University of Houston researchers studying COVID-19 prevention and treatment
research roundup
Researchers across the country are focusing on all things COVID-19 — from biotherapies and treatment to vaccines and prevention. A handful of researchers based out of the University of Houston are doing their best to move the needle on a cure or reliable vaccine.
Here are three research projects currently ongoing at UH.
UH pharmacy professors take it back to basics
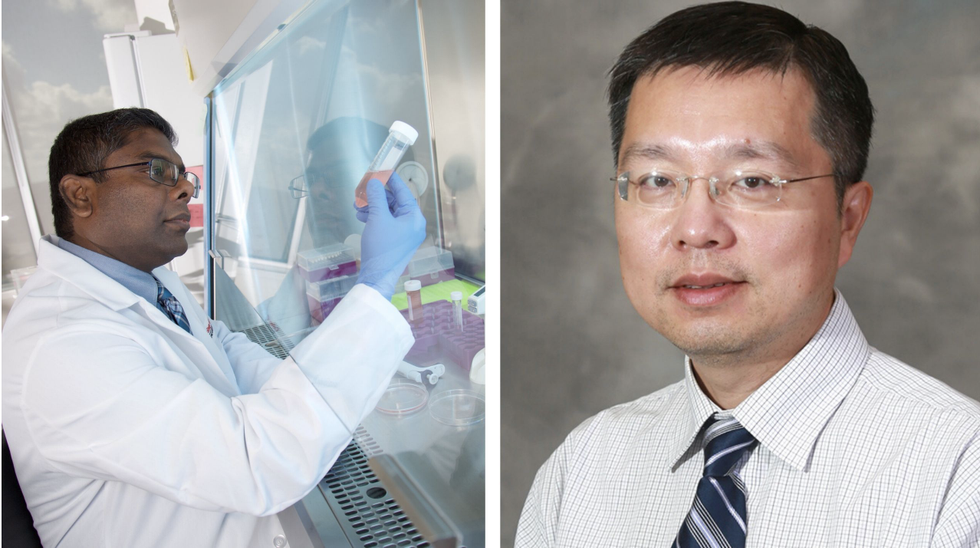
UH College of Pharmacy professors Gomika Udugamasooriya (left) and Bin Guo are studying how the virus enters the human body. Photo via uh.edu
When thinking about how to prevent the spread of COVID-19, two UH pharmacy professors are looking at how the virus enters the body. Then, this information can help develop protection of that entry point.
"The human entry of coronaviruses depends on first binding of the viral spike proteins to human cellular receptors that basically offer a cellular doorknob," says Gomika Udugamasooriya, associate professor of pharmacological and pharmaceutical sciences, in a press release. "The virus latches onto the specific human cellular receptor, ACE2, and sneaks inside to replicate itself within the cell to spread throughout the body."
Now, the goal of new drugs and vaccines is to protect that ACE2. Udugamasooriya is working with Bin Guo, associate professor of pharmaceutics, on this research, which is in the initial screening levels and identified drug-lead validations. They are working to apply their unique cell-screening technology to identify specific synthetic chemical drug leads called peptoids that can bind to ACE2 receptor, according to the release.
"Peptoids are easier to make, compatible with biological systems and economical to produce," says Udugamasooriya.
Duo aims to create inhalation vaccine for COVID-19
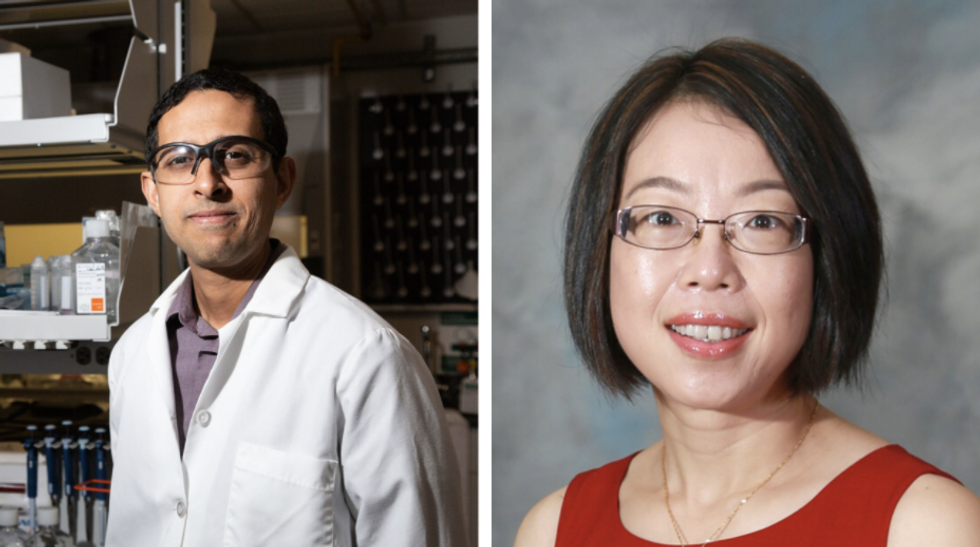
Navin Varadarajan, UH engineering professor (left), and pharmaceutics professor Xinli Liu, pharmaceutics professor, are collaborating on development and testing of a COVID-19 inhalation vaccine. Photo via uh.edu
If the disease itself is airborne, can't the vaccine be too? That's what M.D. Anderson Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Navin Varadarajan looking into.
