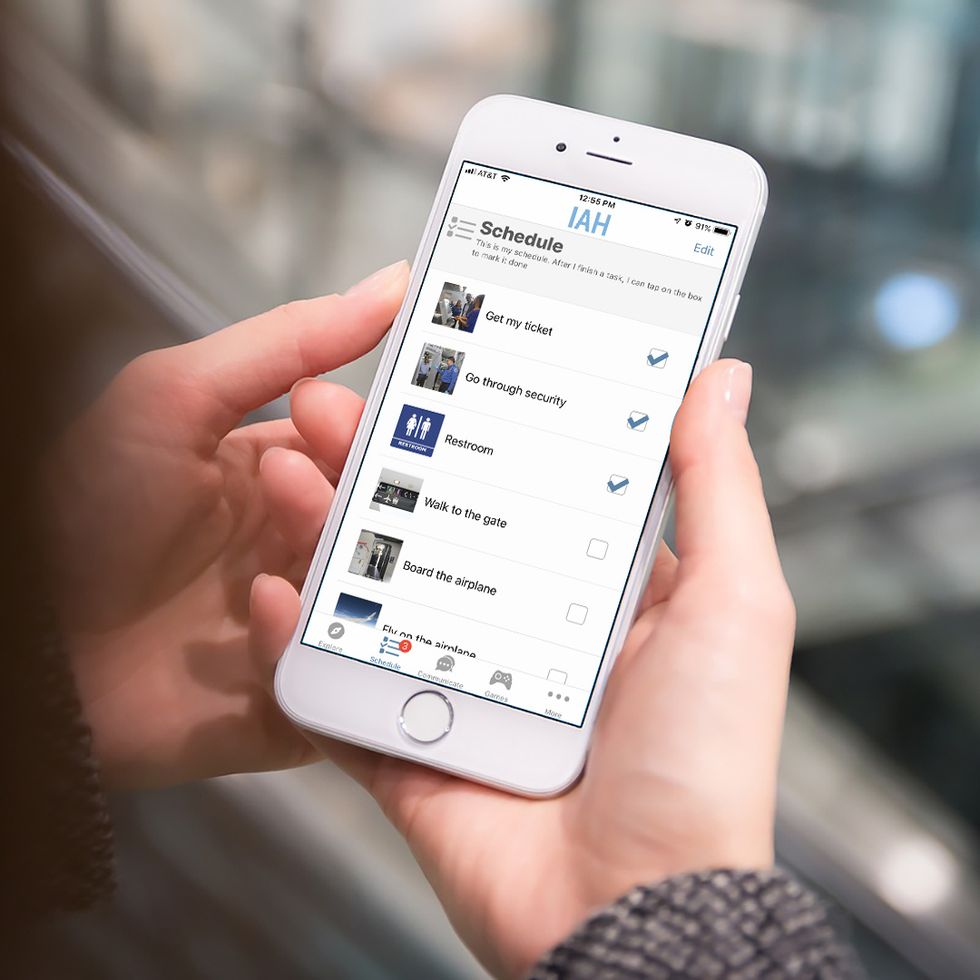
Houston's two airports have a new digital tool to help its passengers with developmental disabilities better navigate their journey in and out of town.
George Bush Intercontinental Airport and William P. Hobby Airport have partnered with Chicago-based Autism innovation company, Infiniteach, to launch the Access Houston Airports mobile app. The free technology provides tools to children with autism or other conditions — as well as their caregivers — throughout their Houston Airport System experience.
"Houston Airports continues to embrace technology to go the extra mile to assist passengers of all abilities on their journey through our airports," says Jesus Saenz, Houston Airports' COO, in a news release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 13 percent of the United states have an "invisible" developmental disability like autism. Tim Joniec, the director of government relations and Americans with Disability Act coordination at HAS, says in the release that this translates to 20,000 daily Houston travelers.
"Houston Airports is introducing this app to ease anxiety for these families and provide information and resources that will make their visit to the airport an engaging and meaningful experience," Joniec says in the release.
The app uses researched-based strategies and features, including guides, short picture stories, scheduling tool, checklist feature, as well as caregiver information like terminal maps and support.
The app launch is just one improvement HAS has made. The organization has also conducted employee disability awareness training, Aira technology for the blind or low vision, service dog familiarization training, and nonprofit involvement through Southwest Airlines and United Airlines' annual Wings for all event.