Houston biotech company closes $120M Series B, Chevron taps local startup for program, and more innovation news
Short stories
Big things are happening in Houston — from a $120 million close to the U.S. Department of Energy picking a Houston-area company for nuclear energy research. Here are the highlights of Houston innovation news you might have missed.
Need more news rounded up for you? Subscribe to our daily newsletter that sends fresh stories straight to your inboxes every morning.
Houston immunotherapy company raises $120 million in funding

Getty Images
AlloVir, a Houston biotech company founded at Baylor's Center for Cell and Gene Therapy, has closed a $120 million Series B round that was led by Fidelity Management and Research Company. Other contributors included Gilead Sciences, F2 Ventures, Redmile Group, Invus, EcoR1 Capital, Samsara BioCapital, and Leerink Partners Co-investment Fund, LLC.
The company is currently in clinical trials for its immunotherapy technology and also announced it is joining the ElevateBio — a Boston-based organization that combines a group of cell and gene therapy companies — portfolio.
"We are excited to now be building AlloVir as an ElevateBio portfolio company," says Ann Leen, AlloVir co-founder, CSO, and Professor of Pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine, in a release. "This partnership provides AlloVir with fully integrated bench-to-bedside capabilities to accelerate the development and commercialization of our allogeneic, off-the-shelf, multi-virus specific T- cell immunotherapies."
Allovir, which until recently was known as ViraCyte, was founded in 2013.
Chevron taps Houston startup for pilot program
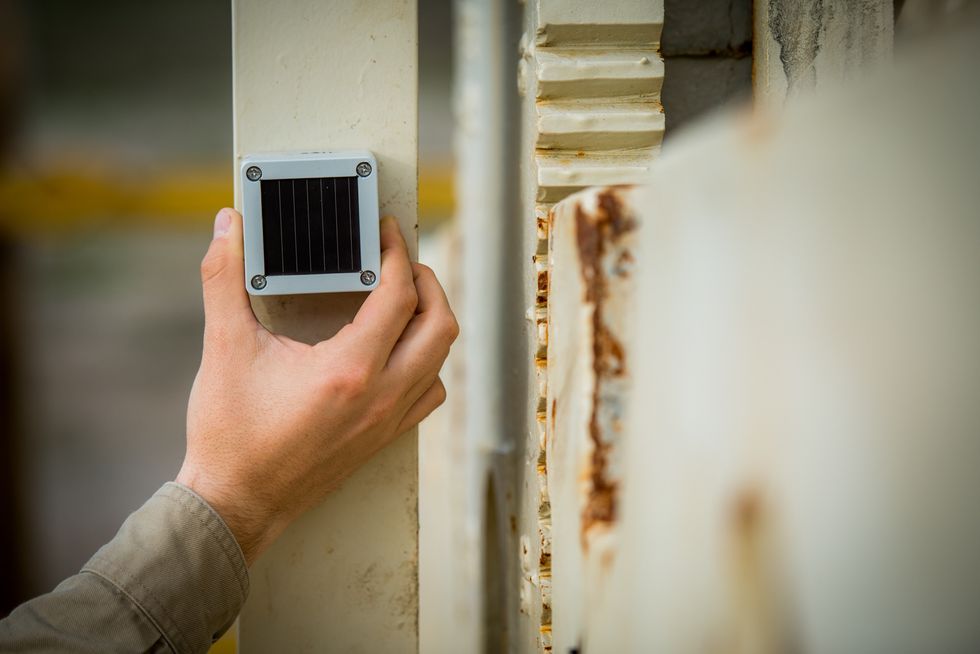

