These are 4 medical innovations coming out of Houston institutions
Research roundup
Houston — home to one of the largest medical centers in the world — isn't a stranger when it comes to medical innovations and breakthrough research discoveries.
In the latest roundup of research innovations, four Houston institutions are working on innovative and — in some cases — life-saving research projects.
Houston Methodist study observes that strep throat germ is becoming resistant to antibiotics
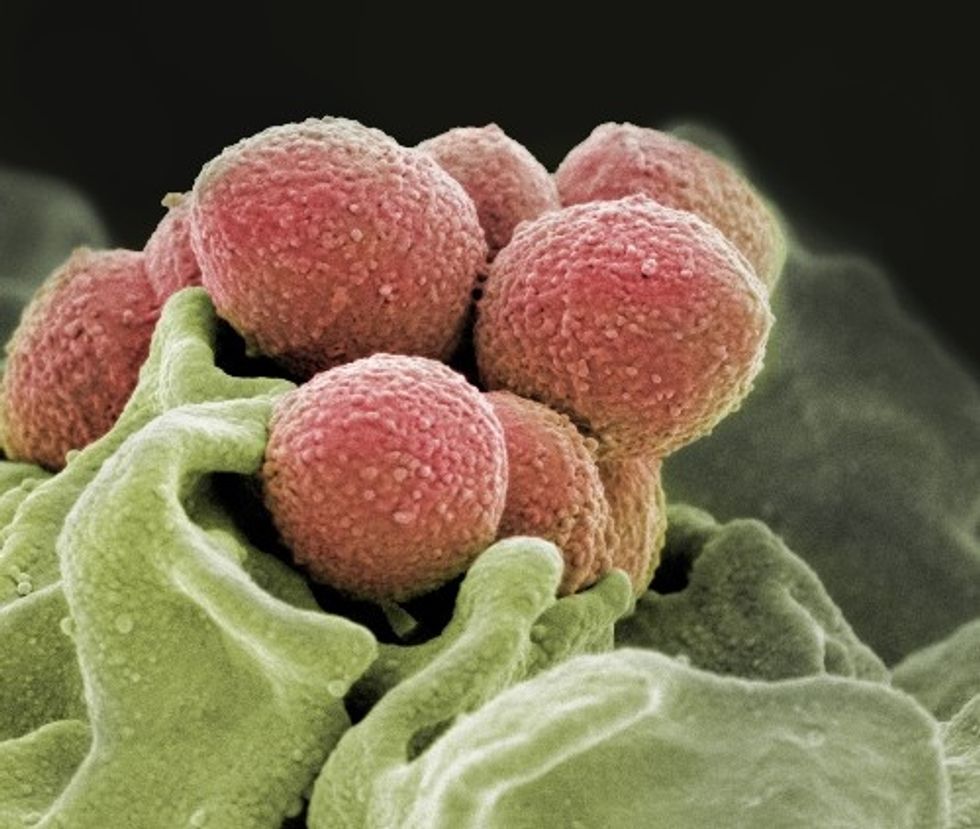
If the germ, group A streptococcus, continues to grow resistant to antibiotics, it can have a profoundly negative affect on the millions who get the illness annually. Photo via houstonmethodist.org
Researchers at Houston Methodist have discovered some troubling information about the strains of group A streptococcus that cause strep throat and a flesh-eating disease are becoming more resistant to beta-lactams antibiotics like penicillin.
James M. Musser is the lead author of the study and chair of Methodist's Department of Pathology and Genomic Medicine. The study — which received funding from grants from the Fondren Foundation, Houston Methodist Hospital and Houston Methodist Research Institute, and the National Institutes of Health — appeared in the Jan. 29 issue of the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, according to a news release.
"If this germ becomes truly resistant to these antibiotics, it would have a very serious impact on millions of children around the world," Musser says in the release. "That is a very concerning but plausible notion based on our findings. Development of resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics would have a major public health impact globally."
Musser and his team found 7,025 group A streptococcus strains that have been recorded around the world over the past several decades. Of those strains, 2 percent had gene mutations that raised the alarm for the researchers and, upon investigation, Musser's team came to the conclusion that antibiotic treatments can eventually be less effective — or even completely ineffective. This, Musser says, calls for an urgent need to develop a vaccine.
