Houston innovator makes major headway on his portable stroke rehab device
research milestone
A University of Houston professor has taking a huge step in advancing his game-changing stroke recovery tech.
Jose Luis Contreras-Vidal, the director of the UH BRAIN Center, recently published his work on a noninvasive brain-machine in a summer issue of the journal Sensors. InnovationMap first reported on Contreras-Vidal's technology in 2022, when it was being tested.
Contreras-Vidal's device uses a wireless, mobile dry-electrode headset placed on the scalp to convert electroencephalography (EEG) recordings (or measurements of electrical activity in different parts of the brain) to interface with a closed-loop brain–computer (BCI) and communicate with exoskeleton devices. Together, the technology triggers robotic movement based on the wearer's brain activity.
The technology has potential to boost cortical plasticity after a stroke, which can improve motor skills recovery.
According to a statement from UH, a patent is pending on Contreras-Vidal's BCI algorithm and the self-positioning dry electrode bracket used on the scalp. The technology has also now been validated and tested at the University of Houston.
Contreras-Vidal says the technology makes stroke recovery easier for the user and even possible at home.
“Most commercial EEG-based BCI systems are tethered to immobile processing hardware or require complex programming or set-up, making them difficult to deploy outside of the clinic or laboratory without technical assistance or extensive training," he says in a statement. "A portable and wireless BCI system is highly preferred so it can be used outside lab in clinical and non-clinical mobile applications at home, work, or play.”
Additionally, the technology uses off-the-shelf components and is adjustable to fit about 90 percent of the population, according to UH.
"Current commercial EEG amplifiers and BCI headsets are prohibitively expensive, lack interoperability, or fail to provide a high signal quality or closed-loop operation, which are vital for BCI applications,” Contreras-Vidal adds.
The development of this technology was originally funded in part by an $813,999 grant from the National Science Foundation’s Division of Translational Impacts. UH reports that about 795,000 people in the United States suffer from a stroke annually.
Other leaders in Houston’s medical industry have tapped into innovative ways to treat and rehabilitate stroke patients in recent years. Baylor St. Luke's Hospital began using AI to reduce the time it takes to treat patients who've suffered from a stroke in 2021.
- Houston researchers develop new battery prototype to impact wearable technology ›
- University of Houston plans to build new central campus innovation hub ›
- UH lab using mixed reality to optimize designs for the Moon and Mars ›
- University of Houston, Intel team up to prepare workforce for AI revolution ›
- Greentown Houston announces grand opening, clean energy accelerators open apps, and more innovation news ›
- Here are 3 breakthrough innovations coming out of research at Houston institutions ›

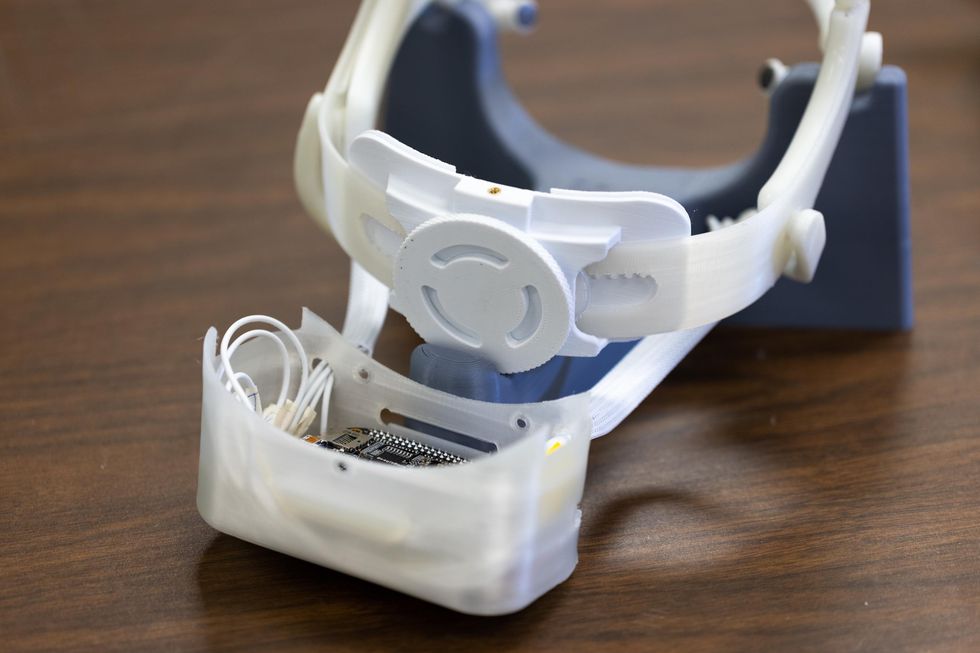 Both parts of the device — a part that attaches to the patient's head and a part affixed to their arm — are noninvasive. Photo courtesy of UH
Both parts of the device — a part that attaches to the patient's head and a part affixed to their arm — are noninvasive. Photo courtesy of UH