Last year, TMCx, the Texas Medical Center's health tech startup accelerator pivoted to digital programming.
The accelerator revamped its program to allow for an initial Bootcamp stage that would bring in a larger group of startups and then, after the boot camp, the program would move forward with a smaller group through the official acceleration process.
"We hosted 21 companies, representing six countries and 10 states, who each engaged with subject matter experts, clinical leaders, and corporate partners," writes Emily Reiser, senior manager of Innovation Community Engagement at TMC Innovation, in a blog post. "Over half of which ended Bootcamp in advanced discussions with hospitals and/or corporate partners."
Through the bootcamp, TMCx has accepted seven startups into the program. These companies are currently engaged with the TMC community and are receiving support, mentorship, and other opportunities.
Cardiosense
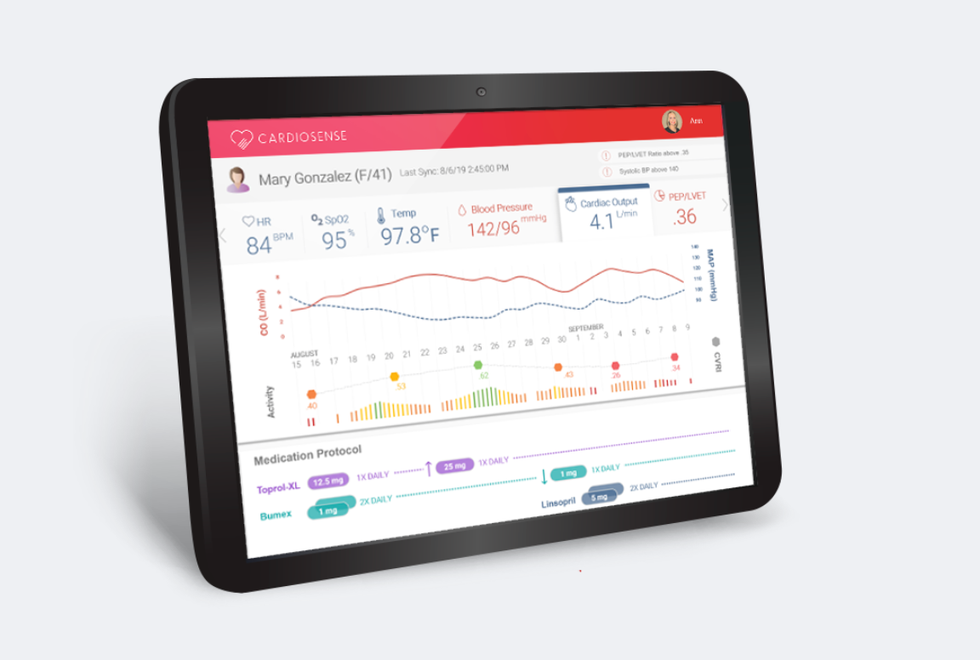
Image via cardiosense.com
Chicago-based Cardiosense, a medical device company with heart health tracking technology, is familiar with Houston innovation. The company won sixth place in the 2020 Rice Business Plan Competition, and the TMC's prize at the event.
Cognetivity Neurosciences

