These 5 Houston-area research institutions have bright minds at work to battle COVID-19
research roundup
Since even the early days of COVID-19's existence, researchers all over the world were rallying to find a cure or potential vaccine — which usually take years to make, test, and get approved.
Houston researchers were among this group to put their thinking caps on to come up with solutions to the many problems of the coronavirus. From the testing of existing drugs to tapping into tech to map the disease, here are some research projects that are happening in Houston and are emerging to fight the pandemic.
Baylor College of Medicine evaluating potential COVID-fighting drug
 Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)
Human Body Organs (Lungs Anatomy)Baylor College of Medicine has identified a drug that could potentially help heal COVID-19 patients. Photo via bcm.edu
While Baylor College of Medicine has professionals attacking COVID-19 from all angles, one recent discovery at BCM includes a new drug for treating COVID-caused pneumonia.
BCM researchers are looking into Tocilizumab's (TCZ), an immunomodulator drug, effect on patients at Baylor St. Luke's Medical Center and Harris Health System's Ben Taub Hospital.
"The organ most commonly affected by COVID-19 is the lung, causing pneumonia for some patients and leading to difficulty breathing," says Dr. Ivan O. Rosas, chief of the pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine section at BCM, in a news release.
TCZ, which has been used to successfully treat hyperimmune responses in cancer patients being treated with immunotherapy, targets the immune response to the coronavirus. It isn't expected to get rid of the virus, but hopefully will reduce the "cytokine storm," which is described as "the hyper-immune response triggered by the viral pneumonia" in the release.
The randomized clinical trial is looking to treat 330 participants and estimates completion of enrollment early next month and is sponsored by Genentech, a biotechnology company.
Texas A&M University leads drug testing

A Texas A&M University researcher is trying to figure out if an existing vaccine has an effect on COVID-19. Screenshot via youtube.com
A researcher from Texas A&M University is working with his colleagues on a short-term response to COVID-19. A vaccine, called BDG, has already been deemed safe and used for treatment for bladder cancer. BDG can work to strengthen the immune system.
"It's not going to prevent people from getting infected," says Dr. Jeffrey D. Cirillo, a Regent's Professor of Microbial Pathogenesis and Immunology at the Texas A&M Health Science Center, in a news release. "This vaccine has the very broad ability to strengthen your immune response. We call it 'trained immunity.'"
A&M leads the study in partnership with the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, as well as Harvard University's School of Public Health and Cedars Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
Texas A&M Chancellor John Sharp last week set aside $2.5 million from the Chancellor's Research Initiative for the study. This has freed up Cirillo's team's time that was previously being used to apply for grants.
"If there was ever a time to invest in medical research, it is now," Sharp says in the release. "Dr. Cirillo has a head start on a possible coronavirus treatment, and I want to make sure he has what he needs to protect the world from more of the horrible effects of this pandemic."
Currently, the research team is recruiting 1,800 volunteers for the trial that is already underway in College Station and Houston — with the potential for expansion in Los Angeles and Boston. Medical professionals interested in the trial can contact Gabriel Neal, MD at gneal@tamu.edu or Jeffrey Cirillo, PhD at jdcirillo@tamu.edu or George Udeani, PharmD DSc at udeani@tamu.edu.
"This could make a huge difference in the next two to three years while the development of a specific vaccine is developed for COVID-19," Cirillo says in the release.
Rice University is creating a COVID-19 map
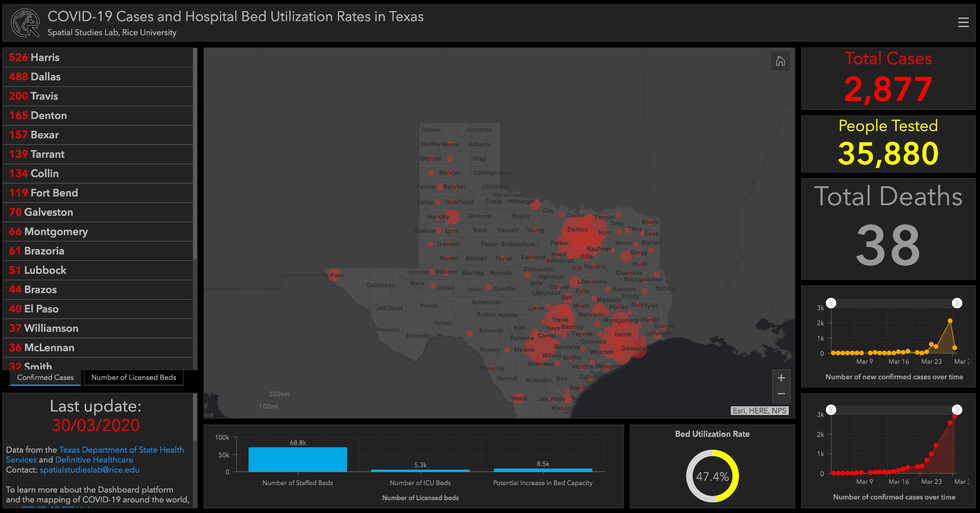
Researchers at Rice University's Center for Research Computing's Spatial Studies Lab have mapped out all cases of COVID-19 across Texas by tapping into public health data. The map, which is accessible at coronavirusintexas.org, also identifies the number of people tested across the state, hospital bed utilization rate, and more.
The project is led by Farès el-Dahdah, director of Rice's Humanities Research Center. El-Dahdah used open source code made available by ESRI and data from the Texas Department of State Health Services and Definitive Healthcare.
"Now that the Texas Division of Emergency Management released its own GIS hub, our dashboard will move away from duplicating information in order to correlate other numbers such as those of available beds and the potential for increasing the number of beds in relation to the location of available COVID providers," el-Dahdah says in a press release.
"We're now adding another layer, which is the number of available nurses," el-Dahdah continues. "Because if this explodes, as a doctor friend recently told me, we could be running out of nurses before running out of beds."
Texas Heart Institute is making vaccines more effective
A new compound being developed at Texas Heart Institute could revolutionize the effect of vaccines. Photo via texasheart.org
Molecular technology coming out of the Texas Heart Institute and 7 HIlls Pharma could make vaccines — like a potential coronavirus vaccine — more effective. The oral integrin activator has been licensed to 7 Hills and is slated to a part of a Phase 1 healthy volunteer study to support solid tumor and infectious disease indications in the fall, according to a press release.
The program is led by Dr. Peter Vanderslice, director of biology at the Molecular Cardiology Research Laboratory at Texas Heart Institute. The compound was first envisioned to improve stem cell therapy for potential use as an immunotherapeutic for certain cancers.
"Our research and clinical colleagues are working diligently every day to advance promising discoveries for at risk patients," says Dr. Darren Woodside, co-inventor and vice president for research at the Texas Heart Institute, in the release. "This platform could be an important therapeutic agent for cardiac and cancer patients as well as older individuals at higher risk for infections."
University of Houston's nanotech health monitor

UH researchers have developed a pliable, thin material that can monitor changes in temperature. Photo via uh.edu
While developed prior to the pandemic, nanotechnology out of the University of Houston could be useful in monitoring COVID patients' temperatures. The material, as described in a paper published by ACS Applied Nano Materials, is made up of carbon nanotubes and can indicate slight body temperature changes. It's thin and pliable, making it ideal for a wearable health tech device.
"Your body can tell you something is wrong before it becomes obvious," says Seamus Curran, a physics professor at the University of Houston and co-author on the paper, in a news release.
Curran's nanotechnology research with fellow researchers Kang-Shyang Liao and Alexander J. Wang, which also has applications in making particle-blocking face masks, began almost 10 years ago.
