WeWork selects Houston as one of its markets for a 3D printing pilot program
press print
WeWork has teamed up with two leading 3D printing companies to bring their technology into five WeWork Labs markets — including Houston's downtown location. The other locations tapped for the pilot program are London, San Francisco, New York, and Seattle.
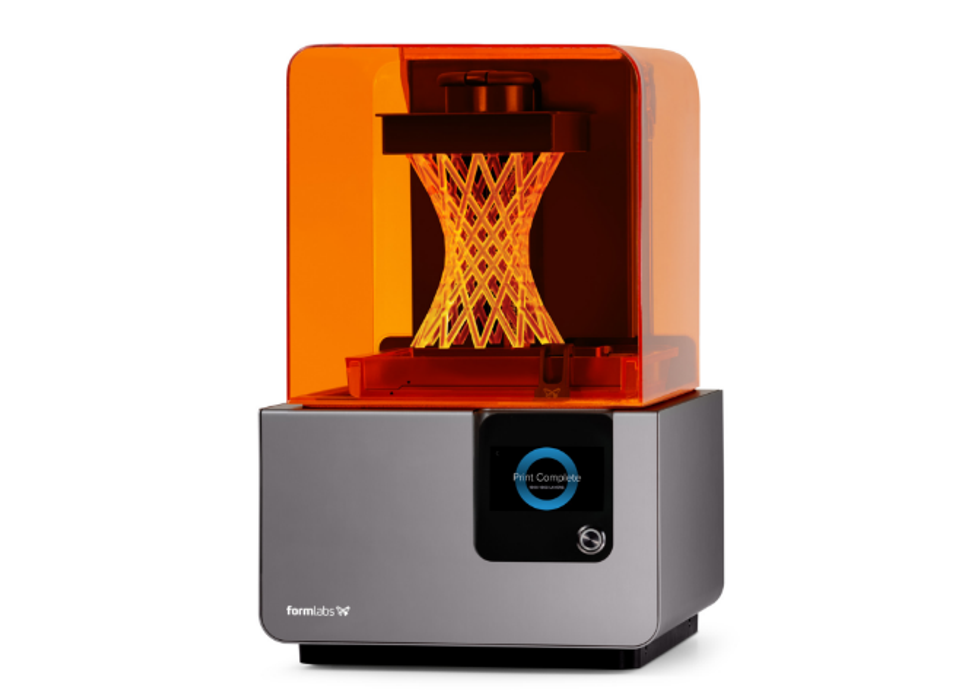
Massachusetts-based Formlabs' Form 2 printer has over 20 different material resins WeWork Labs members can use to prototype and print products using desktop stereolithography.
"Formlabs was founded eight years ago on the basis of empowering anyone to make anything," says Max Lobovsky, CEO and co-founder of Formlabs in a release. "Today, our customers have printed more than 40 million parts, they vary from early stage entrepreneurs changing the status quo and developing new applications to Fortune 500s experimenting with new business models or production methods."
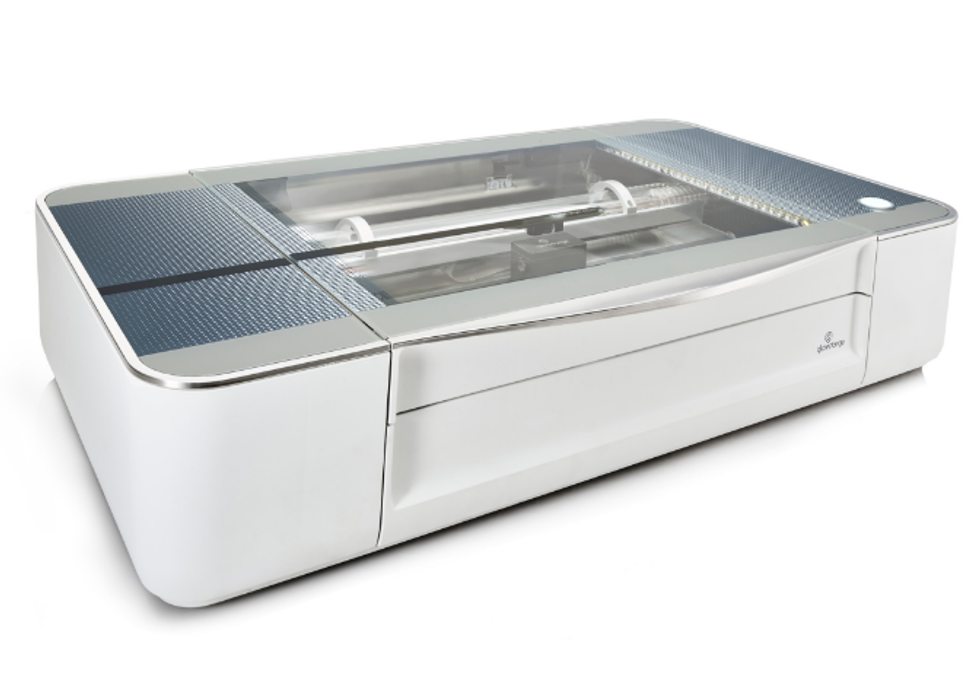
The other company involved in the program is Seattle-based Glowforge, which created a 3D laser printer. Glowforge Plus uses subtractive laser technology to cut and sculpt projects from materials like wood, leather, acrylic, stone — and even stickers. The company, which was founded in 2014, has had over three million prints on its devices — everything from jewelry and clothing to machinery.
"We are thrilled to partner with WeWork Labs to provide their community of entrepreneurs and startups alike access to the tools that will help them create corporate giveaways, new product prototypes, and full production runs — everything to take their dreams from idea to creation," says Dan Shapiro, CEO of Glowforge, in the release.
The printers will be revealed at various launch events celebrating the National Week of Making, which begins June 21 and goes through June 27. Houston's launch event will be on June 28, but the specifics have not yet been finalized.
"We see WeWork Labs as a platform for creators, innovators and makers alike, and believe partnering with Glowforge and Formlabs will give our members even more of an opportunity to take their ideas, and bring them to life," says Katie Perkins, creative director at WeWork Labs, in the release. "We are incredibly excited to welcome two leading brands and their products into our community, giving creators access to the tools they need and inspiring new creators to be makers themselves."
Houston's WeWork Labs program launched in March in the WeWork Jones Building at 708 Main St. and includes a partnership with local digital startup resource, Alice. The WeWork Labs program started a little over a year ago and is already in over 30 markets worldwide.
"As the fourth largest city, Houston is in a unique position to launch high-impact startups," says Houston Labs Manager Carlos Estrada, in a previous release. "We see WeWork Labs in Houston as a tremendous platform for innovation, as our founder-focused approach to supporting early-stage startups will nurture and accelerate the work of entrepreneurs to scale their solutions to today's biggest challenges."



 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.

