University of Houston receives funding to support diverse cardiovascular researchers
pumping up innovation
University of Houston professors have received a nearly $800,000 grant to create a new summer program that will support diverse future researchers.
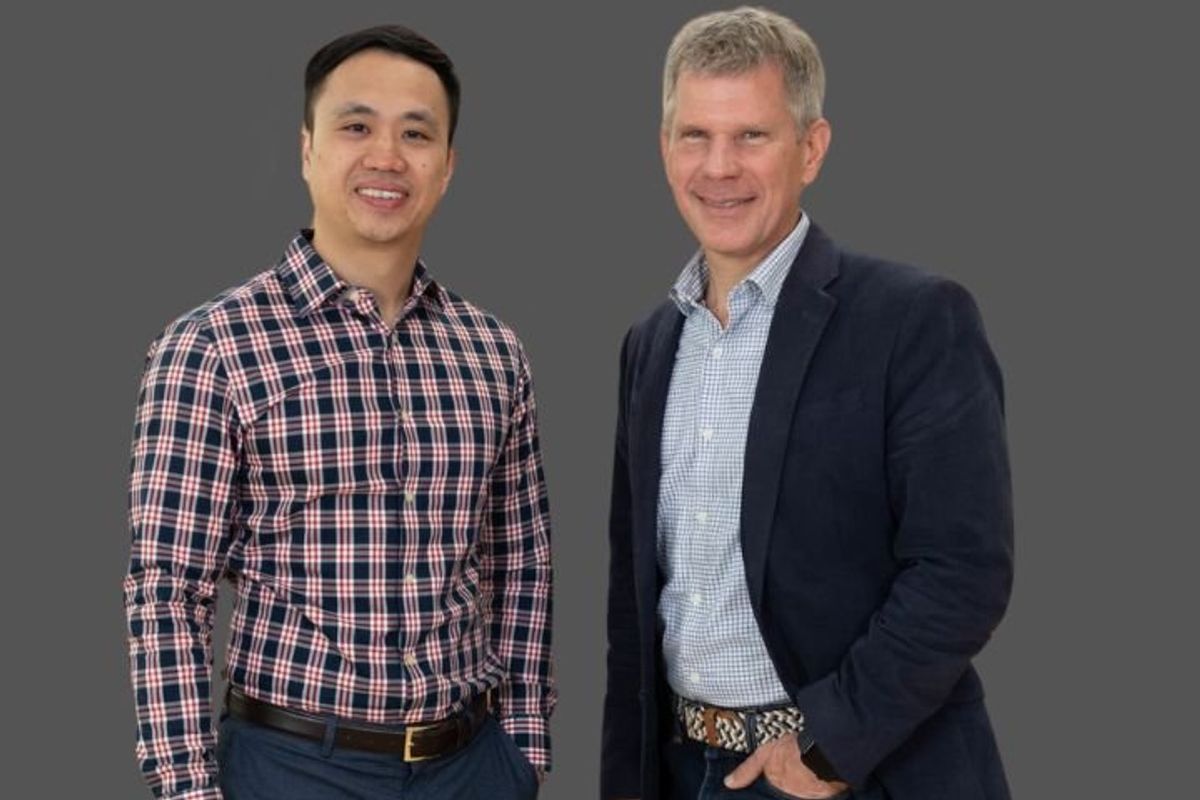
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute provided $792,900 in grant funding to Bradley McConnell, professor of pharmacology at the UH College of Pharmacy, and Tho Tran, research assistant professor of chemistry at the UH College of Natural Sciences and Mathematics.
The funding will go toward created a summer program called the University of Houston Cardiovascular Undergraduate Research Experience, or UH-CURE. Ten undergraduate students per year will be selected for five years in cardiovascular research across disciplinary lines.
"We are so grateful to be able to provide talented students across the U.S. an opportunity to experience our excellent cardiovascular research environment,” Tran says in a news release. “We want UH-CURE participants to gain confidence in their research abilities through our hands-on approach and the skillset to navigate future challenges through our professional training.”
The goal is to increase students’ interest in cardiovascular research, and students have the opportunity to receive a $6,000 stipend, travel to a globally recognized cardiovascular research conference, and take part in on-campus housing and a food allowance. The summer program will also try to develop research skills, increase awareness of transdisciplinary research, promote diversity and collaborations, cultivate transferable skills necessary for succeeding in graduate school and help facilitate undergraduate students to pursue further training in cardiovascular research.
The program will integrate students into a research lab where they will learn research skills, data analysis, and research integrity. The program will be under the mentorship of a faculty member from across UH’s colleges, and include workshop and enrichment activities.
McConnell and Tran previously formed the American Heart Association-funded UH-HEART pilot program, which focused on cardiovascular research. They expanded on that initiative with UH-CURE, which includes cardiovascular research across disciplinary lines from community engagement and population-based research to basic, translational, and applied research. UH-CURE also helps prepare for careers in cardiovascular research.
“We all know that a diverse environment leads to a much better generation of ideas and solutions,” Tran adds. “We hope to bring that strength to the future of cardiovascular research through our students.”