Answering ethical questions posed by the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The fourth industrial revolution is upon us. Also known as "Industry 4.0" or "4IR," it takes the technological advances of the third industrial revolution and connects them into systems that can often operate and adapt without human input. New technologies can create exciting possibilities for positive social impact on diverse issues such as income inequality and the environment.
Yet, at the same time, they often raise new, sometimes difficult, ethical questions. In fact, the irony is this: As we develop technologies that adapt without human input, we are discovering we need human input to address what constitutes the ethical use of these technologies.
As mentioned in a Deloitte article, most leaders want their organizations to create social impact. In today's competitive business environment, social impact initiatives have the ability to separate one company from its competitors in the eyes of consumers. The logic that a company "does well by doing good" has taken hold. And 4IR technologies promise to support companies' efforts to reduce carbon emissions, support diversity initiatives, and other social impact goals.
Yet some leaders are also recognizing that 4IR technologies raise ethical questions in areas such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and potentially a lack of inclusivity in technology design.
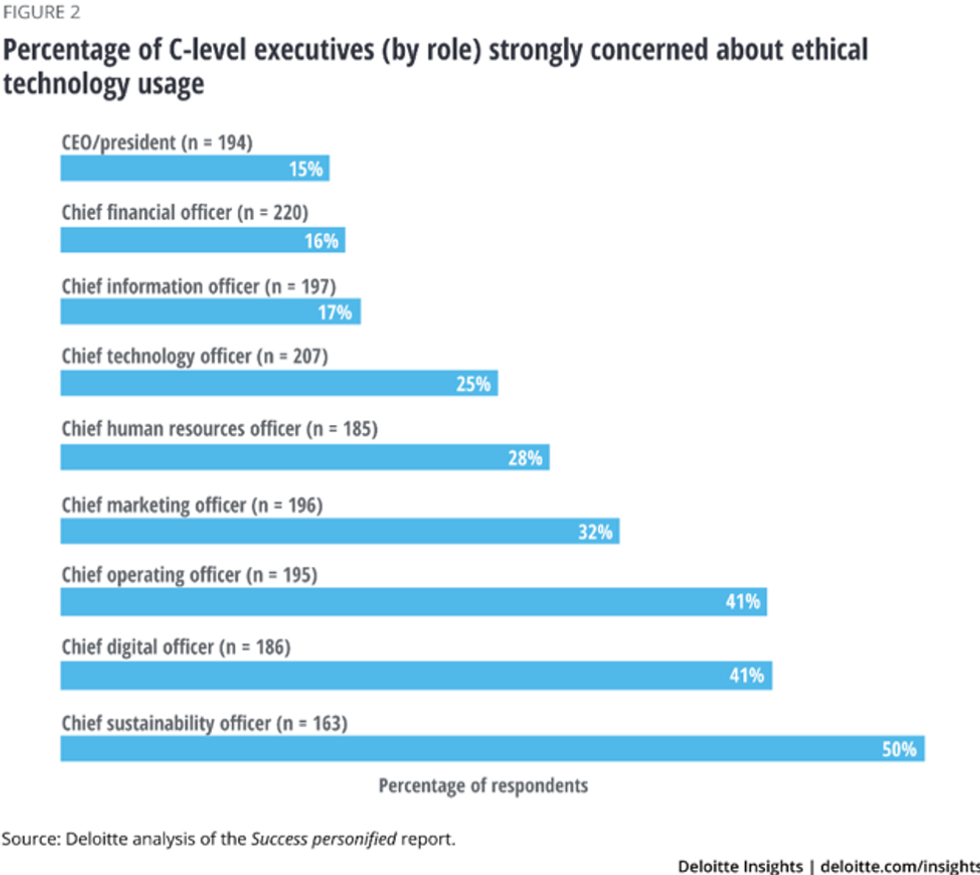
According to Deloitte Global CEO Punit Renjen's report, "Success Personified in the Fourth Industrial Revolution," which is based on a Forbes Insights survey, C-suite executives have varying levels of concern about using technology ethically. From June-August 2018, Forbes Insights surveyed 2,042 executives (with company revenue of $1 billion or more) and public sector leaders (with organization budgets of $500 million or more) from 19 countries and all major industry sectors.
As shown in Figure 2 below, only 15 percent of the 194 CEOs/presidents surveyed are strongly concerned about ethical technology use. Surprisingly, chief information officers and chief technology officers are also at the lower end of the spectrum, at 16 percent and 17 percent, respectively. On the other hand, 41 percent of chief operating officers, 41 percent of chief digital officers, and 50 percent of chief sustainability officers are strongly concerned about ethical technology use.