"We could be looking at a worldwide public health infectious disease problem," says Musser in the release. "When strep throat doesn't respond to frontline antibiotics such as penicillin, physicians must start prescribing second-line therapies, which may not be as effective against this organism."
University of Houston professor is searching for a way to stop persistent cells that cause chronic infections
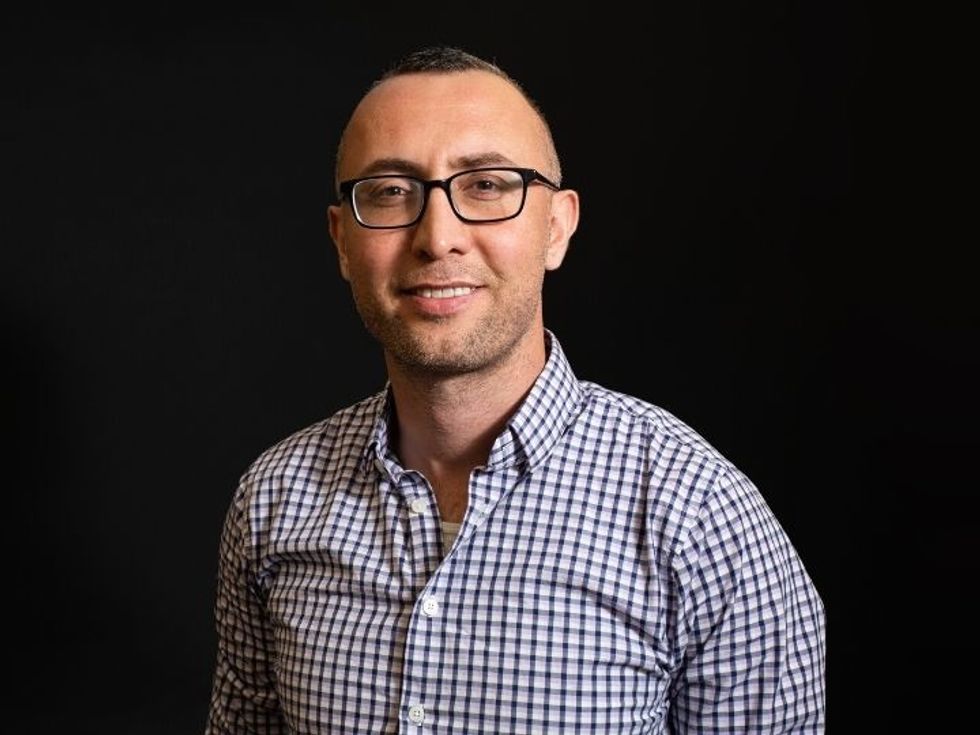

University of Houston Professor Mehmet Orman is looking into cells that are able to persist and cause chronic illnesses. Photo via uh.edu
Mehmet Orman, assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at the University of Houston, is looking into a specific type of persister cells that have been found to be stubborn and drug-resistant.
The research, which is backed by a $1.9 million grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, could answer questions about chronic health issues like airway infections in cystic fibrosis patients, urinary tract infections, and tuberculosis, according to a news release.
"If we know how persister cells are formed, we can target their formation mechanisms to eliminate these dangerous cell types," says Orman in a news release.
Orman is looking into cells' self-digestion, or autophagy, process that is found to stimulate persister formation. Per the release, cells can survive periods of starvation by eating their own elements. Specifically, Orman will analyze self-digestion in E. coli.
"By integrating our expertise in bacterial cell biology with advanced current technologies, we aim to decipher the key components of this pathway to provide a clear and much-needed picture of bacterial self-digestion mechanisms," says Orman in the release.
Baylor College of Medicine is working to understand and prevent post-op kidney failure
 operation
operationSome patients are predisposed to kidney injury following surgery, this study found. Photo via bcm.edu
Scientists at Baylor College of Medicine are looking into the lead cause of kidney failure in patients who undergo surgery. Individuals who have heightened levels of suPAR protein — soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor — have a greater risk of this post-op complication, according to a news release.
