Weather analytics platform with Houston HQ taps Norwegian biz to optimize tech
weatherproof tech
There’s no way around it: Houston floods. And with the deluge comes hurdles for businesses. The only real power we have in the face of such adversity is preparation.
StormGeo, a weather intelligence provider with its United States headquarters in Houston, has partnered with Norwegian company 7Analytics to create technology positioned to revolutionize planning for floods.
StormGeo debuted in Norway in 1997. In 2012, it acquired Houston company Impact Weather, says Bob Weinzapfel, a meteorologist and senior project manager of weather insights for StormGeo. Houston is one of 24 offices spread over 15 countries with more than 600 employees, Weinzapfel adds.
The team at 7Analytics, according to Weinzapfel, “Are a bunch of smart flood experts and machine learning experts.” Together, they are introducing a technology that Weinzapfel calls “a game changer” for Houston businesses.
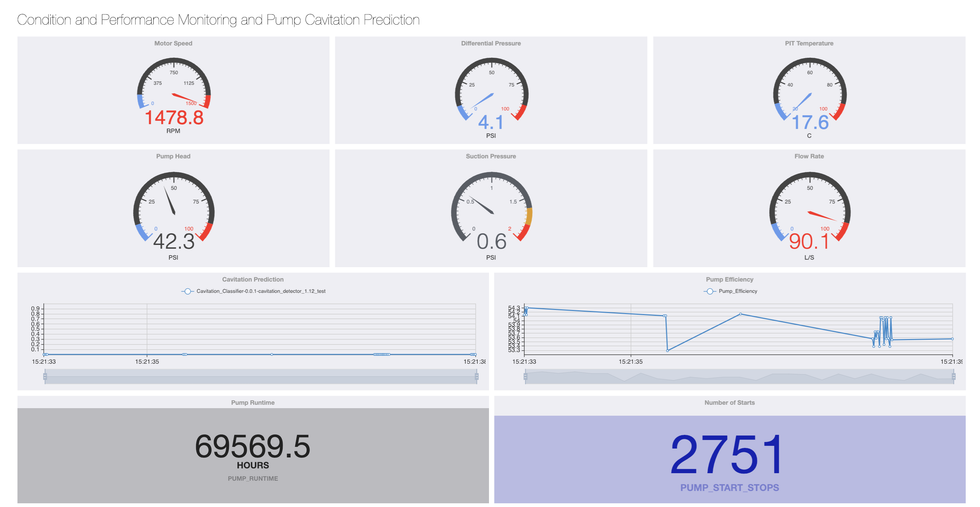
7Analytics uses AI to give users an overview of Houston’s potential flooding based on a 72-hour forecast. “Any business like a grocery store or hospitals or even a refinery—any business with employees or customers, it’s important to know Are the roadways being flooded? Can my employees and customers get in?” says Weinzapfel.
StormGeo has long provided weather insights and guidance to businesses in Houston. Now, detailed maps provide real-time flood forecasting.
The maps forecast the probability of flash flooding in each subbasin, but perhaps more importantly, they can home in on clients’ buildings to show what inundation will look like in parking lots and nearby roads.
"Our product takes a real-time StormGeo weather forecast — for example, the risk of rainfall tomorrow—and translates it into actionable risk info, such as their site is at risk of up to a foot of flooding tomorrow with peak flood occurring at 2 p.m.," explains Jonas Toland, co-founder of 7Analytics.
Armed with such information, businesses can adjust operations ahead. For example, one client is a grocery store chain.
“They have business processes they have to get a jump on. The locations that have customers try to be the last to close and first to open,” Weinzapfel says.
That means that storm tracking can help with letting the store’s team know to purchase more emergency supplies to sell, schedule more employees to help sell them, and know when to close to keep those workers safe.
The Houston version of the solution is the first, but Weinzapfel says that the team is currently working to expand across greater Houston and then into Austin.
“We knew if we could do it here and do a really good job, we could do it anywhere using the same technology,” he adds.
There’s no question that flooding will continue to take place in Houston. But with StormGeo and 7Analytics’ Houston-area flood model, the people that serve us will be prepared.