Brittany Barreto was years ahead of the marketplace when she had her idea for a DNA-based dating app, now called Pheramor. At the time, online dating mostly consisted of eHarmony and sending your DNA through the mail to anyone just wasn't done.
"I had the idea at 18 — almost 10 years ago — and, at that time, 23AndMe was shut down because the FDA wasn't comfortable with it," Barreto says. "But then in 2016, everyone is using dating apps and everyone is sending their spit in the mail. It was a perfect time to introduce a techy way to find love."
Even better, now Pheramor's potential users have swiping fatigue, Barreto says, and are going on chronically bad first dates. For Pheramor, this provided an opportunity, and Barreto took it.
Since its nation-wide launch in September, Pheramor has seen over 5000 messages sent on the app, resulting in 19 happy couples to date. Pheramor has even been nominated for Best New Dating App by iDate, an international conference where Barreto recently gave a keynote speech.
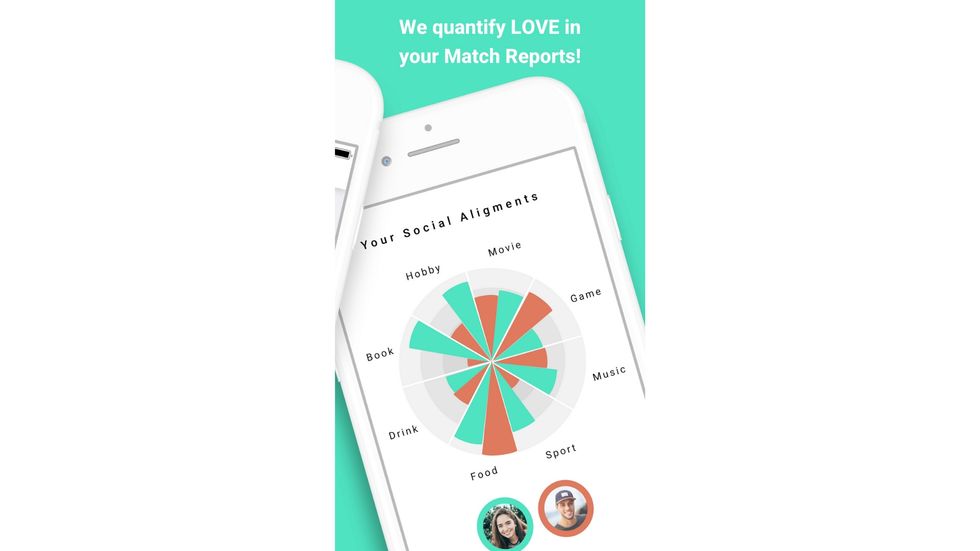
Pheramor works like any other dating app — except instead of swiping through endless possibilities, you see your estimated compatibility with each person based on DNA and interests that are either data mined off your social media or you manually plug into the app. Users first download the app, create an account, and request a kit.
While the B-to-C side of things has been a great approach for Pheramor, the technology has attracted interest from other dating apps. Barreto says she looks to expand into B-to-B opportunities where establishing dating companies can use her technology across the world. She made this clear in here iDate keynote address.
"I said there that if you want to factor in DNA to your dating app, you come to us. We are a B-to-C dating app, but we can also offer our genetic testing services for your platform," she says. "We have a letter of intent with a dating app in Russia. We're speaking with high-end matchmakers."
Barreto sat down with InnovationMap to discuss Pheramor's origins and what she has up her sleeves.
InnovationMap: When did you first have the idea for Pheramor?
Brittany Barreto: I first had the idea when I was 18 at Drew University, where I did my undergraduate research in New Jersey. We were in a genetics seminar, and we were learning about genetic-based human attraction — essentially how scientists for decades can predict who's attracted to whom because of your DNA. I raised my hand and asked if I could make a gene-harmony because of this. The professor and the class kind of laughed, but I said, "No, I'm serious, could I use this science for dating?" The professor said, "I mean, I guess you could." So I thought, one day I'll make gene-harmony.
IM: How did you get involved in the Houston innovation scene?
BB: I finished college and came down here to Houston to get my PhD at Baylor College of Medicine, and I just always had this idea, and I kept thinking about it. When I was working on my PhD, I realized I just had way too much personality to work in a lab my whole life. I started taking some entrepreneurship classes and networking at startup events thinking that I could land a career at a biotech company doing sales or innovation. All of the sudden, people started telling me that I had the founder blood, and I thought well I only have one really crazy idea for a DNA-based dating app, and people told me it was a good idea.
IM: What was your first move launching the company?
BB: I joined an accelerator in the medical center through Enventure. They have about 2,000 members — a lot of PHDs and grad students with a lot of great ideas who have no clue how to start a company. So, Enventure puts on evening classes for free, networking events, brainstorming sessions, and the accelerator. I pitched my idea, and got accepted. That's where I found my co-founder Bin Huang. Between January and March of 2017 we were in the accelerator every Thursday.
IM: How did you first get funding?
BB: We did our Demo Day in March at TMCx, and we won. A few angel investors came up to us after words with the idea for an open round, and Bin and I realized this wasn't a class project any more. This was real. We closed our first round of funding in July of 2017, while Bin and I were full-time students. We met our goal, and then we had another round of funding that was oversubscribed.