This disparity in levels of concern about ethical technology use at the top of the organization often results in lack of clarity throughout the rest of the organization. Deloitte offers three recommendations to address this:
- 1. C-Suite adoption: The CEO must prioritize ethical technology use and encourage the rest of the C-suite to do so too.
- 2. Culture change: The C-suite must set, model, and communicate ethical use of technology and encourage buy-in from employees by allowing them to share ideas about ethical technology use.
- 3. Adapt: As technology continues to change, companies must continue to define how to use it ethically.
Ethics are important in and of themselves. However, there may also be business benefits for prioritizing ethical use of technology.
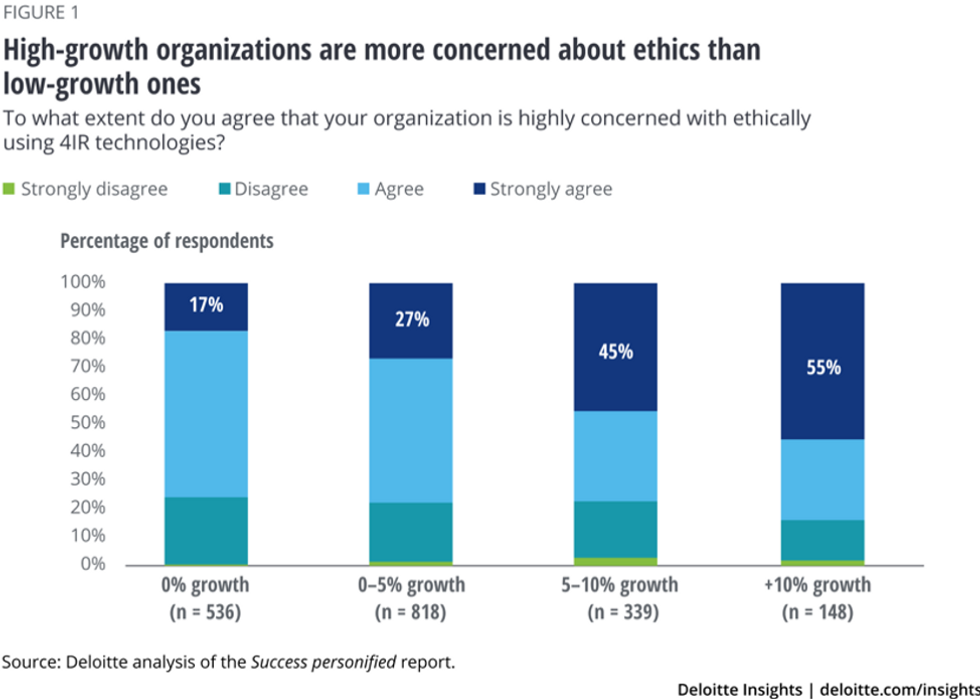
As shown in Figure 1 below, Deloitte's analysis of the Success Personified report found a correlation between high concern for ethical use of 4IR technologies and business growth. Of the 536 respondents whose organizations had 0 percent growth, only 17 percent of them strongly agreed that their organization is highly concerned with ethically using 4IR technologies.
On the other hand, of the 148 respondents whose organizations had 10 percent or more growth, 55 percent of them strongly agreed that their organization is highly concerned with ethically using 4IR technologies.
As more companies aim to make a social impact, C-suite leaders should consider the ethics of 4IR technology implementation to grow as a business and stand out among competitors.
---
This publication contains general information only and Deloitte is not, by means of this publication, rendering accounting, business, financial, investment, legal, tax, or other professional advice or services. This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services, nor should it be used as a basis for any decision or action that may affect your business. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your business, you should consult a qualified professional advisor. Deloitte shall not be responsible for any loss sustained by any person who relies on this publication.
About Deloitte
Deloitte refers to one or more of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, a UK private company limited by guarantee ("DTTL"), its network of member firms, and their related entities. DTTL and each of its member firms are legally separate and independent entities. DTTL (also referred to as "Deloitte Global") does not provide services to clients. In the United States, Deloitte refers to one or more of the US member firms of DTTL, their related entities that operate using the "Deloitte" name in the United States and their respective affiliates. Certain services may not be available to attest clients under the rules and regulations of public accounting. Please see www.deloitte.com/about to learn more about our global network of member firms.