"For airborne pathogens, the nasal mucosa is the first point of defense that needs to be breached," says Varadarajan in a news release. "Mucosal immunity and vaccines are fundamentally important for a wide range of pathogens including influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the current SARS-CoV-2."
Varadarajan is focusing on the spike protein to protect at virus entry. These proteins are known for building strong immune responses, flexibility and scalability, and absence of infectious particles. He is working with Xinli Liu, associate professor of pharmaceutics.
"As with any vaccine, a variety of factors determine their efficacy including the antigen used for electing a response, the adjuvants and immunomodulators, the efficient delivery of the antigen to appropriate target cells, and the route of vaccination," Varadarajan says.
The man with three different vaccine options
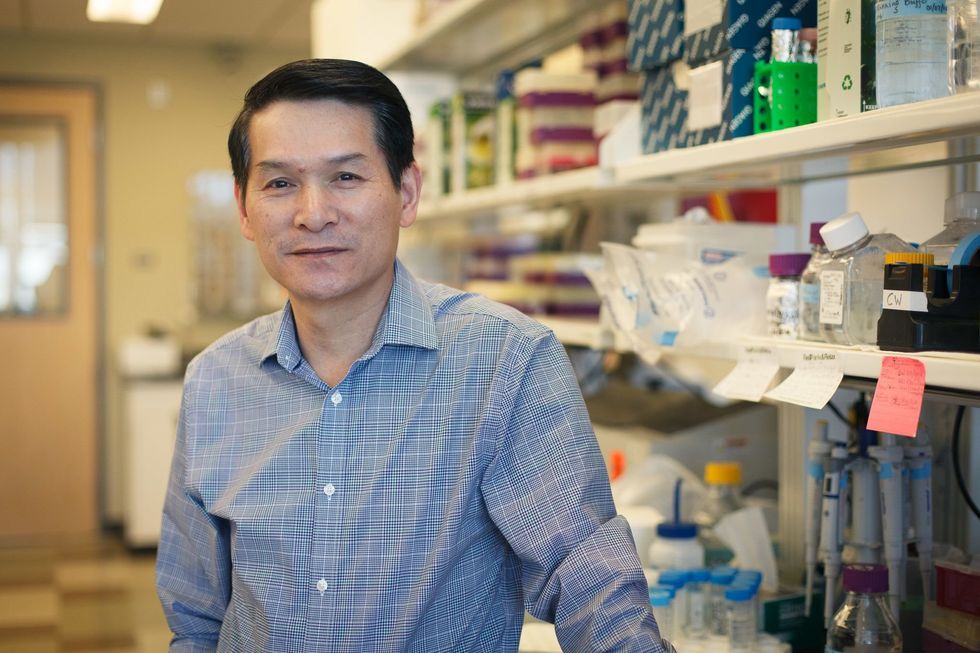

UH Professor Shaun Zhang is in the process of developing three COVID-19 vaccine candidates for injection. Photo via uh.edu
Shaun Zhang, director for the Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling, usually works on developing treatment or vaccines for cancer and viral infection. Now, he's switched gears to work on three different vaccine candidates for COVID-19.
"The data collected from our studies show that our vaccine candidates can generate neutralizing antibodies, which can protect cells from infection by SARS-CoV-2 when tested in vitro," says Zhang in a press release. "We are now working on further improvement for the vaccine design."
Zhang's approach is neutralizing antibody production, and he's tapped into using "subunit vaccine containing either the entire spike protein or the receptor binding portion, which helps the virus enter the target cell, and delivered either by DNA formulation or by a herpes simplex virus-based vector," according to the release. Low cost and simplicity are two priorities for Zhang's work.