Image via Getty Images
Cognetivity Neurosciences, founded in the United Kingdom, is a digital health platform that taps into neuroscience and artificial intelligence to measure cognitive performance of patients in order to more effectively allow for early detection and management of neurodegenerative disorders.
Eleos Health
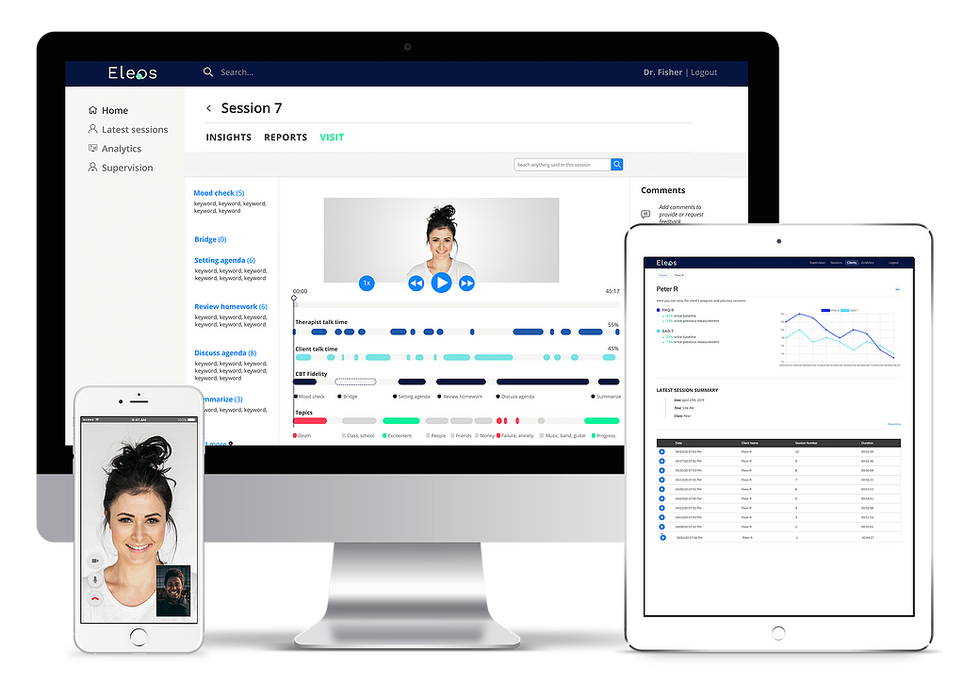
Image via eleos.health
Cambridge, Massachusetts-based Eleos Health is focused on helping behavioral health clinicians to optimize their efforts with an all-in-one behavioral health platform. It combines telehealth, measurement-based, and evidence-based care in one holistic solution, and is powered by therapy-specific voice analysis and natural language processing.
Harmonic Bionics
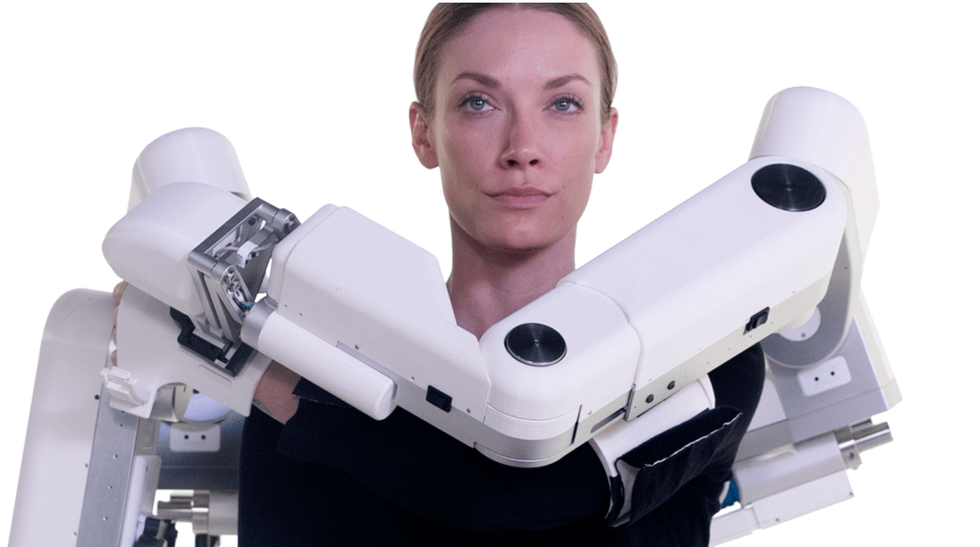

Image via harmonicbionics.com
Harmonic Bionics is one of two Lone Star State companies in the program. The Austin-based robotics startup is working on technology that can help improve upper extremity rehabilitation for patients.
Native Cardio
Photo via Getty Images
Florida-based Native Cardio is tapping into technology to help find a solution to postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF), which is the most frequent complication after cardiac surgery, occurring in up to 60 percent of patients, according to the company's website. The goal is to help reduce costs, increase accessibility, and improve quality of care.
Progenerative Medical

Image via progenerative.com
Progenerative Medical, based in San Antonio, is working on a clinically-proven reduced pressure therapy to spinal and orthopedic indications to significantly improve clinical outcomes.
RCE Technologies
Image via rce.ai
Atlanta-based RCE Technologies is an artificial intelligence-enabled medical device company that has created a technology that can detect heart attacks early using non-invasive wearables.




