New technology is helping Houston companies reimagine a socially distant workspace
feng shui
The COVID-19 pandemic has displaced many Houstonians from their office jobs to makeshift work-from-home setups. With coronavirus cases climbing in Houston, the obstacle of returning to work safely is undoubtedly on the minds of business owners across the city.
Thankfully, there's an algorithm for that. Gensler, a global architecture firm, has unveiled its ReRun program as a pandemic response tool to help offices create workspace layouts for safe social distancing.
ReRun allows Gensler to upload a floorplan into the program, which applies generative algorithms to determine safe separation between workplaces by creating circles ranging from six to eight-foot diameters. The tool can quickly generate scenarios and identify the most optimized capacity to meet social distancing demands, easing the role of operations and human resources.
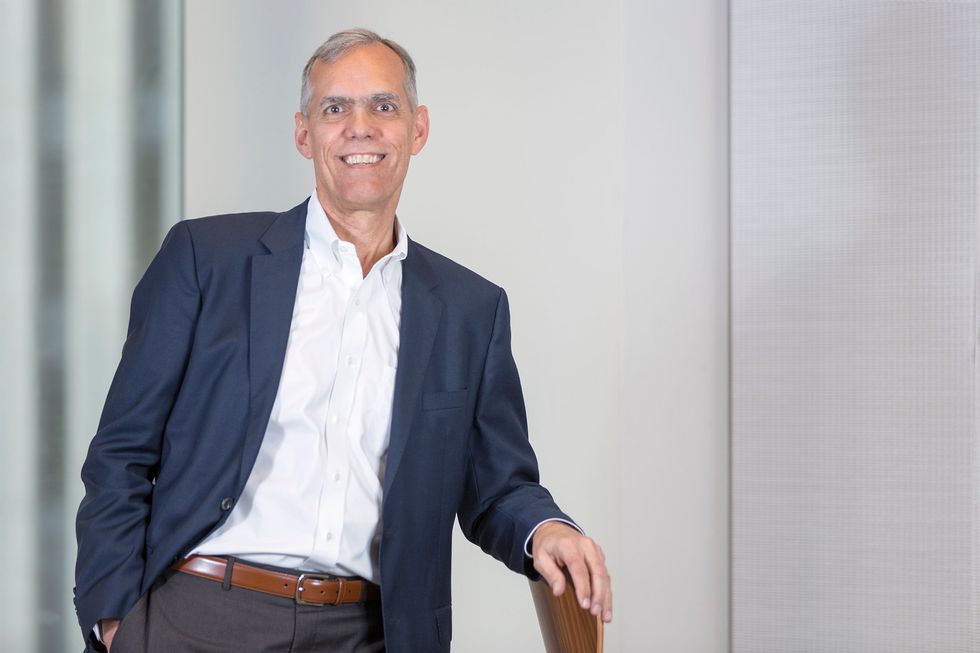
"It's really just a tip of the spear in terms of occupancy planning, because once you know that information, then the next question is what do I do with that?" says Dean Strombom, strategy lead and principal at Gensler's Houston office.
"ReRun is the first tool we utilize to help [clients] determine how many people might be able to come back and still achieve the social distancing side. Then we work with them on how they should come back, whether it's a percentage of employees, staggered shift work or alternating days," Strombom says. Circulation patterns are also taken into account by the Gensler team, who analyze the traffic of hallways, meeting spaces and lounge areas.

The international firm, with 50 offices around the world, has rolled out the ReRun tool to its database of clientele. The platform is also available to businesses outside of the firm's existing portfolio, who can use the tool by providing a simple CAD design of their workplace. ReRun is applied through the company's SaaS space management software, Wisp. Using occupancy planning, Wisp provides clients with color-coded floor plans to help visualize and communicate to their teams which seats are available or assigned for occupancy as employees phase back into the office.
The response has been positive among clientele. Strombom is currently applying Gensler's social distancing tool with a large financial services company with locations throughout the Houston area.
"We are loading the information from ReRun into the Wisp program, and then we'll be helping them determine how they will return to work, and specifically where people will sit," he shares. The company plans to come back with 20 percent of the workforce, increasing overtime with the help of Gensler's team. "Who comes back when and specifically where is what they're most excited about."
The company has determined four work modes employees exhibit: focus, collaboration, socialization, and learning. By categorizing the work modes, Gensler is looking ahead at how interior architecture can accommodate these phases.
"More recently, we've been talking about a need for regenerative spaces so that people can become more engaged in the workplace," says Strombom.
As described in a Gensler blog, isolation rooms were optioned as a way to contain an employee who begins to feel symptomatic but these rooms can also serve a different purpose for employees acclimating to a new normal.
"The isolation room is what we often call a wellness room in an office where people can get away from the general tensions that they may be feeling in a workplace where they can relax and reinvigorate themselves in a quiet space," says Strombom.