"suPAR is a circulating protein that is released by inflammatory cells in the bone marrow and produced by a number of cell/organs in the body," says Dr. David Sheikh-Hamad, professor of medicine – nephrology at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating author of the study, in the release.
The study, which was published in The New England Journal of Medicine, conducted research on mice that were engineered to hive high suPAR levels in their blood. Compared to the control mice, the suPAR mice had more risk of kidney industry. These mice were given suPAR-blocking antibodies, which then helped reduce kidney injury.
"This protective strategy may be used in humans expressing high suPAR levels prior to contrast exposure, or surgery to decrease the likelihood of developing kidney failure," Sheikh-Hamad says in the release.
Rice University research finds expressing emotions during mourning is healthier
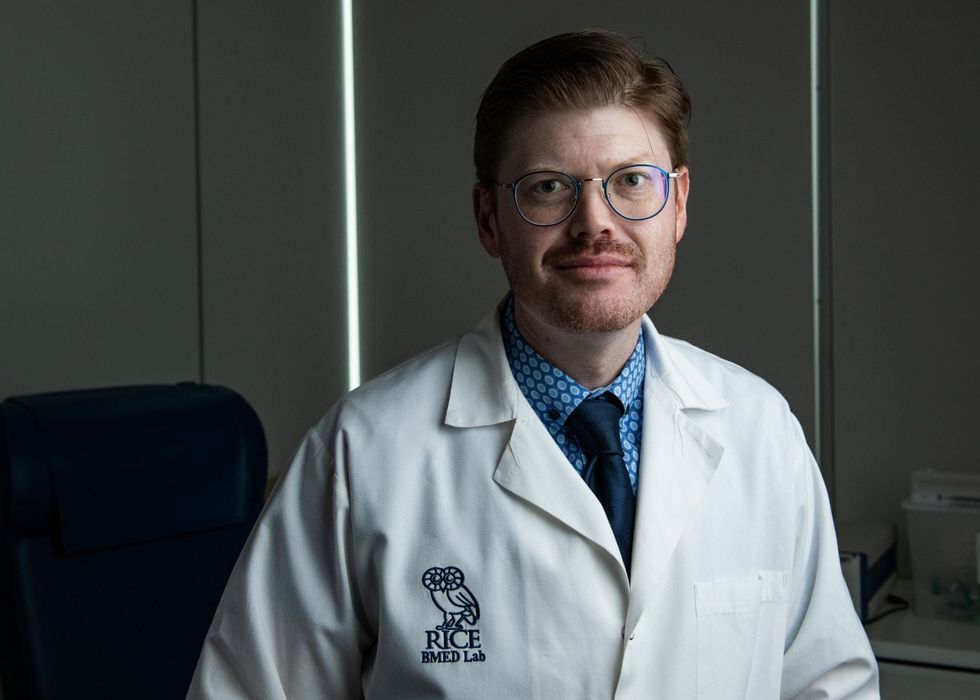

Christopher Fagundes of Rice University analyzed the emotions of 99 widows and widowers. Jeff Fitlow/Rice University
A new study done by researchers at Rice University finds that spouses that lose their husband or wife and try to suppress their grief are not doing themselves any favors. The study monitored 99 people who had recently lost a spouse, according to a news release.
"There has been work focused on the link between emotion regulation and health after romantic breakups, which shows that distracting oneself from thoughts of the loss may be helpful," says Christopher Fagundes, an associate professor of psychology and the principal investigator, in a news release. "However, the death of a spouse is a very different experience because neither person initiated the separation or can attempt to repair the relationship."
The study included asking participants to respond to how they felt about certain coping strategies, as well as blood tests to measure cytokines levels‚ an inflammatory marker.
"Bodily inflammation is linked to a host of negative health conditions, including serious cardiovascular issues like stroke and heart attack," Fagundes says in the release.
The research, which was funded by a grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, found that the participants who avoided their emotions suffered more of this bodily inflammation.
"The research also suggests that not all coping strategies are created equal, and that some strategies can backfire and have harmful effects, especially in populations experiencing particularly intense emotions in the face of significant life stressors, such as losing a loved one," adss Richard Lopez, an assistant professor of psychology at Bard College and lead author of the study, in the release.