IM: When did you start accepting swabs and daters?
BB: Our first swab actually came from a swab party I had at my apartment. I invited about 50 friends over, and we had a party. We had a swab station set up in my bedroom and people waited in line in the hallway. That was our first 50 swabs. It was in the spring of 2017, right after our Demo Day.
IM: So, how does Pheramor work?
BB: The science behind attraction based on your DNA is that people are attracted to one another when their immune systems are different — opposites attract is biologically true. This is what all of the animal kingdom does. When we were cavewomen and cavemen, we didn't know who was our uncle and who was our cousin, so we used our nose to figure out who is genetically diverse compared to us, and if you're genetically diverse, then you're probably not my relative, and therefore we'd have healthier children. So, that's the baseline of attraction. We have these HLA genes that make up our immune system, and your pheromones are giving off essentially like a fingerprint of what your immune system is.
At Pheramor, we look at those 11 genes of attraction — we don't look at anything else. Some people might be concerned that I'll know their ancestry or their diseases and sell their data, but we don't look at that. I actually don't even know your gender based on the swab.
My co-founder and I have written this machine-learning algorithm that looks at the genes and figures out quantitatively how likely it is for you to have physical chemistry with one another. Then, in the app, you can have a score and match report to see that.
IM: What were some of the early challenges?
BB: The biggest one when I was 18 was that the market wasn't ready. I called it "geneharmony" because eHarmony and Match were the only players in the game back then. Also, sending your spit in the mail was really weird. It's not so weird any more.
The next one was being a PhD student working in a field that expects everyone to go into academia. There's not enough academic jobs for scientists anymore. We have to start branching out — work in biotech, become consultants, work in other industries. But the issue is there's an old guard in academia. I had a mentor — a woman I worked for — who had only ever trained academics and thinks that that's what scientists do. So, I didn't experience a lot of support in school for starting a company. It's super cool and I'm successful, and it gives Baylor College of Medicine a great name, but when I was in there, I kept Pheramor a secret. I had to essentially sneak around to do it. Get to the lab really early in the mornings to start experiments so I could leave early for investor meetings or hide in the storage closet to make calls to investors.That was definitely difficult.
Another challenge was starting to pitch and being called the "student team." Right off the bat, they felt like they were doing us a favor for letting us pitch. It was cute. So, I had to start doing some strategies to make my company seem more valuable because I was going uphill. I would wear a lab coat and if any other scientist wore a lab coat to a presentation with scientists, it would be weird, but no investor ever asked me why I was in a lab coat.
IM: A year and a half later since your first swab party, how have things changed?
BB: It's funny, I was just thinking a while back about having a Halloween party and thinking, "we could swab people!" So, I'm not above swab parties. For most of 2017, we did a lot of grassroots efforts. We were at Pride Festival, swab parties at bars, Day For Night — some were successful, and others were a waste of money. It was a science of figuring out what works. There's so much education we have — what the swab is, how it works, etc. In person, we got to explain all that and hear what their questions were and take that and turn it into a FAQ section on our site.
IM: Where can people use your app?
BB: We're nationwide. We're actually downloaded in every state in the country. We did what the market told us to. One day I came into the office and asked my co-founder why we wanted to only be in Houston. He told me that people want to date other daters. And I asked him if we knew that or if we just think that. We never actually asked them. So, we surveyed our user base and asked them if they had highly compatible numbers with someone in, say, Chicago, would they want to know. And something like 89 percent said yes. We realized that our consumers are 28- to 38-year-old singles seeking commitment. They are highly educated and have really great paying jobs, and they travel a lot anyways. So, we opened it up on September 7, and in 30 days we saw over 50 percent growth in our user base.
IM: Are you marketing in specific metros?
BB: At first, we did a blanket marketing effort. Then, we looked into which cities had the lowest CAD — the cost to acquire a download. New York City and Boston are the cheapest. San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Miami are also cheaper than Houston.
IM: What are some goals for you and Pheramor?
BB: Short term, it's to continue to improve our app. We're slowly building it in response to what consumer feedback says. I also want to build our team. With the next round of funding, that's what I'm focused on. Our CMO and CFO are part time, and I want them full time. I also want to be hitting critical mass in Boston, New York, LA, Miami. We have a few hundred people in each of those cities, but I want to make those to be a really healthy number.
And something the market has asked for a lot is testing for couples. So, we have a we a website that's about to launch called "WeHaveChemistry.com" for couples to buy two kits and receive a report.
As an academic in genetics, I had to take a lot of ethics classes — for good reason. We've really taken a stance here at Pheramor saying that we will only use genetic data for good. We do not sell our data to anyone, except one organization with the user's consent. The organization is Gift of Life, a national bone marrow registry. The genes for attraction are also genes that fight leukemia and lymphoma. To register to be a bone marrow donor, you have to get your cheek swabbed and you have to get your HLA genes typed. That's what we're doing as a dating app. So through our app, you can consent to be a donor. That to me is how you could use data for good. We're finding people love, and we're finding a girl with leukemia a bone marrow donor.
------
Portions of this interview have been edited.