As the architecture industry adjusts to a post-pandemic world, Gensler is working with developer clients and building owners to share the near-term and long-term changes the company foresees. Strombom says clients have flexibility as a priority.
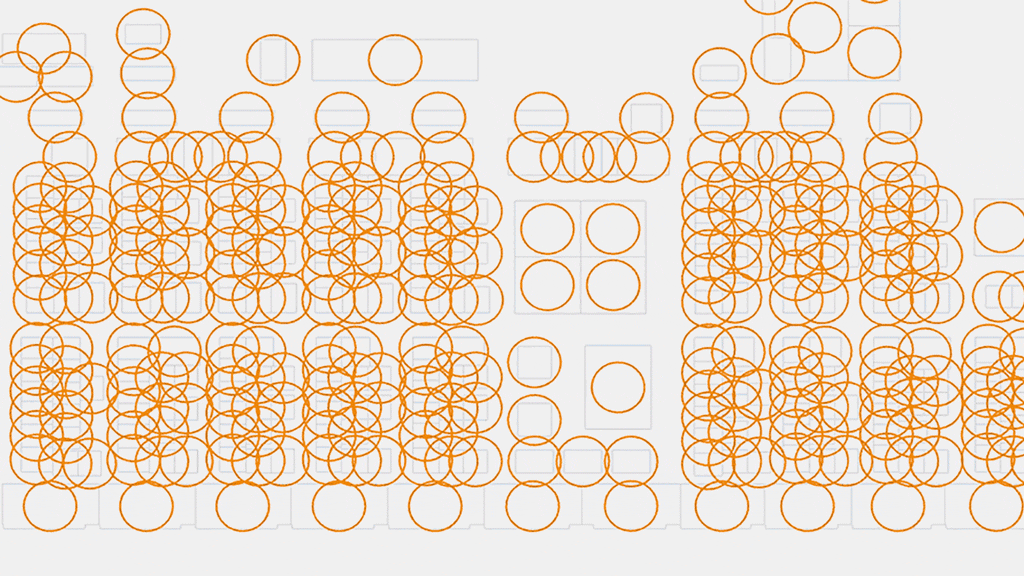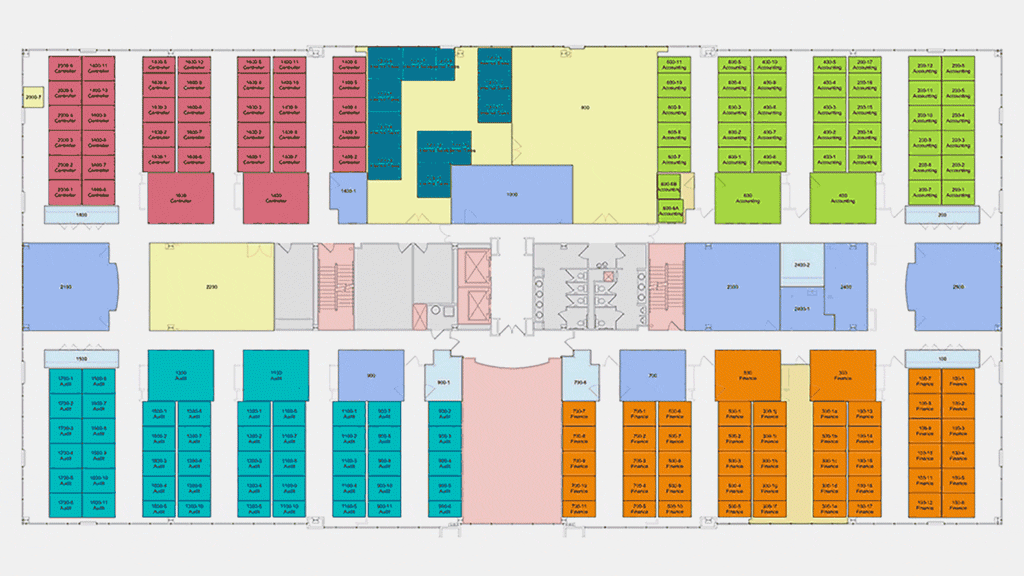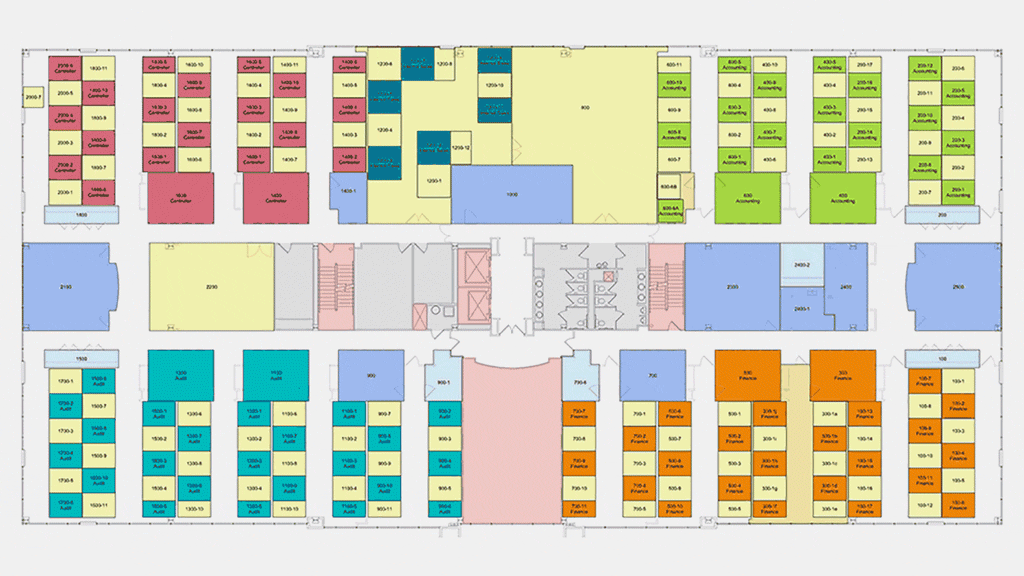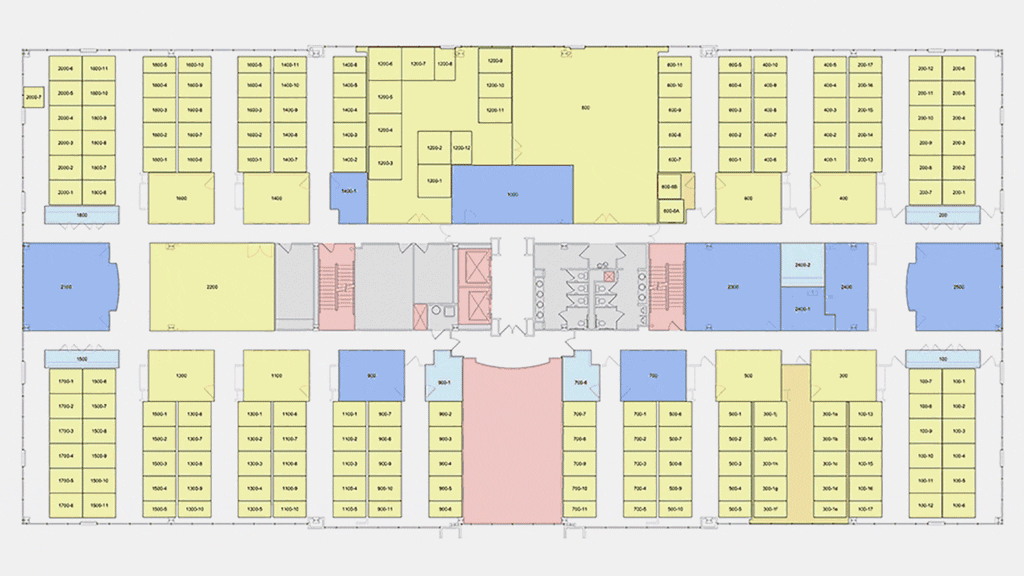
"We have to think about the entire path or the entire entry sequence in office buildings that is true for residential as well. From the moment that you pull into the garage, what are all of those points along the way where you've got to be concerned about contact and cleanliness?" Strombom shares.
Strombom foresees new building systems coming to the forefront, for example air conditioners with a focus on keeping clean air circulation within the office building. He also predicts a need for flexible spaces that can change depending on the circumstances.
"You hear a lot about temperature readings and separations of people within building lobbies during pandemics. We need systems in place that you can rapidly deploy when something like this happens, but the majority of the time it can revert to a more normal circumstance," he says.
Tight spaces also require a new way of thinking.
"We've realized that the elevator cab is really one of the pinch points in office buildings if you're trying to maintain this social distancing," Strombom shares. "There's technology [out there] that can identify how many people are going to be entering a cab and restrict that occupancy. So that is something that's going to need to be done for the near term."
In a Gensler survey of its Houston office, 72 percent of respondents expect a maintained or increased level of virtual collaboration compared to these pre-COVID levels.
"As people have been semi-forced to work at home, they've realized that not only is it possible, but for some people it's the preferred way to work," says Strombom, who predicts virtual meetings will continue on.
While platforms like Zoom and Skype make meetings tenable, company employees are still anticipating a future in the office.
"Those of us that are now working from home, if you ask people the majority of respondents to the question of what they miss most, it's really the people," Strombom says.



 Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.
Apple doubles down on Houston with new production facility, training centerPhoto courtesy Apple.

