most pressing unmet medical needs,” Swingle added in the release. “My research in women’s health has shown me how innovation at the intersection of biomaterials and medicine can tackle challenges that have been overlooked for far too long. I am thrilled to join a team that shares this vision of designing cutting-edge technologies to create meaningful impact for underserved patient populations.”
The Rice Biotech Launch Pad opened in 2023. It held the official launch and lab opening of RBL LLC, a biotech venture creation studio in May. Read more here.


 operation
operation