Photo courtesy of Sensorfield
Houston-based Sensorfield LLC, which has developed a suite of wireless sensors for industrial monitoring, has announced that it has been selected for Chevron Technology Ventures' Catalyst Program.
"Technology has finally reached the point where embedded solar-powered, plug-and-play industrial wireless sensors are possible at a low cost,'' says Sensorfield founder and CEO, Strode Pennebaker, in a release. "Our exciting new association with Chevron is a major step in our goal to bring cost-effective, high-quality intelligent remote monitoring to asset owners at any scale."
Department of Energy selects a Houston-area company for funding
Courtesy of the DOE
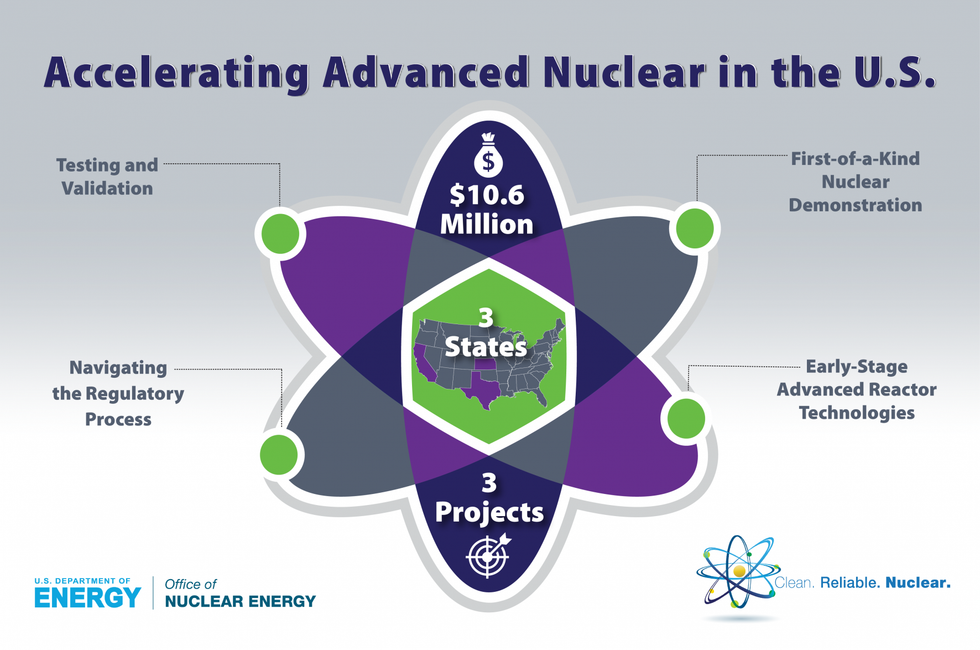
U.S. Department of Energy is awarding $10.6 million for nuclear technology development across three projects in three states — one is in Wadsworth, Texas, about 80 miles outside of Houston.
The company, STP Nuclear Operating Company, will receive $1.18 million in DOE funding, according to a release, to develop and implement advanced fire probabilistic risk assessment — or PRA — modeling techniques.
"These projects are important because they will help the U.S. continue to develop advanced reactors and technologies to support nuclear energy as a safe, zero-emissions baseload energy source," says Carrie Edwards, senior adviser for the Office of Nuclear Energy at the DOE, in an email.
Rice University launches executive education program in The Woodlands
Rice University's Jones Graduate School of Business — in partnership with The Woodlands Area Economic Development Partnership — has created The Leadership Accelerator. It's the first time Rice has brought an open enrollment program to the area.
The program will take place from October 7 to 10 program at the former Chicago Bridge & Iron Co. office buildings in Hughes Landing (2103 Research Forest Drive). Professor Brent Smith will lead the course .
The four-day course will build upon established managers' careers and give them an opportunity to study best practices for creating a more productive organization.
Carnrite Ventures expands to Austin

Courtesy of Nick Carnrite
Houston-based The Carnrite Group's investment arm, Carnrite Ventures, has agreed to invest with Seraph Group. The partnership allows for the Houston VC group to expand its portfolio to Austin, as that's where Seraph's last fund focused on.
"Austin's venture capital funds have moved up-market to series B and C funding rounds, which has created a need for more capital in earlier stages and provides us with an opportunity," says Nick Carnrite, Managing Director of The Carnrite Group and Carnrite Ventures, in a release.
Houston scientifically-designed athleticwear startup launches men's line

Courtesy of Accel Lifestyle
Accel Lifestyle, a Houston-based athletic clothing line made with its patented anti-stink material, has launched its menswear line.
"After three years in the making, I'm beyond thrilled to announce that Accel Lifestyle Men's Collection has launched," says Megan Eddings, founder of Accel. "We are focusing on shirts (t-shirts and tanks), and we are planning to launch the women's collection late next month."
The products are made in America and all ethically sourced — even the product's shipping material, as it has zero plastic involved.
