California B2B medical care concept enters Houston market with HP Inc. already signed on as a client
One-stop shop
Information technology provider HP Inc. and other major employers in the Houston area are exploring a new way to offer medical care to their employees.
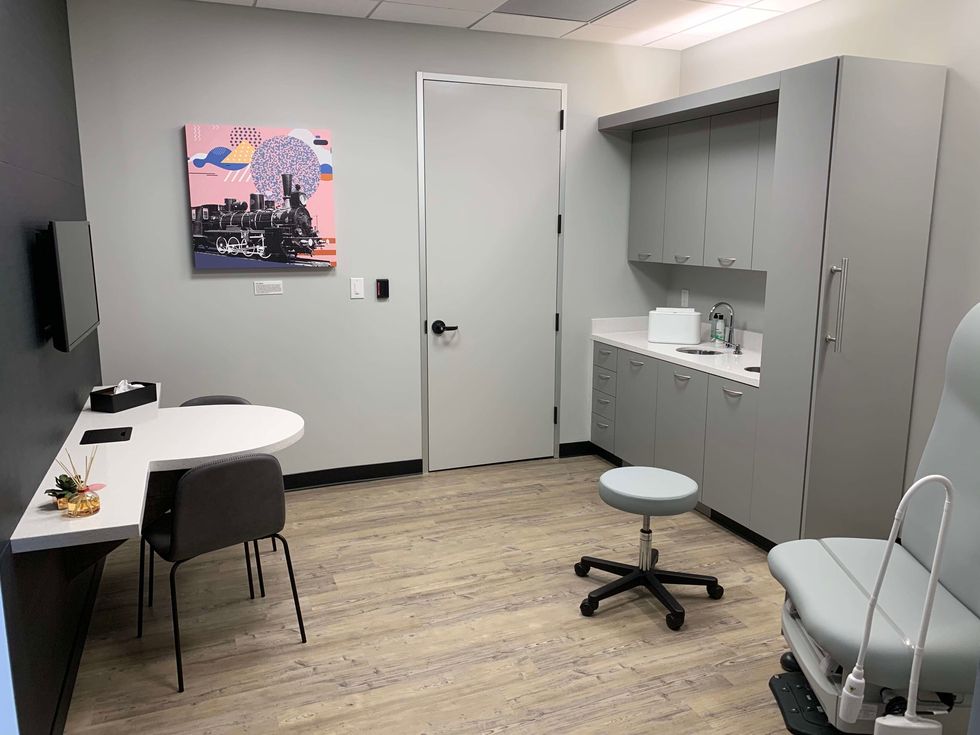
A California company called Crossover Health just opened a 5,300-square-foot medical clinic in Spring. The clinic — Crossover Health's first in the Houston area — enables several self-insured employers to share one provider of primary healthcare services for their employees in an effort to cut costs and promote convenience.
Aside from primary medical care, offerings at the Spring clinic include physical therapy, and chiropractic, acupuncture, and fitness services. Each employer pays a monthly per-employee fee for access to Crossover Health.
At the Spring center, Crossover Health seeks to act on its "belief that healthcare should be convenient, simple to navigate, affordable, and personalized."
The Spring location, at 28420 Hardy Toll Road, features four rooms for primary care, and two each for physical therapy, acupuncture, and health coaching. At the outset, the clinic employs 13 people, but more hires are planned as Crossover Health adds clients there.
Palo Alto, California-based HP is the only client of the Spring clinic that Crossover Health is permitted to identify. In February, HP moved about 2,400 employees into its new two-building, 12-acre campus at Springwoods Village, a master-planned community just west of the Crossover Health clinic. Later this year, San Jose, California-based Hewlett Packard Enterprise Co., a sister company of HP, is scheduled to kick off construction of a new campus at Springwoods Village.
Neighboring employers include ExxonMobil, Southwestern Energy, and the American Bureau of Shipping.
For employers, Crossover Health operates medical clinics that are at or near worksites. Outside the Houston area, Crossover Health's corporate clients include Apple, LinkedIn, and Visa.
Larry Boress, executive director of the Dallas-based National Association of Worksite Health Centers, says clinics like Crossover Health's can reduce travel time for employees heading to medical appointments and, as a result, can improve productivity.
"The value of a worksite health and wellness center for both large and small employers in Houston is that it offers the ability to gain real value on their healthcare investment," Boress says.
Aside from trimming healthcare costs, such centers can boost employee satisfaction and decrease absenteeism, he says.
"These centers have also been found to help employers be an employer of choice, benefiting recruitment and retention of employees," Boress says.
A 2018 survey by consulting firm Mercer and the National Association of Worksite Health Centers found that in 2017, one-third of U.S. employers with at least 5,000 employees provided worksite medical clinics, up from almost one-fourth in 2012.
A different survey — this one conducted in 2018 by the National Association of Worksite Health Centers and Benfield, a market research, strategy, and communications consulting firm that focuses on the healthcare industry — showed that among large employers with some sort of medical arrangement, 63 percent offered on-site clinics, 16 percent offered nearby clinics, and 21 percent offered a mix of the two.
"The hope with on-site or near-site clinics is to make healthcare more convenient for employees, and along the way ideally cheaper by cutting down on visits," Business Insider reported in 2018. "Crossover says it can save as much as $970 per member compared to what employers would be paying if that employee went through the traditional healthcare system. That savings can add up for a company with thousands of employees."
Crossover Health already has brought its brand of healthcare delivery to Austin and San Antonio. Now that the company has planted its flag in the Houston market, it's eyeing its first location in Dallas-Fort Worth.
"Texas, which has consistently ranked as the top U.S. state for business and job growth, is one of our most important markets as we continue to expand our national footprint," Dr. Scott Shreeve, co-founder and CEO of Crossover Health, says in a release. "The new Spring center allows us to introduce our new model of primary care to an increasing number of corporations moving to the Lone Star State."